一、处理请求的核心流程
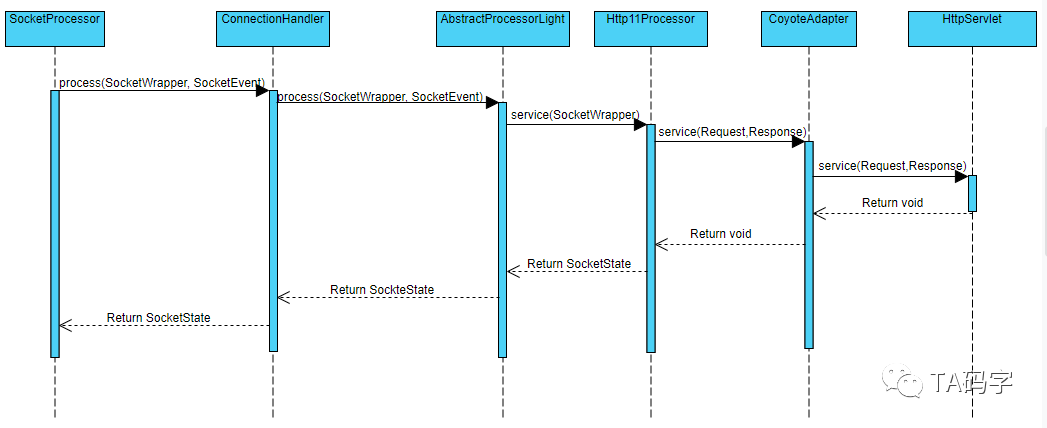
SocketProcessor.doRun()-->
ConnectionHandler.process()-->
AbstractProcessorLight.process()-->
Http11Processor.service-->
CoyoteAdapter.service() --> container 调用标准 servlet API。
涉及的关键类有:
SocketProcessor,ConnectionHandler
AbstractProcessorLight,
Http11Processor,CoyoteAdapter
二、SocketProcessor的doRun()方法
protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {
@Override
protected void doRun() {
NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();
SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
try {
int handshake = -1;
try {
if (key != null) {
//如果时https则之前创建的是SecureNioChannel的实例
if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) {
//握手完成直接赋值0
handshake = 0;
} else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT ||
event == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
handshake = -1;
} else {
//如果还没有SSL握手,则先进行握手,成功返回0
handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable());
event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ;
}
}
} catch (IOException x) {
···
}
if (handshake == 0) {
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
// Process the request from this socket
if (event == null) {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);
} else {
//ConnectionHandler 实例的 process() 方法
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
}
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
close(socket, key);
}
} else if (handshake == -1 ) {
getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL);
close(socket, key);
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){
socketWrapper.registerReadInterest();
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){
socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException cx) {
···
} finally {
socketWrapper = null;
event = null;
//缓存SocketProcessor
if (running && !paused) {
processorCache.push(this);
}
}
}
}
}
首先会处理 handshake,如果 handshake 没有问题则返回 handshake 的结果为 0。
如果 handshake 过程处理正常没问题,则会通过调用 getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event) 方法从而来间接触发 ConnectionHandler 实例的 process() 方法,并返回期望原始 socket 的状态 SocketState 枚举。
如果返回的 SocketState 为 CLOSED ,则最终调用poller.cancelledKey() 方法,会把原始 sockte 关闭。
最后会把 SocketProcessor 实例回收到缓存 processorCache 中,以便下次使用不需要重新创建对象,从而提高效率。
另外 ConnectionHandler是global对象,也就是说所有的连接处理均由这个对象处理,该实例中有一个 Map 对象,key 为SocketWrapper 对象类型,对应的 value 为 Http11Processor 类型。也就是说为连接中的每一个请求(request)都去分配了相应处理类 Http11Processor 实例,可以保存连接上请求的状态信息(例如解析请求行,请求头等数据)。
三、ConnectionHandler.process( wrapper, status)
protected static class ConnectionHandler<S> implements AbstractEndpoint.Handler<S> {
private final Map<S,Processor> connections = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final RecycledProcessors recycledProcessors = new RecycledProcessors(this);
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) {
···
S socket = wrapper.getSocket();
Processor processor = connections.get(socket);
···
if (processor != null) {
// Make sure an async timeout doesn't fire
getProtocol().removeWaitingProcessor(processor);
} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no
// longer a processor associated with this socket.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
ContainerThreadMarker.set();
try {
if (processor == null) {
String negotiatedProtocol = wrapper.getNegotiatedProtocol();
// OpenSSL typically returns null whereas JSSE typically
// returns "" when no protocol is negotiated
if (negotiatedProtocol != null && negotiatedProtocol.length() > 0) {
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getNegotiatedProtocol(negotiatedProtocol);
if (upgradeProtocol != null) {
processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor));
}
} else if (negotiatedProtocol.equals("http/1.1")) {
// Explicitly negotiated the default protocol.
// Obtain a processor below.
} else {
// TODO:
// OpenSSL 1.0.2's ALPN callback doesn't support
// failing the handshake with an error if no
// protocol can be negotiated. Therefore, we need to
// fail the connection here. Once this is fixed,
// replace the code below with the commented out
// block.
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",
negotiatedProtocol));
}
return SocketState.CLOSED;
/*
* To replace the code above once OpenSSL 1.1.0 is
* used.
// Failed to create processor. This is a bug.
