一、Django项目创建
(一)虚拟环境创建
首先创建一个虚拟环境,用于Django项目使用,在CMD窗口中通过下面的命令:
mkvirtualenv celery_test
其中celery_test 为虚拟环境名称,这里使用的python解释器就是默认安装的,你也可以指定python解释器:
mkvirtualenv [--python==d:Python3.5.2python.exe] celery_test
(二)创建项目
最简单的方式是可以通过Pycharm来进行创建,当然也可以命令行的方式创建,但是在创建前需要在虚拟环境中将Django的包安装上:
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip install django==2.0 Collecting django==2.0 Using cached Django-2.0-py3-none-any.whl (7.1 MB) Collecting pytz Using cached pytz-2019.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl (509 kB) Installing collected packages: pytz, django Successfully installed django-2.0 pytz-2019.3
此时,再创建项目:
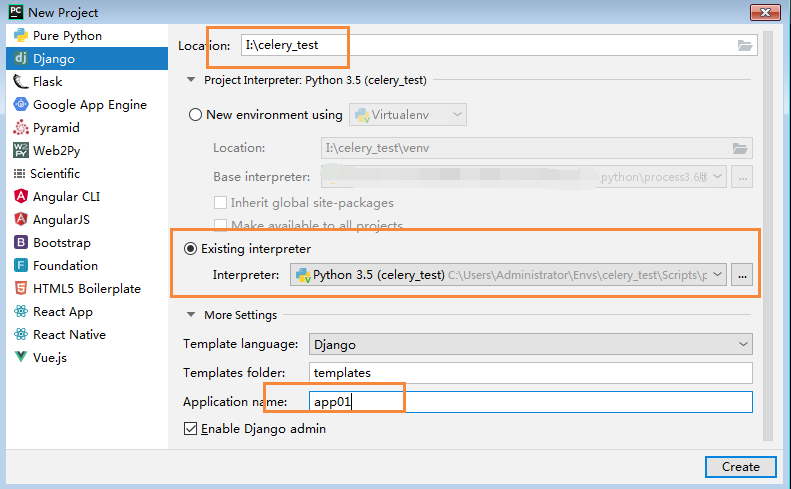
只需要填写上面的部分即可完成django项目的创建。
二、Celery的使用
(一)环境配置
Django与Celery可以配合使用,但是需要安装django-celery的包,这样更利于celery中任务的管理,注意这些包的版本:
1、celery安装
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip install celery==3.1.26.post2 Collecting celery==3.1.26.post2 Downloading celery-3.1.26.post2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (526 kB) |███████▌ | 122 kB 20 kB/s eta 0:00:20
2、django-celery安装
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip install django-celery==3.2.2 Collecting django-celery==3.2.2 Downloading django-celery-3.2.2.tar.gz (90 kB) |███████████ | 30 kB 56 kB/s eta 0:00:02
3、redis安装
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip install redis==2.10.6 -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
4、进行注册
在django的settings文件中将djcelery进行注册:
INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'djcelery', #注册 'app01', ]
5、settings中导入celeryconfig
# Internationalization # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/i18n/ LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' USE_I18N = True USE_L10N = True USE_TZ = True # Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images) # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/howto/static-files/ STATIC_URL = '/static/' #Celery Config from .celeryconfig import * # celery的相关配置文件 BROKER_BACKEND = 'redis' BROKER_URL = 'redis://localhost:6379/1' CELERY_RESULT_BACKEND='redis://localhost:6379/2'
(二)异步任务
1、新建celery相关的文件
- 在工程的根目录下新建celeryconfig文件,用于存放配置参数
- 在appo1目录下新建tasks.py文件,用于存放与app01相关的异步和定时任务
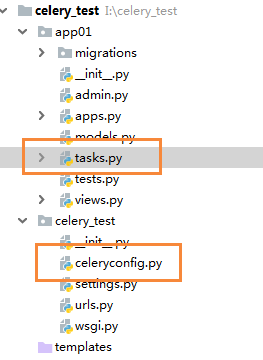
(1)celeryconfig.py
import djcelery from datetime import timedelta djcelery.setup_loader() CELERY_QUEUES = { #定时任务队列 'beat_tasks':{ 'exchange':'beat_tasks', 'exchange_type':'direct', 'binding_key':'beat_tasks' }, #普通任务队列 'work_tasks': { 'exchange': 'work_tasks', 'exchange_type': 'direct', 'binding_key': 'work_tasks' } } #设置默认的队列 CELERY_DEFAULT_QUEUE = 'work_tasks' #将每一个app下的tasks进行导入 CELERY_IMPORTS = ( 'app01.tasks', ) #有些情况防止死锁 CELERYD_FORCE_EXECV = True #设置并发的workers数量,根据cpu的数量 CELERYD_CONCURRENCY = 4 #任务失败允许重试 CELERY_ACKS_LATE = True #每个worker最多执行的任务数,超过这个就将worker进行销毁,防止内存泄漏 CELERYD_MAX_TASKS_PER_CHILD = 100 #单个任务运行的最大时间,超过这个时间,task就会被kill CELERYD_TASK_TIME_LIMIT = 12 * 30
首先定义了两个任务队列,一个用于存放异步任务,一个用于存放定时任务;其次将每一个app下的tasks导入,tasks.py中定义的都是任务;最后都是一些参数定义。
(2)app01.tasks.py
from celery.task import Task import time class Upload(Task): name = 'upload-task' #给任务一个名称 def run(self, *args, **kwargs): time.sleep(2) print('run upload task')
定义了一个任务并且指定了一个名称,这个名称在定时任务中会用的上。当这个任务执行时会运行run方法,那么如果它是个异步任务,应该怎么触发和执行呢?
