一、SGI 标准的空间配置器,std::allocator
SGI也定义了一个符合部分标准,名为allocator的配置器,但是它自己不使用,也不建议我们使用,主要原因是效率不佳。
它只是把C++的操作符::operator new和::operator delete做了一层简单的封装而已。

二、SGI 特殊的空间配置器,std::alloc
由于SGI 标准的空间配置器只是把C++的操作符::operator new和::operator delete做了一层简单的封装,没有考虑到任何效率上的强化。
所以 SGI 出现了一个特殊的空间配置器,供 STL标准模板库 使用。
通常,C++中用new操作符来分配内存都包括两个阶段:
(1)调用::operator new配置内存
(2)调用构造函数来构造对象内容
同理,delete操作也包括两个阶段:
(1)调用析构函数将对象析构
(2)调用::operator delete释放内存
为了精密分工,SGI STL allocator将两个阶段分开:
内存配置操作由alloc:allocate负责,内存释放由alloc:deallocate负责;对象构造操作由::contructor()负责,对象析构由::destroy()负责。
配置器定义在头文件<memory>中,它里面又包括两个文件:
#include <stl_alloc.h> // 负责内存空间的配置和器释放 #include <stl_construct.h> // 负责对象的构造和析构

三、STL 空间配置器:
STL 空间配置器解决的问题
1:内存碎片问题(外碎片)
内碎片,外碎片简介:
内碎片:操作系统在分配给申请者未被利用的部分。产生原因:内存对齐(效率高);
外碎片:内存充足时但分配不出大块内存。产生原因:由于多次分配小块内存,将大块内存分割成小块;

2.频繁系统分配,释放小块内存,调用 malloc,delete 系统调用产生性能问题;
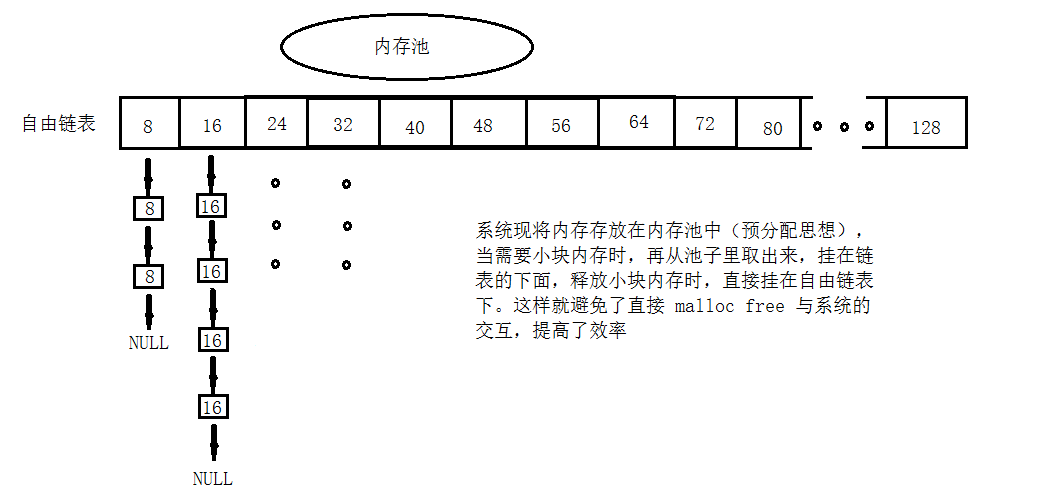
STL 空间配置器的实现机制:
双层级的配置器:

注:
当需要开辟的空间大于 128 bytes 时,视为“足够大”,调用一级配置器,直接调用 malloc,free;
当需要开辟的空间小于 128 bytes 时,视为“过小”,为了降低额外负担,调用二级空间配置器
一级空间配置器的剖析:
(set_new_handler 机制)

