图解:
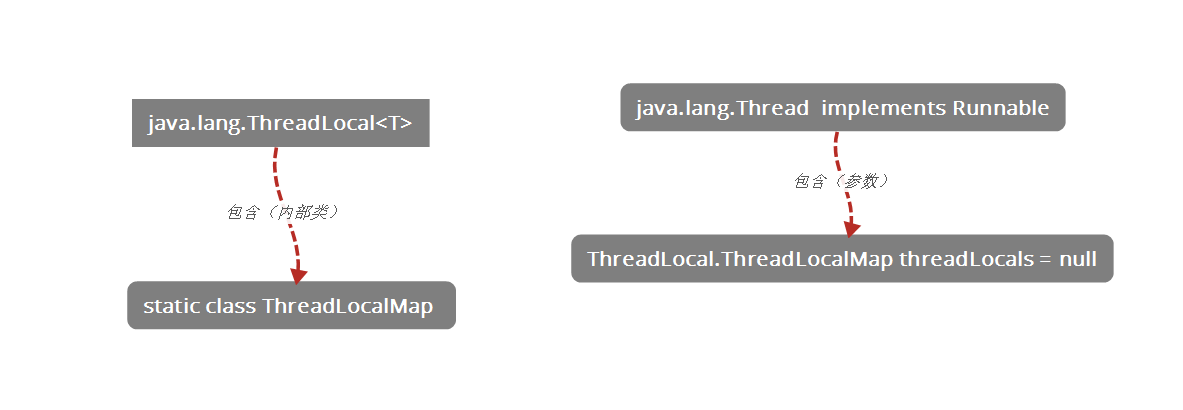
说明:在我们Thread 的类里面,存在一个属性,这个属性是:ThreadLocal类实现的内部类(ThreadLocalMap),所以对于每一个线程来说,他都具有一个本地的map,保存属于自己的参数,
对于回收,ThreadLocalMap的实现使用了弱引用,
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
另外注意使用规范:
private static final ThreadLocal<List<Runnable>> RUNNABLES = new ThreadLocal<List<Runnable>>(); private ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { List<Runnable> threadRunnables = RUNNABLES.get(); if (threadRunnables == null) { threadRunnables = new ArrayList<Runnable>(); RUNNABLES.set(threadRunnables); TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(this); } threadRunnables.add(runnable); }
TheadLocal的添加,是通过用户自己先判断,get(),是否为null,如果为空,set一个new值
java.lang.ThreadLocal<T>实现
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
与java.lang.Thread implements Runnable (){。。。}的关联
此类的变量中存在
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;