学习任何一门框架,都不可能一股脑儿的从入口代码从上到下,把代码看完,
这样其实是很枯燥的,我想也很少有人这么干,或者这么干着干着可能干不下去了。
因为肯定很无聊。
我们先从一个最最简单的小例子,来查看new Vue(options)实例,这个过程发生了什么。
vm实例上的属性又如何添加上去的,又如何渲染到浏览器页面上的。
关于vue的数据依赖和虚拟dom都是重点,必然会在以后的帖子记录。
这篇帖子就根据下例子,看看实例化一个vm实例做了啥吧。
先把小例子贴出来:
<div id="app">
<p>这是<span>静态内容</span></p>
<p>{{message}}</p>
</div>
<script src="../../dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hi vue!'
}
})
console.log(vm)
</script>
根据上篇介绍了vue的调式笔记,那我们快快进入源码吧
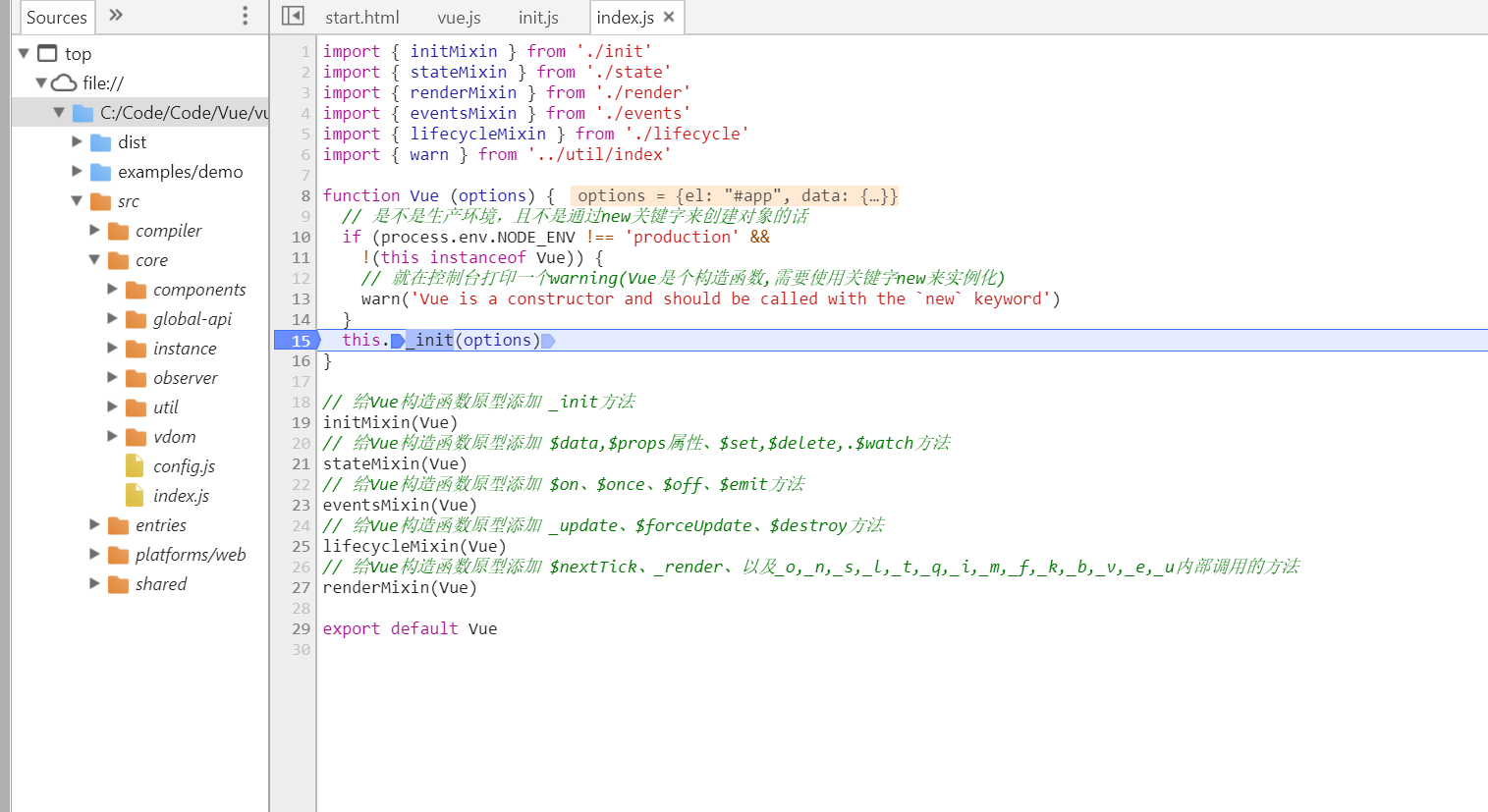
根据vue构造函数那篇笔记,我们知道了Vue原型上有哪些方法,_init方法就是其中一个方法
我们看到_init就把实例要做的事情都做完了,当然其中有的语句所做的事,太多了。我们先一点一点开see see吧。
看图不好玩,我把源码取出 来 好好瞧瞧
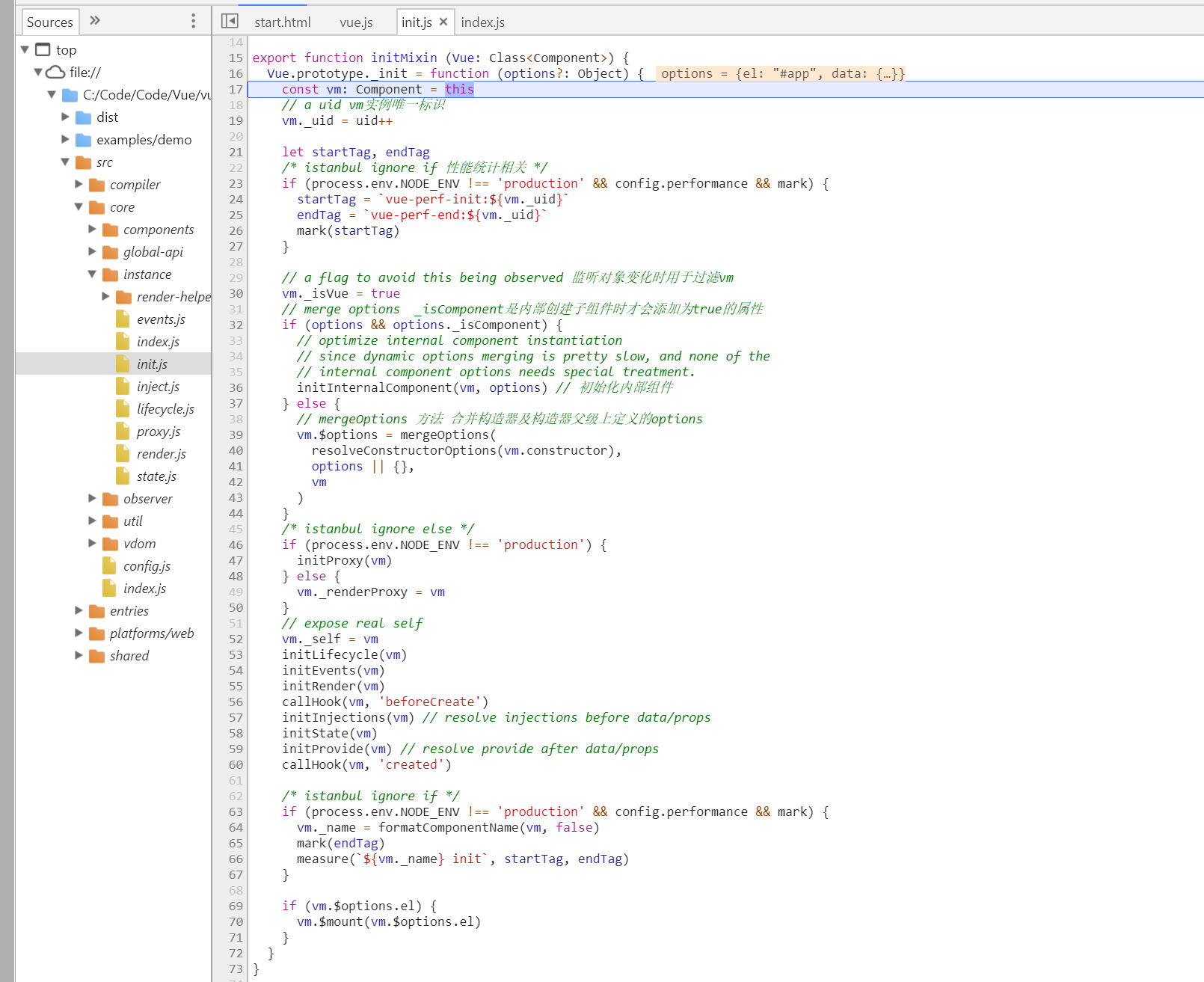
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) { Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { const vm: Component = this // a uid vm实例唯一标识 vm._uid = uid++ let startTag, endTag /* istanbul ignore if 性能统计相关 */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { startTag = `vue-perf-init:${vm._uid}` endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}` mark(startTag) } // a flag to avoid this being observed 监听对象变化时用于过滤vm vm._isVue = true // merge options _isComponent是内部创建子组件时才会添加为true的属性 if (options && options._isComponent) { // optimize internal component instantiation // since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the // internal component options needs special treatment. initInternalComponent(vm, options) // 初始化内部组件 } else { // mergeOptions 方法 合并构造器及构造器父级上定义的options vm.$options = mergeOptions( resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor), options || {}, vm ) } /* istanbul ignore else */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { initProxy(vm) } else { vm._renderProxy = vm } // expose real self vm._self = vm initLifecycle(vm) initEvents(vm) initRender(vm) callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props initState(vm) initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props callHook(vm, 'created') /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false) mark(endTag) measure(`${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag) } if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) } } }
1. 给实例添加了唯一标识uid
2.性能统计相关,先忽略
3. 给实例添加_isVue,监听对象变化时用于过滤vm
4. 选项对象如果有_isComponent,就初始化内部组件,_isComponent是内部创建子组件时才会添加为true的属性
5. 小例子会走分支,mergeOptions 方法 合并构造器及构造器父级上定义的options,resolveConstructorOptions方法后面笔记会详解,
mergeOptions方法接受3个参数。我们先简单看下resolveConstructorOptions方法的定义