/*****************************************************************************
功能描述:一级空间配置器
类 /函数:template<int inst> class __MallocAllocTemplate;
简 介:直接调用 malloc/free,内存分配失败后调用句柄处理函数
*****************************************************************************/
typedef void(*ALLOC_OOM_FUN)(); //内存分配失败以后处理的句柄handler类型
template<int inst>
class __MallocAllocTemplate
{
private:
static ALLOC_OOM_FUN __sMallocAllocOomHandler;
static void* OomMalloc(size_t n) //模仿 c++ 的 set_new_handler 机制
{
ALLOC_OOM_FUN handler = __sMallocAllocOomHandler;
void* result;
for (;;) //一直循环,直到内存分配成功为止
{
if (handler == 0) //检查是否设置处理的 handler
{
cout << "out of memory " << endl;
exit(-1);
}
handler(); //调用客户自己的内存管理函数,释放内存
result = malloc(n);
if (result) //分配成功
return result;
}
}
static void* OomRealloc(void*p, size_t n)
{
ALLOC_OOM_FUN handler = __sMallocAllocOomHandler;
void* result;
for (;;) //一直循环,直到内存分配成功为止
{
if (handler == 0) //检查是否设置处理的 handler
{
cout << "out of memory " << endl;
exit(-1);
}
handler(); //调用客户自己的内存管理函数,释放内存
result = remalloc(n);
if (result) //分配成功
return result;
}
}
public:
static void* Allocate(size_t n) //直接调用 malloc
{
void* result = malloc(n);
return result == 0 ? OomMalloc(n) : result;
}
static void Deallocate(void* p) //直接 free
{
free(p);
}
static void *Reallocate(void*p,size_t new_sz)
{
void* result = realloc(p, new_sz);
return result == 0 ? OomRealloc(p, new_sz) : result;
}
static void(*SetMallocHandler(void(*f)()))() //重新设置句柄处理函数
{
ALLOC_OOM_FUN result = __sMallocAllocOomHandler;
__sMallocAllocOomHandler = f;
return result;
}
};
//初始化分配内存失败处理函数的句柄函数指针
template<int inst>
ALLOC_OOM_FUN __MallocAllocTemplate<inst>::__sMallocAllocOomHandler = 0;
二级空间配置器:



template<bool threads, int inst>
class __DefaultAllocTemplate
{
public:
enum{ __ALIGN = 8 }; //排列基准值(也是排列间隔)
enum{ __MAX_BYTES = 128 }; //最大值
enum{ __NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES / __ALIGN }; //排列链大小
static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes)
{
return (bytes + __ALIGN - 1 & ~(__ALIGN - 1)); //内存与 8 对齐
}
static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes)
{
return ((bytes + __ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1); //返回在自由链表中的下标
}
union Obj
{
union Obj* _freeListLink; //指向下一个内存块的指针
char _clientData[1]; /* The client sees this.*/
};
static Obj* volatile _freeList[__NFREELISTS]; //自由链表
static char* _startFree; //内存池起始地址
static char* _endFree; //内存池结束地址
static size_t _heapSize; //内存池的容量
//从内存池中获取内存插入到自由链表中
static void* Refill(size_t n);
//从内存池中分配内存
static char* ChunkAlloc(size_t size, int& nobjs);
//用户调用申请内存函数
static void* Allocate(size_t n);
//内存释放函数
static void Deallocate(void*p, size_t n);
//重新分配内存
static void* Reallocate(void*p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz);
};
//初始化全局静态对象
//1.自由链表
template<bool threads, int inst>
typename __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::Obj* volatile
__DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::_freeList[__DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::__NFREELISTS];
//2.内存池
template<bool threads, int inst>
char* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::_startFree = 0;
template<bool threads, int inst>
char* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::_endFree = 0;
template<bool threads, int inst>
char* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::_heapSize = 0;
//类中声明函数的定义
template<bool threads, int inst>
void* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::Refill(size_t n)
{
int nobjs = 20;
char* result = ChunkAlloc(n, nobjs);
if (nobjs == 1)
return result;
Obj* cur = (Obj*)(result + n);
size_t index = FREELIST_INDEX(n);
_freeList[index] = cur;
for (int i = 2; i < nobjs; ++i) //链表的头插
{
cur->_freeListLink = i*n + result;
cur = cur->_freeListLink;
}
cur->_freeListLink = NULL;
return result;
}
template<bool threads, int inst>
char* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::ChunkAlloc(size_t size, int&nobjs)
{
char* result;
size_t bytesNeed = size*nobjs;
size_t bytesHave = _endFree - _startFree;
if (bytesHave >= bytesNeed) //内存池中所剩内存大于需要的内存
{
result = _startFree;
_startFree += bytesNeed;
}
else if (bytesHave >= size) //至少能满足一个 size 的分配
{
result = _startFree;
nobjs = bytesHave / size;
_startFree += size*nobjs;
}
else //内存池中所剩空间不够一个 size
{
//清空内存池,准备往内存池中补充空间
Obj* cur = _startFree;
size_t index = FREELIST_INDEX(bytesHave);
cur->_freeListLink = _freelist[index];
_freelist[index] = cur;
_startFree = NULL, _endFree = NULL;
//重新向系统申请 bytesNeed*2 + _heapSize/16
size_t bytesToGet = bytesNeed * 2 + (_heapSize >> 4);
_startFree = (char*)malloc(bytesToGet);
if (_startFree == NULL) //向系统申请内存失败
{
//先向自由链表上游中的大块内存链中寻找
for (int i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN)
{
Obj* head = _freeList[FREELIST_INDEX(size)];
if (head)
{
_startFree = (char*)head;
_endFree = (char*)head + i;
_freeList[FREELIST_INDEX(size)] = head->_freeListLink;
return ChunkAlloc(size, nobjs);
}
}
//链表中也没有了,实在无奈,调用一级配置器中的内存分配函数
_startFree = (char*)MallocAlloc::Allocate(byteToGet);
}
_heapSize += bytesToGet;
_endFree = _startFree + bytesToGet;
return ChunkAlloc(size, nobjs); //函数的复用
}
return result;
}
template<bool threads, int inst>
void* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::Allocate(size_t n)
{
void* result;
if (n > __MAX_BYTES)
result = MallocAlloc::Allocate(n);
//
//自由链表有,就直接取
//没有,就通过 Refill进行填充
//
size_t index = FREELIST_INDEX(n);
if (_freeList[index])
{
result = _freeList[index];
_freelist[index] = ((Obj*)result)->_freeListLink;
}
else
{
result = Refill(ROUND_UP(n));
}
return result;
}
template<bool threads, int inst>
void __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::Deallocate(void*p, size_t n)
{
if (n > __MAX_BYTES)
MallocAlloc::Deallocate(p);
//不大于 __MAX_BYTES ,将此空间插回自由链表
else
{
size_t index = FREELIST_INDEX(n);
Obj* cur = (Obj*)p;
cur->_freeListLink = _freeList[index];
_freeList[index] = cur;
}
}
template<bool threads, int inst>
void* __DefaultAllocTemplate<threads, inst>::Reallocate(void* p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz)
{
void* result;
if (old_sz > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES && new_sz > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) //
return realloc(p, old_sz, new_sz);
if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz))
return p;
result = Allocate(new_sz);
size_t size = old_sz > new_sz ? old_sz : new_sz;
meycpy(result, p, size);
Deallocate(p, old_sz);
return result;
}
typedef __DefaultAllocTemplate<false, 0> Alloc;
#endif // __USE_MALLOC
STL 空间配置器的缺点:
1.有内碎片问题
2.内存池中的内存在程序结束前不能还给操作系统,被分割为小块的内存一直挂在自由链表下面,会使得内存的占用率过高。
解决方案:
①在二级空间配置器的内存池上面设置一个分配内存的上限,也就是当 _heapsize 到达一定的值时,程序就会自动的抛出异常,提醒用户二级空间配置器占用的内存过多了;
②实现一个机制,保存每次 malloc 出来的空间的首地址,并记录开辟的空间在自由链表中(已分为小块)挂的位置。当发现开辟的空间分成小块全都挂在自由链表下时,说明可以释放空间了,现将每个小块从自由链表中删除,然后 free 的掉这块空间;
关于打印调试信息的技巧(打trace)
应用场景:在很难调试/无法调试的情况下(release版),想了解程序的运行情况
解决方案:打印出程序中关键部位的状态,根据这些信息推断程序的运行情况
具体做法:
//铺垫:
调试有关的宏: 编译器内置宏,这些宏定义不仅可以帮助我们完成跨平台的源码编写,灵活使用也可以巧妙地帮我们输出非常有用的调试信息 例:__FILE__, __LINE__,__FUNCTION__ void main() { cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl << __FILE__ << endl << __LINE__ << endl; }
可变参数宏__VA_ARGS__ 在 GNU C 中,宏可以接受可变数目的参数,就象函数一样,例如: #define _MYPRINTF_(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__) ; 缺省号代表一个可以变化的参数表。使用保留名 __VA_ARGS__ 把参数传递给宏。当宏的调用展开时,实际的参数就传递给 printf()了。例如: _MYPRINTF_(“Y = %d ”, y); 而处理器会把宏的调用替换成: printf(“Y = %d ”, y); 因为debug()是一个可变参数宏,你能在每一次调用中传递不同数目的参数: debug(“test”); //一个参数 #define _MYPRINTF_(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__) ; void main() { _MYPRINTF_("%d ", 10); }
//打trace
static string GetFileName(const string& path) { char ch = '/'; #ifdef _WIN32 ch = '\'; #endif size_t pos = path.rfind(ch); if (pos == string::npos) { return path; } else { return path.substr(pos + 1); } } // 用于调试追溯的trace log inline static void __trace_debug(const char* function, const char* filename, int line, char* format, ...) { #ifdef __DEBUG__ // 输出调用函数的信息 fprintf(stdout, "【%s:%d】-%s", GetFileName(filename).c_str(), line, function); // 输出用户打的trace信息 va_list args; va_start (args, format); vfprintf (stdout, format, args); va_end (args); #endif } #define __TRACE_DEBUG(...) __trace_debug(__FUNCTION__, __FILE__, __LINE__, __VA_ARGS__);
可变参数列表:http://www.cnblogs.com/shihaochangeworld/p/5563120.html
欢迎讨论,不吝赐教~~