我们可以在views.py文件的view函数中进行调用这个任务:
from django.shortcuts import render from django.http.response import JsonResponse from app01.tasks import Upload # Create your views here. def doTask(request): print('start task!') Upload.delay() #异步任务,这里不会卡住,尽管有延时 print('end task!') return JsonResponse({"type":'success'})
这里定义了一个视图函数,在视图只要访问某个url对应的这个视图就会触发,我们在任务中睡了2s但是这里不会停顿,因为它是是异步任务。
(2)运行异步任务
- 启动django项目
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0
- 启动celery worker
python manage.py celery worker -l info
- 访问视图,触发任务
http://127.0.0.1:8000/doTask/
(三)定时任务
定时任务也是需要启动worker的,需要在celeryconfig加入定时任务的配置,假设刚刚那个任务时定时任务:
... ... #单个任务运行的最大时间,超过这个时间,task就会被kill CELERYD_TASK_TIME_LIMIT = 12 * 30 #定时任务 CELERYBEAT_SCHEDULE = { 'task1':{ 'task':'upload-task', #指定任务名称 'schedule':timedelta(seconds=5), #任务执行时间,每5秒执行一次 'options':{ 'queue':'beat_tasks' } } }
指定了定时任务,其中名称upload-task就是刚刚任务中定义的name属性。同样的在我们添加完定时任务后,需要启动celery worker和celery beat。
#celery worker python manage.py celery worker -l info #celery beat python manage.py celery beat -l info
这样就完成了定时任务。
值得注意的是,如果使用crontab来进行定时任务的话。就会存在时区问题,比如在app01.tasks.py中再加入一个任务:
from celery.task import Task import time ... ... class scrawl(Task): name = 'spider' def run(self, *args, **kwargs): time.sleep(3) print('执行爬取任务')
然后再进行配置:
import djcelery from datetime import timedelta from celery.schedules import crontab ... ... #定时任务 CELERYBEAT_SCHEDULE = { 'task1':{ 'task':'upload-task', #指定任务名称 'schedule':timedelta(seconds=5), #任务执行时间,每5秒执行一次 'options':{ 'queue':'beat_tasks' } }, 'task2': { 'task': 'spider', # 指定任务名称 'schedule':crontab(minute='19', hour='16', day_of_week='*',day_of_month='*', month_of_year='*'), # 任务执行时间,每5秒执行一次 'options': { 'queue': 'beat_tasks' } }, }
在task2中使用了crontab,那么响应的应该在django的settings.py中将TIME_ZONE 参数进行更改:
... # TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai' ...
