Vuex作用
自己实现变量共享可以通过Vue.prototype.shareObj = shareObj 来实现,但不是响应式
Vuex状态管理图
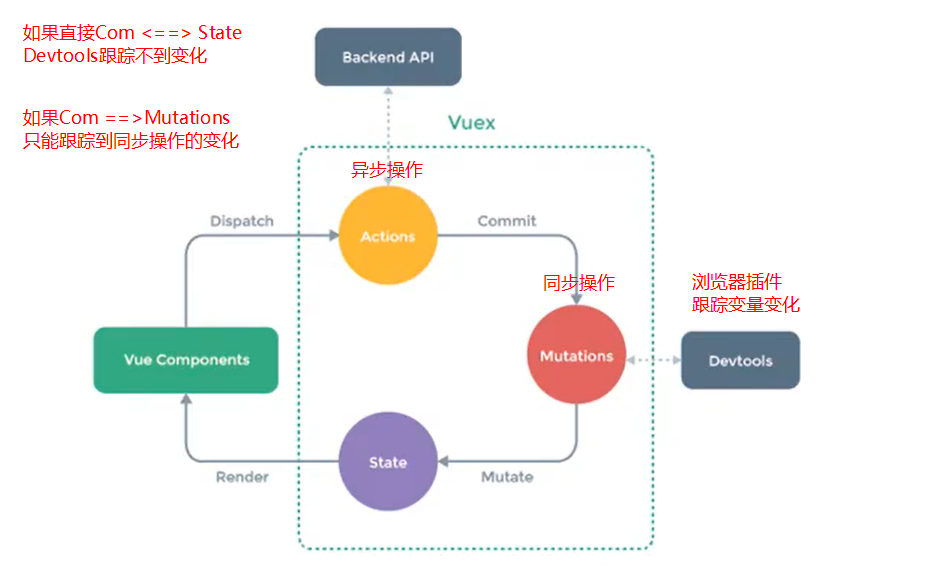
具体代码参考案例6
参考视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15741177Eh?p=128
1、Vuex的基本结构

import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex'; Vue.use(Vuex); const store = new Vuex.Store({ // 状态 state: {}, // 状态更新 // 同步方法 mutations: {}, // 异步操作 actions: {}, getters: {}, // 模块划分 modules: {} });
2、State单一状态树
一个项目使用一个Store对象来存储所有的信息,形成单个数据源

state: { counter: 1000, students: [{ id: 110, name: 'bot1', age: 18 }, { id: 111, name: 'bot2', age: 20 }, { id: 112, name: 'bot3', age: 14 }, { id: 113, name: 'bot4', age: 24 } ], info: { name: 'Smallstars', age: 18, height: 1.83 } },
3、mutations+mutations-types(同步方法)
实现:自带state参数

mutations: { // 同步方法 // 通过mutations-types.js进行统一,错了也能用(此处是ES6语法,INCREMENT=increment) [INCREMENT](state) { state.counter++; }, decrement(state) { state.counter--; }, // 用特殊提交参数变成一个对象 incrementCount(state, payload) { state.counter += payload.count }, addStuden(state, stu) { state.students.push(stu) }, updateInfo() { store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo', '我是携带信息').then( res => { console.log('完成提交'); console.log(res); } ) }, },
调用:使用commit,注意传参的两种方式

addition() { this.$store.commit(INCREMENT); }, subtraction() { this.$store.commit("decrement"); }, addCount(count) { // 1.普通提交 // this.$store.commit("incrementCount", count); // 2.特殊提交 this.$store.commit({ type: "incrementCount", count }); },
4、getters(相当于计算属性)
实现:自带state、getters参数

getters: { powerCounter(state) { return state.counter * state.counter }, more18stu(state) { return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 18); }, more18stuLength(state, getters) { return getters.more18stu.length; }, moreAgeStu(state) { return age => { return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age) } } },
如果getters被传入参数的时候,需要在getters中的函数中再写一个函数,不能直接传参
调用:

<h2>-------APP内容: getters相关信息-------</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.powerCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.more18stu }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.more18stuLength }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.moreAgeStu(15) }}</h2>
5、actions(异步方法)
实现:自带context <==> {state,commit,(rootState)}

actions: { // 异步操作 // 默认为上下文不再是state aUpdateInfo(context, payload) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { // 通过mutations更改 context.commit('updateInfo') console.log(payload); resolve('1111') }, 1000); }) } },
调用:(虽然在这里可以直接更改,但是如果不通过mutations的话,Devtools检测不到,属性变化都需要通过mutations,所以调用mutations来进行数据操作)

aUpdateInfo() { this.$store.dispatch("aUpdateName"); }
6、modules(将Store分割成各个模块,每个模块都拥有上述属性)
实现:

const moduleA = { state: { name: '张三' }, mutations: { updateName(state, payload) { state.name = payload } }, getters: { fullName(state) { return state.name + '111' }, fullName2(state, getters) { return getters.fullName + '222' }, // 模块中可以有第三个模块 rootState是主模块 fullName3(state, getters, rootState) { return getters.fullName2 + rootState.counter } }, actions: { aUpdateName(context) { // 主模块都是commit本身中的mutations setTimeout(() => { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { context.commit('updateName', '王五') resolve }) }, 1000); } }, }
调用:
- state要解析到模块
- mutations从主模块向下寻找
- getters直接解析(state为模块的state,getters为模块的getters,rootState为主模块的state)
- actions中的commit只调用模块的mutations

<h2>-------APP内容: modules中的内容-------</h2>
<!-- 属性要解析到模块 -->
<h2>{{ $store.state.a.name }}</h2>
<!-- 同步方法从主模块开始寻找 -->
<button @click="updateName">修改名字</button>
<!-- 直接解析即可 -->
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName2 }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName3 }}</h2>
<button @click="asyncUpdateName">模块修改信息</button>
7、目录划分