1、创建ini文件,如(db_config.ini)
内容如下(自己本地的数据库):
[mysql] host=127.0.0.1 port=3306 user=root password=******* db_name=guest # user/password/db_name 根据自己设置填写即可
2、ini 文件的读取
创建读取operateConf.py 文件读取配置信息
2.1、如果 db_config.ini 和 operateConf.py 文件在同一目录下
import configparser # 导库
conf = configparser.ConfigParser()
conf.read('db_config.ini') # 读取 ini 文件
host = conf.get('mysql','host') # 获取host
port = conf.get('mysql','port') # 获取端口号
user = conf.get('mysql','user') # 获取用户名
password = conf.get('mysql','password ') # 获取密码
db = conf.get('mysql','db_name') # 获取数据库的名称
2.2、如果 db_config.ini 和 operateConf.py 文件不在同一目录下---通过os来获取目录,拼接目录
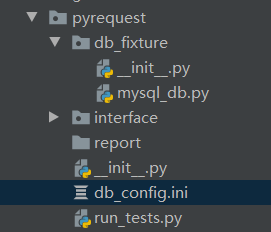
如下为我的目录结构
import configparser
import os
os.path.dirname(__file__) 目录结构为 ../pyrequest/db_fixture/
os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)) 目录结构为 ../pyrequest/
base_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)),'db_config.ini') 文件目录为 ..../pyrequest/db_config.ini
conf = configparser.ConfigParser()
conf.read(base_dir)
host = conf.get('mysql','host')
port = conf.get('mysql','port')
user = conf.get('mysql','user')
password = conf.get('mysql','password ')
db = conf.get('mysql','db_name')
2.3、总结
import configparser
import os
def base_dir(filename=None):
''' 获取文件路径'''
return os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),filename)
def getLinux(name='mysql'):
''' 1.实例化类
2.对文件进行读取
'''
lst = []
conf = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(base_dir('db_config.ini'))
host = conf.get('mysql','host')
port = conf.get('mysql','port')
user = conf.get('mysql','user')
password = conf.get('mysql','password ')
db = conf.get('mysql','db_name')
lst.append(host) # 将元素加入列表中
lst.append(port)
lst.append(user)
lst.append(password)
lst.append(db)
return lst
getLinux() # 调用函数