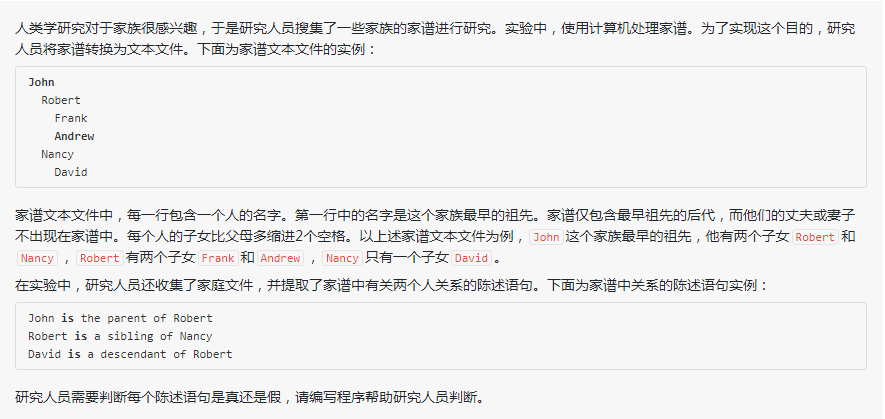
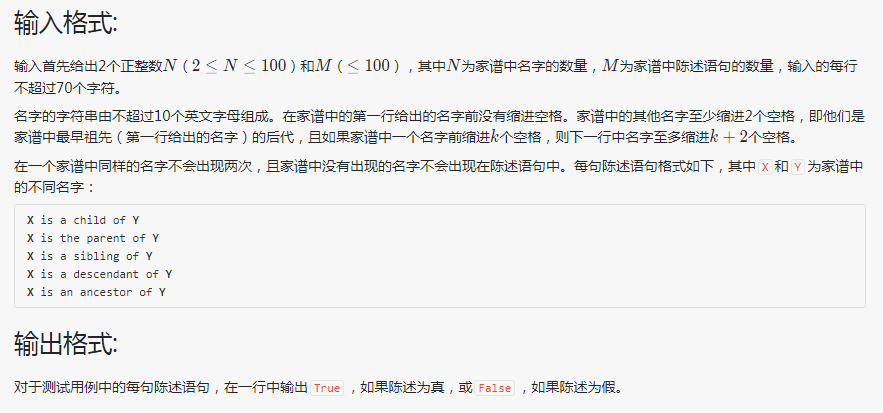
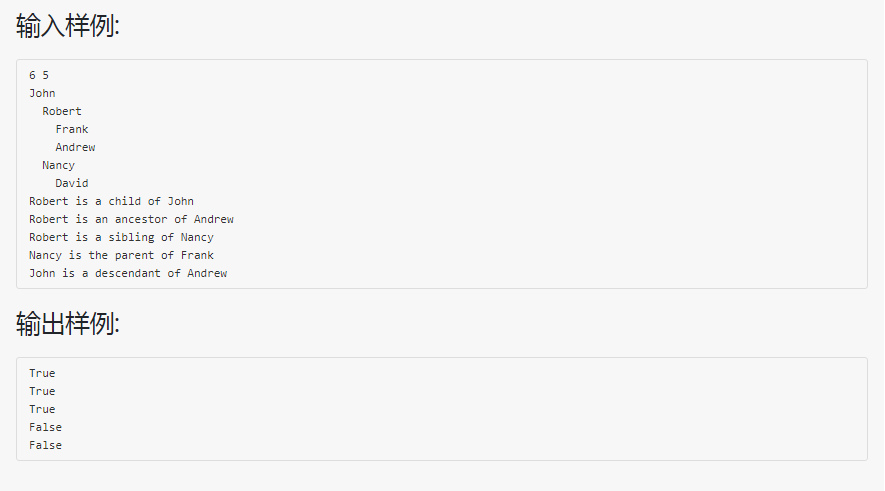
解题思路:采用结构体来存储家谱
其中需要注意的是祖先和后代的判断
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef char Element[11]; typedef struct { Element Name; int parent; int space; } Genealogy; Genealogy G[100]; int n,m; void Initial(); int GetWord(Element word); int FindPos(Element x); int JudgeChild(int x,int y); int JudgeParent(int x,int y); int JudgeSibling(int x,int y) ; int JudgeDescendant(int x,int y); int JudgeAncestor(int x,int y); void Judge(); int main(int argc,char **argv) { Initial(); Judge(); return 0; } int GetWord(Element word) { char c; int p=0; int space=0; scanf("%c",&c); while(!isalpha(c)&&c!=' ') scanf("%c",&c); while(c==' ') { space++; scanf("%c",&c); } while(isalpha(c)) { word[p++]=c; scanf("%c",&c); } if(c==' ') { word[p]='�'; return space; } } int FindPos(Element x) { int i; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { if(strcmp(x,G[i].Name)==0) return i; } } //X is a child of Y int JudgeChild(int x,int y) { if(G[x].parent==y) return 1; return 0; } //X is the parent of Y int JudgeParent(int x,int y) { return JudgeChild(y,x); } //X is a sibling of Y int JudgeSibling(int x,int y) { if(G[x].parent==G[y].parent) return 1; return 0; } //X is a descendant of Y int JudgeDescendant(int x,int y) { if(!y) return 1; while(G[x].parent!=-1&&G[x].parent!=y) x=G[x].parent; if(G[x].parent==-1) return 0; if(G[x].parent==y) return 1; } //X is an ancestor of Y int JudgeAncestor(int x,int y) { return JudgeDescendant(y,x); } void Initial() { Element word; int i,j; scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { G[i].space=GetWord(word); strcpy(G[i].Name,word); if(G[i].space==0) G[i].parent=-1; else { for(j=i-1; j>=0; j--) { if(G[i].space-G[j].space==2) { G[i].parent=j; break; } } } } } void Judge() { Element n1,n2,c1,c2,c3,c4; int i; for(i=0; i<m; i++) { int flag=0; scanf("%s%s%s%s%s%s",n1,c1,c2,c3,c4,n2); int x=FindPos(n1),y=FindPos(n2); if(!strcmp(c3,"child")) flag=JudgeChild(x,y); else if(!strcmp(c3,"parent")) flag=JudgeParent(x,y); else if(!strcmp(c3,"sibling")) flag=JudgeSibling(x,y); else if(!strcmp(c3,"descendant")) flag=JudgeDescendant(x,y); else if(!strcmp(c3,"ancestor")) flag=JudgeAncestor(x,y); if(flag) printf("True "); else printf("False "); } }