这样就ok了。
(四)版本问题及其它问题
1、安装包版本
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip list Package Version ------------- ------------ amqp 1.4.9 anyjson 0.3.3 Babel 2.8.0 billiard 3.3.0.23 celery 3.1.26.post2 Django 2.0 django-celery 3.2.2 flower 0.9.3 kombu 3.0.37 pip 20.0.2 pytz 2019.3 redis 2.10.6 setuptools 46.1.1 tornado 5.1.1 wheel 0.34.2
注意的是celkery、django-celery、Django、以及redis的版本,这是很容易出现各种问题的地方。
2、pip问题
另外下载过程中会出现timeout或者其它问题,一般解决通过:
pip install flower -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
就可以解决。如果永久的替换pip源可以在windows下的user目录下新建pip文件夹,然后新建pip.ini文件

写入:
[global] index-url = https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple [install] trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
三、flower任务监控
通过pip命令直接进行安装:
(celery_test) C:UsersAdministrator>pip install flower -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
接下来可以直接启动flower,在django中可以直接这样启动:
(celery_test) I:celery_test>python manage.py celery flower
这样就可以直接启动flower了。当然也可以这样执行命令启动。
celery flower --address=0.0.0.0 --port=5555 --broker='redis://localhost:6379/1' #如果加入认证通过--basic_auth=username:password
四、supervisor进程管理
1、安装
(django3) [root@localhost celery_test]# pip install supervisor -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
2、配置文件管理与启动
进入到项目的根目录下,与settings同级:
(1)创建配置文件夹
(django3) [root@localhost celery_test]# mkdir conf (django3) [root@localhost celery_test]# ls conf __init__.py settings.py urls.py wsgi.py (django3) [root@localhost celery_test]#
(2)生成配置文件
(django3) [root@localhost celery_test]# echo_supervisord_conf > conf/supervisord.conf

; Sample supervisor config file. ; ; For more information on the config file, please see: ; http://supervisord.org/configuration.html ; ; Notes: ; - Shell expansion ("~" or "$HOME") is not supported. Environment ; variables can be expanded using this syntax: "%(ENV_HOME)s". ; - Quotes around values are not supported, except in the case of ; the environment= options as shown below. ; - Comments must have a leading space: "a=b ;comment" not "a=b;comment". ; - Command will be truncated if it looks like a config file comment, e.g. ; "command=bash -c 'foo ; bar'" will truncate to "command=bash -c 'foo ". ; ; Warning: ; Paths throughout this example file use /tmp because it is available on most ; systems. You will likely need to change these to locations more appropriate ; for your system. Some systems periodically delete older files in /tmp. ; Notably, if the socket file defined in the [unix_http_server] section below ; is deleted, supervisorctl will be unable to connect to supervisord. [unix_http_server] file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; the path to the socket file ;chmod=0700 ; socket file mode (default 0700) ;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket file uid:gid owner ;username=user ; default is no username (open server) ;password=123 ; default is no password (open server) ; Security Warning: ; The inet HTTP server is not enabled by default. The inet HTTP server is ; enabled by uncommenting the [inet_http_server] section below. The inet ; HTTP server is intended for use within a trusted environment only. It ; should only be bound to localhost or only accessible from within an ; isolated, trusted network. The inet HTTP server does not support any ; form of encryption. The inet HTTP server does not use authentication ; by default (see the username= and password= options to add authentication). ; Never expose the inet HTTP server to the public internet. ;[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default ;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface ;username=user ; default is no username (open server) ;password=123 ; default is no password (open server) [supervisord] logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; main log file; default $CWD/supervisord.log logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; max main logfile bytes b4 rotation; default 50MB logfile_backups=10 ; # of main logfile backups; 0 means none, default 10 loglevel=info ; log level; default info; others: debug,warn,trace pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; supervisord pidfile; default supervisord.pid nodaemon=false ; start in foreground if true; default false minfds=1024 ; min. avail startup file descriptors; default 1024 minprocs=200 ; min. avail process descriptors;default 200 ;umask=022 ; process file creation umask; default 022 ;user=supervisord ; setuid to this UNIX account at startup; recommended if root ;identifier=supervisor ; supervisord identifier, default is 'supervisor' ;directory=/tmp ; default is not to cd during start ;nocleanup=true ; don't clean up tempfiles at start; default false ;childlogdir=/tmp ; 'AUTO' child log dir, default $TEMP ;environment=KEY="value" ; key value pairs to add to environment ;strip_ansi=false ; strip ansi escape codes in logs; def. false ; The rpcinterface:supervisor section must remain in the config file for ; RPC (supervisorctl/web interface) to work. Additional interfaces may be ; added by defining them in separate [rpcinterface:x] sections. [rpcinterface:supervisor] supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface ; The supervisorctl section configures how supervisorctl will connect to ; supervisord. configure it match the settings in either the unix_http_server ; or inet_http_server section. [supervisorctl] serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket ;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket ;username=chris ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set ;password=123 ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set ;prompt=mysupervisor ; cmd line prompt (default "supervisor") ;history_file=~/.sc_history ; use readline history if available ; The sample program section below shows all possible program subsection values. ; Create one or more 'real' program: sections to be able to control them under ; supervisor. ;[program:theprogramname] ;command=/bin/cat ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args) ;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s) ;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1) ;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd) ;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None) ;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999) ;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true) ;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1) ;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3) ;autorestart=unexpected ; when