FatFS源代码中的函数逻辑关系
第一 调用函数 f_mount()
result = f_mount(&fs, FS_VOLUME_NAND, 0); /* Mount a logical drive */
FS_VOLUME_NAND 代表 “路径”
第二 进入函数 f_mount()内
1 /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 2 /* Mount/Unmount a Logical Drive */ 3 /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 4 5 FRESULT f_mount ( 6 FATFS* fs, /* Pointer to the file system object (NULL:unmount)*/ 7 const TCHAR* path, /* Logical drive number to be mounted/unmounted */ 8 BYTE opt /* 0:Do not mount (delayed mount), 1:Mount immediately */ 9 ) 10 { 11 FATFS *cfs; 12 int vol; 13 FRESULT res; 14 const TCHAR *rp = path; 15 16 17 vol = get_ldnumber(&rp); 18 if (vol < 0) return FR_INVALID_DRIVE; 19 cfs = FatFs[vol]; /* Pointer to fs object */ 20 21 if (cfs) { 22 #if _FS_LOCK 23 clear_lock(cfs); 24 #endif 25 #if _FS_REENTRANT /* Discard sync object of the current volume */ 26 if (!ff_del_syncobj(cfs->sobj)) return FR_INT_ERR; 27 #endif 28 cfs->fs_type = 0; /* Clear old fs object */ 29 } 30 31 if (fs) { 32 fs->fs_type = 0; /* Clear new fs object */ 33 #if _FS_REENTRANT /* Create sync object for the new volume */ 34 if (!ff_cre_syncobj((BYTE)vol, &fs->sobj)) return FR_INT_ERR; 35 #endif 36 } 37 FatFs[vol] = fs; /* Register new fs object */ 38 39 if (!fs || opt != 1) return FR_OK; /* Do not mount now, it will be mounted later */ 40 41 res = find_volume(&fs, &path, 0); /* Force mounted the volume */ 42 LEAVE_FF(fs, res); 43 }
代码中第17行 vol = get_ldnumber(&rp) 将路径转换为 logical drive number
第三 进入函数 get_ldnumber()
1 /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 2 /* Get logical drive number from path name */ 3 /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 4 5 static 6 int get_ldnumber ( /* Returns logical drive number (-1:invalid drive) */ 7 const TCHAR** path /* Pointer to pointer to the path name */ 8 ) 9 { 10 const TCHAR *tp, *tt; 11 UINT i; 12 int vol = -1; 13 14 15 if (*path) { /* If the pointer is not a null */ 16 for (tt = *path; (UINT)*tt >= (_USE_LFN ? ' ' : '!') && *tt != ':'; tt++) ; /* Find ':' in the path */ 17 if (*tt == ':') { /* If a ':' is exist in the path name */ 18 tp = *path; 19 i = *tp++ - '0'; 20 if (i < 10 && tp == tt) { /* Is there a numeric drive id? */ 21 if (i < _VOLUMES) { /* If a drive id is found, get the value and strip it */ 22 vol = (int)i; 23 *path = ++tt; 24 } 25 } else { /* No numeric drive number */ 26 #if _STR_VOLUME_ID /* Find string drive id */ 27 static const char* const str[] = {_VOLUME_STRS}; 28 const char *sp; 29 char c; 30 TCHAR tc; 31 32 i = 0; tt++; 33 do { 34 sp = str[i]; tp = *path; 35 do { /* Compare a string drive id with path name */ 36 c = *sp++; tc = *tp++; 37 if (IsLower(tc)) tc -= 0x20; 38 } while (c && (TCHAR)c == tc); 39 } while ((c || tp != tt) && ++i < _VOLUMES); /* Repeat for each id until pattern match */ 40 if (i < _VOLUMES) { /* If a drive id is found, get the value and strip it */ 41 vol = (int)i; 42 *path = tt; 43 } 44 #endif 45 } 46 return vol; 47 } 48 #if _FS_RPATH && _VOLUMES >= 2 49 vol = CurrVol; /* Current drive */ 50 #else 51 vol = 0; /* Drive 0 */ 52 #endif 53 } 54 return vol; 55 }
本函数获取 path 后解析 path 得到 logical drive number
代码中
第15行 判断 path 的内容是否为空字符 NULL
第16行 检测冒号 ‘:’,for循环的条件为 路径名中的字符 >= (_USE_LFN ? ' ': '!') 且 != ‘:’,只要_USE_LFN>0则第一个条件恒满足,找到冒号‘:’后则第二个条件失败,即跳出循环
第17行 再次确认当前路径字符为冒号‘:’
第18行 暂存*path
第19行 得到路径中的首字符那个数字字符对应的数字
第20行 判断该数字在0~9之中,且路径中的第二个字符为冒号‘:’
第21行 判断该数字在定义的范围内
第22行 将该数字赋值给vol
第46行 最终将vol值返回
帮助理解的代码示例
示例一 指针与字符串
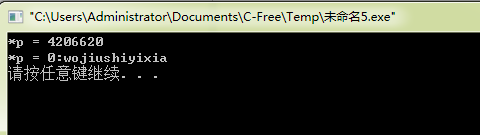
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 3 void ptf(char **p); 4 5 int main(void) 6 { 7 char *pstr = "0:wojiushiyixia"; 8 9 ptf(&pstr); 10 11 return 0; 12 } 13 14 void ptf(char **p) 15 { 16 if(*p) 17 { 18 printf("*p = %d ", *p); 19 printf("*p = %s ", *p); 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 printf("*p = NULL "); 24 } 25 26 }
运行环境 C-Free5.0
运行结果
示例二 多参数宏定义
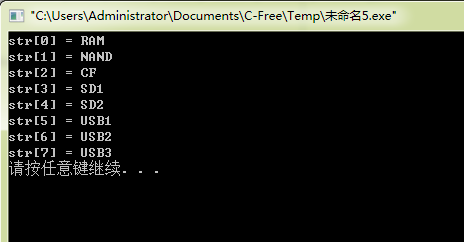
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 3 #define _VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD1","SD2","USB1","USB2","USB3" 4 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 int i; 9 static const char* const str[] = {_VOLUME_STRS}; 10 11 for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) 12 { 13 printf("str[%d] = %s ", i, str[i]); 14 } 15 16 return 0; 17 }
运行环境 C-Free5.0
运行结果