转自:https://blog.csdn.net/eydwyz/article/details/56671023
都只有一个的情况下,否则也要加锁。下面就内核中提取出来,而经过修改后的fifo进
行简要的分析。
先看其只要数据结构:
struct my_fifo {
unsignedchar *buffer;/* the buffer holding the data*/
unsignedint size;/* the size of the allocated buffer*/
unsignedint in;/* data is added at offset (in % size)*/
unsignedint out;/* data is extracted from off. (out % size)*/
}
也不用多说,一看就明白。size, in, out 都设成无符号型的,因为都不存在负值的情型。
/*form kernel/kfifo.c
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fifo.h>
#define min(a,b) ((a) < (b) ? (a):(b))
/*
my_fifo_init
*/
struct my_fifo *my_fifo_init(unsignedchar *buffer,unsigned int size){
struct my_fifo *fifo;
fifo = malloc(sizeof(struct my_fifo));
if (!fifo)
returnNULL;
fifo->buffer = buffer;
fifo->size = size;
fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
return fifo;
}
这个初始化fifo结构的函数一般也不会在应用层里进行调用,而是被下面的fifo_alloc
调用。依我的观点来看,这两个函数合成一个函数会更加的清晰,但是这一情况只针对
buffer是系统开辟的空间,如果buffer的空间是由其它的函数来提供,就只能用上面的这个函数。
/*
my_fifo_alloc
*/
struct my_fifo *my_fifo_alloc(unsignedint size)
{
unsignedchar *buffer;
struct my_fifo *ret;
/*
* round up to the next power of 2, since our 'let the indices
* wrap' tachnique works only in this case.
*/
buffer = malloc(size);
if (!buffer)
returnNULL;
ret = my_fifo_init(buffer, size);
if (ret ==NULL)
free(buffer);
return ret;
}
/*
* my_fifo_free
*/
void my_fifo_free(struct my_fifo *fifo)
{
free(fifo->buffer);
free(fifo);
}
这两个函数也不作过多的分析,都很清晰。
/*
my_fifo_put()
*/
unsignedint my_fifo_put(struct my_fifo
*fifo,
unsignedchar *buffer, unsigned int len)
{
unsignedint l;
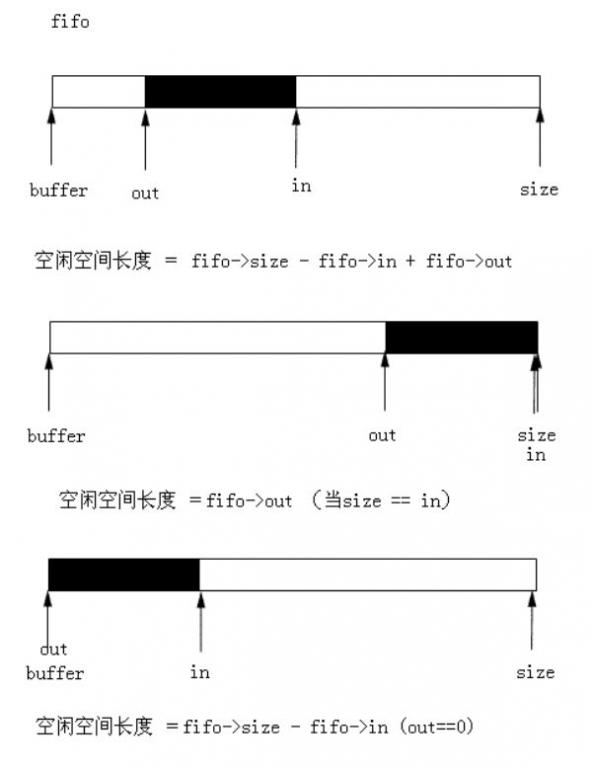
len = min(len, fifo->size - fifo->in + fifo->out);/*可能是缓冲区的空闲长度或者要写长度*/
/* first put the data starting from fifo->in to buffer end*/
l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->in & (fifo->size -1)));
memcpy(fifo->buffer + (fifo->in & (fifo->size -1)), buffer, l);
/* then put the rest (if any) at the beginning of the buffer*/
memcpy(fifo->buffer, buffer + l, len - l);
fifo->in += len;
return len;
}
/*
my_fifo_get
*/
unsignedint my_fifo_get(struct my_fifo
*fifo,
unsignedchar *buffer, unsigned int len)
{
unsignedint l;
len = min(len, fifo->in - fifo->out); /*可读数据*/
/* first get the data from fifo->out until the end of the buffer*/
l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->out & (fifo->size -1)));
memcpy(buffer, fifo->buffer + (fifo->out & (fifo->size -1)), l);
/* then get the rest (if any) from the beginning of the buffer*/
memcpy(buffer + l, fifo->buffer, len - l);
fifo->out += len;
return len;
}
这两个读写结构才是循环缓冲区的重点。在fifo结构中,size是缓冲区的大小,是由用
户自己定义的,但是在这个设计当中要求它的大小必须是2的幂次。
当in==out时,表明缓冲区为空的,当(in-out)==size 时,说明缓冲区已满。
我们看下具体实现,在86行处如果size-in+out ==0,也即获得的len值会0,而没有数
据写入到缓冲区中。所以在设计缓冲区的大小的时候要恰当,读出的速度要比定入的速
度要快,否则缓冲区满了会使数据丢失,可以通过成功写入的反回值来做判断尝试再次
写入.
另一种情况则是缓冲区有足够的空间给要写入的数据,但是试想一下,如果空闲的空间
在缓冲的首尾两次,这又是如何实现呢?这部分代码实现得非常巧妙。
我们看fifo->in &(fifo->size-1) 这个表达式是什么意思呢?我们知道size是2的幂次
项,那么它减1即表示其值的二进制所有位都为1,与in相与的最终结果是in%size,比
size要小,所以看in及out的值都是不断地增加,但再相与操作后,它们即是以size为
周期的一个循环。89行就是比较要写入的数据应该是多少,如果缓冲区后面的还有足够
的空间可写,那么把全部的值写到后面,否则写满后面,再写到前面去93行。
读数据也可以作类似的分析,108行表示请求的数据要比缓冲区的数据要大时,只
读取缓冲区中可用的数据。
staticinline void my_fifo_reset(struct my_fifo
*fifo)
{
fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
}
staticinline unsigned int my_fifo_len(struct my_fifo
*fifo)
return fifo->in - fifo->out;
}
在头文件里还有缓冲区置位及返回缓冲区中数据大小两个函数,很简单,不必解释