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString(
"abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",
negotiatedProtocol));
*/
}
}
}
//recycledProcessors用来保持已经回收的 Http11Processor 实例,避免下次使用重新创建对象,提高效率
if (processor == null) {
processor = recycledProcessors.pop();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorPop", processor));
}
}
if (processor == null) {
processor = getProtocol().createProcessor();
register(processor);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor));
}
}
processor.setSslSupport(
wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider()));
// Associate the processor with the connection
connections.put(socket, processor);
SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
do {
//核心方法
state = processor.process(wrapper, status);
if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {
···
}
} while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING);
if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
if (processor.isAsync()) {
getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);
}
} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {
connections.remove(socket);
release(processor);
wrapper.registerReadInterest();
} else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {
} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {
if (status != SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);
}
} else if (state == SocketState.SUSPENDED) {
} else {
···
}
return state;
} catch(java.net.SocketException e) {
···
} finally {
ContainerThreadMarker.clear();
}
// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current
// connections
connections.remove(socket);
release(processor);
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
}
1、如果返回的状态是代表 upgrade 协议(例如websocket连接等),则处理 upgrade 协议。
2、如果回的状态为 SocketState.LONG ,则代表要么是数据(请求行/请求头)没有解析完(因为 client 端没有发送完请求行/请求头数据),要么是执行了 servlet 的异步请求。
//ConnectionHandler
protected void longPoll(SocketWrapperBase<?> socket, Processor processor) {
// servlet 非异步请求(请求行/请求头数据没有解析完)的情况
if (!processor.isAsync()) {
// This is currently only used with HTTP
// Either:
// - this is an upgraded connection
// - the request line/headers have not been completely
// read
socket.registerReadInterest();
}
}
//NioSocketWrapper
public void registerReadInterest() {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.debug.registerRead", this));
}
// 把socket 包装对象注册 OP_READ 事件,并添加到 poller 线程的事件队列里,让 poller 线程继续监听 client 端可读事件
getPoller().add(getSocket(), SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
3、SocketState.OPEN 一般代表 servlet API 调用正常,返回 OPEN 表示该连接为长连接,不关闭原始 socket 。所以在 connections中会去移除 socket 和Http11Processor 的对应关系,来释放当前 Http11Processor 实例以便后续重用。由于是长连接,所以和异步处理方式一样,对 socket 包装对象注册 OP_READ 事件,并添加到 poller 线程事件队列中,让 poller 线程继续监听 client 端可读事件。
4、在最后的 else 分支中(代码省略)代表返回的状态为 CLOSED ,表示该连接需要关闭,则在 Map 中移除 socket 和 Http11Processor 的对应关系,然后会释放当前 Http11Processor 实例以便后续重用。根据上面 ConnectionHanlder 的分析,如果返回的 SocketState 枚举的结果为 CLOSED,则会去调用 poller.cancelledKey() 方法,从而把原始 socket 关闭。
四、Http11Processor.service()
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper)
throws IOException {
···
while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&
sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
try {
//解析请求行,如果请求行没有解析完(例如client没有发完数据),可能直接跳出循环
if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {
if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
break;
}
}
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
···
} else {
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
// Don't parse headers for HTTP/0.9
//解析请求头,如果没有解析完(client没有发完数据),跳出循环
if (!http09 && !inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) {
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false;
break;
}
···
}
} catch (IOException e) {
···
}
// 协议 upgrade 的处理(例如websocket)
if (isConnectionToken(request.getMimeHeaders(), "upgrade")) {
···
}
···
// Process the request in the adapter
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
//当请求头和请求行完全解析完毕时,会调用 CoyoteAdapter.service() 方法,该方法会通过 servlet container 调用标准 servlet API
getAdapter().service(request, response);
//
if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() &&
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
}
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
···
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
//Servlet API 正常调用完毕,对于非异步请求回去调用 endRequest() 方法表示结束。
//在其内部用 Http11InputBuffer.endRequest() 结束请求,用 Http11OutputBuffer.end() 将剩余 response 数据发送到 client 端。
if (!isAsync()) {
endRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
···
//同时对于非异步模式下的 servlet 请求,还会去调用 Http11InputBuffer.nextRequest() 方法和 Http11OutputBuffer.nextRequest() 方法来回收两个实例,以便后续重用,可以提高效率。
if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) {
request.updateCounters();
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
inputBuffer.nextRequest();
outputBuffer.nextRequest();
}
}
···
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
if (getErrorState().isError() || (endpoint.isPaused() && !isAsync())) {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
} else if (isAsync()) {
//如果是异步请求,请求行并且未处理完成的,返回SocketState.LONG
return SocketState.LONG;
} else if (isUpgrade()) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else {
if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) {
return SocketState.SENDFILE;
} else {
if (openSocket) {
//对于非异步请求正常结束后,返回的 socket 状态是 SocketState.OPEN
if (readComplete) {
return SocketState.OPEN;
} else {
return SocketState.LONG;
}
} else {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
}
}
}
五、CoyoteAdapter.service()
@Override
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws Exception {
//创建 servlet 的标准 request 和 response
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
···
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// 核心方法,调用servlet的API
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(
request, response);
}
if (request.isAsync()) {
···
} else {
//如果不是异步请求,完成servlet API后,通过HttpServletRequest.finishRequest() 方法调用和HttpServletResponse.finishResponse() 方法调用结束当前请求和响应
request.finishRequest();
response.finishResponse();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
} finally {
···
// Recycle the wrapper request and response
if (!async) {
updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response);
//通过 HttpServletRequest.recycle() 调用和 HttpServletResponse.recycle() 调用来回收请求和响应,以便后面可以重用提高效率。
request.recycle();
response.recycle();
}
}
}