export function resolveConstructorOptions (Ctor: Class<Component>) { let options = Ctor.options // 有super属性,说明Ctor是通过Vue.extend()方法创建的子类 if (Ctor.super) { const superOptions = resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor.super) const cachedSuperOptions = Ctor.superOptions if (superOptions !== cachedSuperOptions) { // super option changed, // need to resolve new options. Ctor.superOptions = superOptions // check if there are any late-modified/attached options (#4976) const modifiedOptions = resolveModifiedOptions(Ctor) // update base extend options if (modifiedOptions) { extend(Ctor.extendOptions, modifiedOptions) } options = Ctor.options = mergeOptions(superOptions, Ctor.extendOptions) if (options.name) { options.components[options.name] = Ctor } } } return options }
可以看出Ctor.options其实就是Vue构造函数自身,在Vue构造函数静态属性那篇笔记,Vue是拥有options属性的,且有截图,等下会再截图看下,
接着在该函数中有个if语句,我们小例子会跳过的,直接返回options。因为有super属性,说明Ctor是通过Vue.extend()方法创建的子类。那么
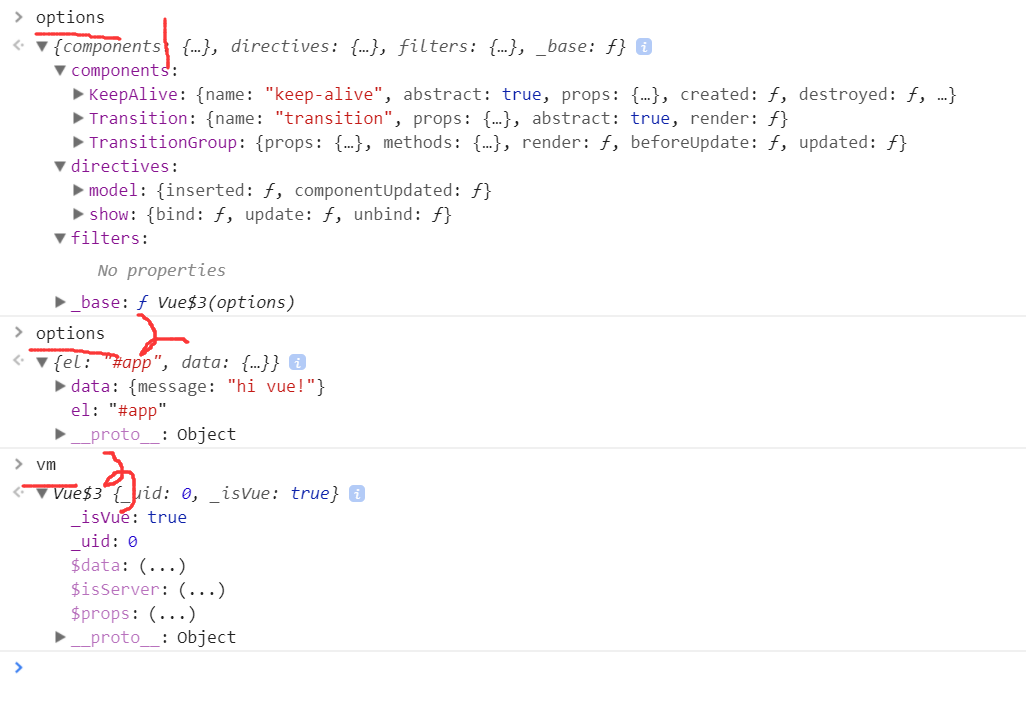
options是啥呢,如下图,

回到_init方法中,mergeOptions方法的第二个参数就是我们传入的options,第三个参数就是vm实例,把参数一起截个图吧,好回忆
mergeOptions是Vue中处理属性的合并策略的地方, 先看下它的定义
export function mergeOptions ( parent: Object, child: Object, vm?: Component ): Object { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { // 如果有options.components,则判断是否组件名是否合法 checkComponents(child) } // 格式化child的props normalizeProps(child) // 格式化child的directives normalizeDirectives(child) const extendsFrom = child.extends if (extendsFrom) { parent = typeof extendsFrom === 'function' ? mergeOptions(parent, extendsFrom.options, vm) : mergeOptions(parent, extendsFrom, vm) } if (child.mixins) { for (let i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) { let mixin = child.mixins[i] if (mixin.prototype instanceof Vue) { mixin = mixin.options } parent = mergeOptions(parent, mixin, vm) } } const options = {} let key for (key in parent) { mergeField(key) } for (key in child) { if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) { mergeField(key) } } function mergeField (key) { const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key) } return options }
该函数主要返回一个数据合并后的options,
我们的小例子比较简单, so关于判断是否组件名是否合法,
格式化child的props, 格式化child的directives
extends, mixins 先跳过。
我们直接看怎么把属性合并到options = {}这个对象上的
首先遍历parent对象,然后通过mergeField函数,把components,
directives, filters, _base属性先添加到options对象上,值为
strats对象上的静态方法。
然后遍历child对象,把el, data属性也添加到options = {} 这个对象上
值为strats对象上对应的静态方法。
那我们先看看strats这个对象上有哪些静态方法,源码如下(src/util/options.js)
const strats = config.optionMergeStrategies if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { strats.el = strats.propsData = function (parent, child, vm, key) { /**/ } } strats.data = function ( parentVal: any, childVal: any, vm?: Component ): ?Function { /**/ } function mergeHook ( parentVal: ?Array<Function>, childVal: ?Function | ?Array<Function> ): ?Array<Function> { return childVal ? parentVal ? parentVal.concat(childVal) : Array.isArray(childVal) ? childVal : [childVal] : parentVal } config._lifecycleHooks.forEach(hook => { strats[hook] = mergeHook }) function mergeAssets (parentVal: ?Object, childVal: ?Object): Object { /**/ } config._assetTypes.forEach(function (type) { strats[type + 's'] = mergeAssets }) strats.watch = function (parentVal: ?Object, childVal: ?Object): ?Object { /* istanbul ignore if */ /**/ } strats.props = strats.methods = strats.computed = function (parentVal: ?Object, childVal: ?Object): ?Object { if (!childVal) return Object.create(parentVal || null) if (!parentVal) return childVal /**/ } const defaultStrat = function (parentVal: any, childVal: any): any { return childVal === undefined ? parentVal : childVal }
以上是缩减版的代码,其实看下截图,会一目了然

可以看到其实就是我们new Vue(options) 中的options对象中的可选参数。我们小例子只传了el, data,
我们看看通过mergeOptions方法合并后的options长的什么鸟样,如图:
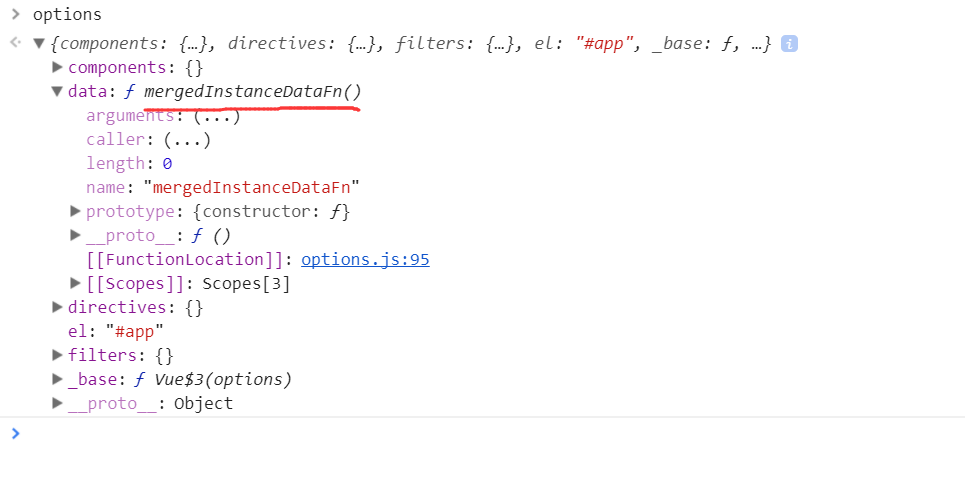
其实小例子只是走个过程,没必要把所有函数代码弄懂,先把大体流程走完,后续代码在一一分析。
6. 回到vm_init()方法中,接着走initProxy(vm)这个语句,这个语句其实就是给vm实例添加了一个_renderProxy属性,值为为一个Proxy代理对象,生产环境就是vm自身。
接下来的每个语句都有好多代码啊,我们一个个 look see see
7. initLifecycle 方法的定义
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) { const options = vm.$options // locate first non-abstract parent let parent = options.parent if (parent && !options.abstract) { while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) { parent = parent.$parent } parent.$children.push(vm) } vm.$parent = parent vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm vm.$children = [] vm.$refs = {} vm._watcher = null vm._inactive = null vm._directInactive = false vm._isMounted = false vm._isDestroyed = false vm._isBeingDestroyed = false }
初始化生命周期,该函数只是给vm添加了
$parent, $root, $children, $refs, _watcher,
_inactive, _directInactive, _isMounted, _isDestroyed
_isBeingDestroyed属性。
options.abstract用于判断是否是抽象组件,
组件的父子关系建立会跳过抽象组件,抽象组件比如keep-alive、transition等。
所有的子组件$root都指向顶级组件。
8. initEvents方法的定义
export function initEvents (vm: Component) { vm._events = Object.create(null) vm._hasHookEvent = false // init parent attached events const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners if (listeners) { updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners) } }
该方法初始化事件相关的属性,给vm实例添加了_events, _hasHookEvent属性
_parentListeners是父组件中绑定在自定义标签上的事件,供子组件处理。
9. initRender方法的定义