to restart if exited after running (def: unexpected) ;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0) ;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM) ;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10) ;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false) ;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false) ;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program ;redirect_stderr=true ; redirect proc stderr to stdout (default false) ;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO ;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB) ;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10) ;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0) ;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false) ;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false) ;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO ;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB) ;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10) ;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0) ;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false) ;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false) ;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions (def no adds) ;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils) ; The sample eventlistener section below shows all possible eventlistener ; subsection values. Create one or more 'real' eventlistener: sections to be ; able to handle event notifications sent by supervisord. ;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername] ;command=/bin/eventlistener ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args) ;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s) ;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1) ;events=EVENT ; event notif. types to subscribe to (req'd) ;buffer_size=10 ; event buffer queue size (default 10) ;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd) ;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None) ;priority=-1 ; the relative start priority (default -1) ;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true) ;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1) ;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3) ;autorestart=unexpected ; autorestart if exited after running (def: unexpected) ;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0) ;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM) ;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10) ;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false) ;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false) ;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program ;redirect_stderr=false ; redirect_stderr=true is not allowed for eventlisteners ;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO ;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB) ;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10) ;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false) ;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false) ;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO ;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB) ;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10) ;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false) ;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false) ;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions ;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils) ; The sample group section below shows all possible group values. Create one ; or more 'real' group: sections to create "heterogeneous" process groups. ;[group:thegroupname] ;programs=progname1,progname2 ; each refers to 'x' in [program:x] definitions ;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999) ; The [include] section can just contain the "files" setting. This ; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or ; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are ; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot* ; include files themselves. ;[include] ;files = relative/directory/*.ini
(3) 开启web服务
... [inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface ;username=user ; default is no username (open server) ;password=123 ; default is no password (open server) ...
开启supervisor的web服务,需要将上述配置文件中的注释去掉;另外开启supervisorctl命令行工具的web服务。
... [supervisorctl] serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket ...
可以看到这个配置文件最后两行:
;[include]
;files = relative/directory/*.ini
将其打开,并且修改为:
[include]
files = *.ini
也就是说凡是.ini的文件都可以将其当作配置文件包含进来,进行启动。
(4)新建supervisor_celery_worker.ini
(django3) [root@localhost conf]# touch supervisor_celery_worker.ini
写入以下内容:
[program:celery_worker] command=python manage.py celery worker -l INFO directory=/root/Envs/celery_test #项目根目录,否则command找不到manage.py文件 environment=PATH="/root/Envs/django3/bin" #虚拟环境目录 stdout_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_worker.log stderr_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_worker.log autostart=true autorestart=true startsecs=10 stopwatisecs=60 priority=998
启动supervisor:
(django3) [root@localhost conf]# supervisord -c supervisord.conf
可以通过:
(django3) [root@localhost conf]# ps -ef | grep supervisor
查看进程,另外通过supervisorctl命令查看具体的服务,比如celery_worker服务。
(5)新建supervisor_celery_beat.ini
[program:celery_beat] command=python manage.py celery beat -l INFO directory=/root/Envs/celery_test environment=PATH="/root/Envs/django3/bin" stdout_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_beat.log stderr_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_beat.log autostart=true autorestart=true startsecs=10 stopwatisecs=60 priority=997 #数字越大越优先
这里通过supervisorctl中的update进行添加即可:
(django3) [root@localhost conf]# supervisorctl supervisor> help default commands (type help <topic>): ===================================== add exit open reload restart start tail avail fg pid remove shutdown status update clear maintail quit reread signal stop version supervisor> update
(6)新建supervisor_celery_flower.ini
[program:celery_flower] command=python manage.py celery flower #这个命令进行了更改 directory=/root/Envs/celery_test environment=PATH="/root/Envs/django3/bin" stdout_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_flower.log stderr_logfile=/root/Envs/celery_test/logs/celery_flower.log autostart=true autorestart=true startsecs=10 stopwatisecs=60 priority=996 #注意优先级,它是最后启动
3、总结
supervisor配置文件中将web界面进行开启,另外将最后的include进行开启,然后分别创建不同的ini文件,里面的文件基本上就是命令、日志文件路径、优先级进行了更改,另外如果添加了服务通过supervisorctl中的update进行添加,你也可以通过本地9001端口的web服务进行访问。