export function initRender (vm: Component) { vm.$vnode = null // the placeholder node in parent tree vm._vnode = null // the root of the child tree vm._staticTrees = null const parentVnode = vm.$options._parentVnode const renderContext = parentVnode && parentVnode.context vm.$slots = resolveSlots(vm.$options._renderChildren, renderContext) vm.$scopedSlots = emptyObject // bind the createElement fn to this instance // so that we get proper render context inside it. // args order: tag, data, children, normalizationType, alwaysNormalize // internal version is used by render functions compiled from templates vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false) // normalization is always applied for the public version, used in // user-written render functions. vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true) }
这里先给vm添加了$vnode, _vnode, _staticTrees, $slots, $scopedSlots, _c, $createElement
属性或者方法(添加了一些虚拟dom、slot等相关的属性和方法)
10. 调用beforeCreate钩子
11. 调用initInjections(vm)方法,我们小例子比较简单,不会进入if语句中
export function initInjections (vm: Component) { const inject: any = vm.$options.inject if (inject) { // inject is :any because flow is not smart enough to figure out cached // isArray here const isArray = Array.isArray(inject) const keys = isArray ? inject : hasSymbol ? Reflect.ownKeys(inject) : Object.keys(inject) for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) { const key = keys[i] const provideKey = isArray ? key : inject[key] let source = vm while (source) { if (source._provided && provideKey in source._provided) { /* istanbul ignore else */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { defineReactive(vm, key, source._provided[provideKey], () => { warn( `Avoid mutating an injected value directly since the changes will be ` + `overwritten whenever the provided component re-renders. ` + `injection being mutated: "${key}"`, vm ) }) } else { defineReactive(vm, key, source._provided[provideKey]) } break } source = source.$parent } } } }
将父组件provide中定义的值,通过inject注入到子组件,且这些属性不会被观察
12. initState(vm)
export function initState (vm: Component) { vm._watchers = [] const opts = vm.$options if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props) if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods) if (opts.data) { initData(vm) } else { observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */) } if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed) if (opts.watch) initWatch(vm, opts.watch) }
该方法主要就是操作数据了,props、methods、data、computed、watch,
从这里开始就涉及到了Observer、Dep和Watcher,下个笔记再记录
13. initProvide(vm)
export function initProvide (vm: Component) { const provide = vm.$options.provide if (provide) { vm._provided = typeof provide === 'function' ? provide.call(vm) : provide } }
也不会进分支,先略过
14. 调用created钩子函数。
可以看到在created钩子函数调用前, 基本就是对传入数据的格式化、数据的双向绑定、以及一些属性的初始化。
现在来看下实例的属性和方法


接下来看看怎么把html模板中的属性出来的
15. vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount // 重写Vue构造函数原型上的$mount方法 Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && query(el) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.` ) return this } const options = this.$options // resolve template/el and convert to render function if (!options.render) { let template = options.template if (template) { if (typeof template === 'string') { if (template.charAt(0) === '#') { template = idToTemplate(template) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) { warn( `Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this ) } } } else if (template.nodeType) { template = template.innerHTML } else { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn('invalid template option:' + template, this) } return this } } else if (el) { template = getOuterHTML(el) } if (template) { /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile') } const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, { shouldDecodeNewlines, delimiters: options.delimiters }, this) options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile end') measure(`${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end') } } } return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) }
该方法主要拿到template模板,然后通过compileToFunctions方法的返回值给vm实例
的$options添加render属性,值为一个匿名函数该匿名函数返回值为:
with(this){return _c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},[_m(0),_v(" "),_c('p',[_v(_s(message))])])}
还添加了一个staticRenderFns属性,值为一个数组,数组元素为匿名函数:
anonymous() {
with(this){return _c('p',[_v("这是"),_c('span',[_v("静态内容")])])}
}
至于compileToFunctions函数先不拿出来看了,目前先知道它干了啥,就行了(至于实例的_c,_v,_m这些方法何时挂载上去的,前面笔记已经说过了)
之后调用 mount.call(this, el, hydrating) 方法
Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) }
该方法又调用mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
export function mountComponent ( vm: Component, el: ?Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { vm.$el = el if (!vm.$options.render) { vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { /* istanbul ignore if */ if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') || vm.$options.el || el) { warn( 'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' + 'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' + 'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.', vm ) } else { warn( 'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.', vm ) } } } callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') let updateComponent /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { updateComponent = () => { const name = vm._name const id = vm._uid const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}` const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}` mark(startTag) const vnode = vm._render() mark(endTag) measure(`${name} render`, startTag, endTag) mark(startTag) vm._update(vnode, hydrating) mark(endTag) measure(`${name} patch`, startTag, endTag) } } else { updateComponent = () => { vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) } } vm._watcher = new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop) hydrating = false // manually mounted instance, call mounted on self // mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook if (vm.$vnode == null) { vm._isMounted = true callHook(vm, 'mounted') } return vm }
小例子在该方法大致流程是这么走的
因为vm.$options.render就是给匿名函数,所以不会走if分支,
然后调用beforeMount钩子函数
再然后定义一个updateComponent函数,这个函数怎么执行是个关键
然后给实例添加了一个_watcher属性,值为Watcher实例
然后如果vm.$vnode == null则把vm._isMounted变量置为true,然后调用mounted钩子函数
最后返回vm实例,可以链式调用。
触发updateCOMPONENT函数是new Watcher,先看看Watcher类的定义
constructor ( vm: Component, expOrFn: string | Function, cb: Function, options?: Object ) { this.vm = vm vm._watchers.push(this) if (options) { this.deep = !!options.deep this.user = !!options.user this.lazy = !!options.lazy this.sync = !!options.sync } else { this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false } ... this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? expOrFn.toString() : '' if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') { this.getter = expOrFn } else { this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn) if (!this.getter) { this.getter = function () {} process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` + 'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' + 'For full control, use a function instead.', vm ) } } this.value = this.lazy ? undefined : this.get() } get () { pushTarget(this) let value const vm = this.vm if (this.user) { try { value = this.getter.call(vm, vm) } catch (e) { handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`) } } else { value = this.getter.call(vm, vm) } if (this.deep) { traverse(value) } popTarget() this.cleanupDeps() return value }
在构造函数中,expOrFn也就是updateComponent赋值给this.getter,
并且在获取this.value的值时会调用this.get(),这里的this.lazy默认值是false,
在computed属性中创建的Watcher会传入true。
在this.get()中,会调用this.getter,所以上面的例子中,updateComponent方法会被调用,
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
回到该函数,先执行实例的_render函数,该函数主要生成虚拟dom
然后执行实例的update方法
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode { const vm: Component = this const { render, staticRenderFns, _parentVnode } = vm.$options if (vm._isMounted) { // clone slot nodes on re-renders for (const key in vm.$slots) { vm.$slots[key] = cloneVNodes(vm.$slots[key]) } } vm.$scopedSlots = (_parentVnode && _parentVnode.data.scopedSlots) || emptyObject if (staticRenderFns && !vm._staticTrees) { vm._staticTrees = [] } // set parent vnode. this allows render functions to have access // to the data on the placeholder node. vm.$vnode = _parentVnode // render self let vnode try { vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement) } catch (e) { handleError(e, vm, `render function`) // return error render result, // or previous vnode to prevent render error causing blank component /* istanbul ignore else */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { vnode = vm.$options.renderError ? vm.$options.renderError.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement, e) : vm._vnode } else { vnode = vm._vnode } } // return empty vnode in case the render function errored out if (!(vnode instanceof VNode)) { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && Array.isArray(vnode)) { warn( 'Multiple root nodes returned from render function. Render function ' + 'should return a single root node.', vm ) } vnode = createEmptyVNode() } // set parent vnode.parent = _parentVnode return vnode }
该函数主要是 vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)语句
函数调用过程中的this,是vm._renderProxy,是一个Proxy代理对象或vm本身。暂且把它当做vm本身。
_c是(a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)。
createElement函数做了这些事:
a是要创建的标签名,这里是div。
接着b是data,也就是模板解析时,添加到div上的属性等。
c是子元素数组,所以这里又调用了_c来创建一个p标签。
_v是createTextVNode,也就是创建一个文本结点。
_s是_toString,也就是把message转换为字符串,在这里,因为有with(this),
所以message传入的就是我们data中定义的第一个vue实例。
所以,render函数返回的是一个VNode对象,也就是我们的虚拟dom对象。
它的返回值,将作为vm._update的第一个参数。
接着看下update方法
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) { const vm: Component = this if (vm._isMounted) { callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate') } const prevEl = vm.$el const prevVnode = vm._vnode const prevActiveInstance = activeInstance activeInstance = vm vm._vnode = vnode // Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points // based on the rendering backend used. if (!prevVnode) { // initial render vm.$el = vm.__patch__( vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */, vm.$options._parentElm, vm.$options._refElm ) } else { // updates vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode) } activeInstance = prevActiveInstance // update __vue__ reference if (prevEl) { prevEl.__vue__ = null } if (vm.$el) { vm.$el.__vue__ = vm } // if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) { vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el } // updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are // updated in a parent's updated hook. }
从mountComponent中知道创建Watcher对象先于vm._isMounted = true。
所以这里的vm._isMounted还是false,不会调用beforeUpdate钩子函数。
下面会调用vm.__patch__,在这一步之前,
页面的dom还没有真正渲染。该方法包括真实dom的创建、虚拟dom的diff修改、dom的销毁等,
具体细节后续笔记在记录。