学习资源:慕课网liyubobobo老师的《玩儿转数据结构》
目录
1、简介
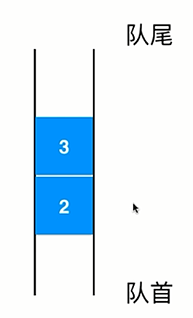
- 队列也是一种线性结构
- 队列对应的操作是数组的子集
- 队列只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素
- 队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,First In First Out (FIFO)
2、队列的接口
public interface Queue<E> {
void enqueue(E e);
E dequeue();
E getFront();
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
}
3、数组队列
3.1、数组对队列简介
- 内部封装一个动态数组对象,直接复用动态数组的方法实现队列接口
- 也可以叫做线性队列
3.2、代码
package queue;
import array.Array;
public class ArrayQueue<T> implements Queue<T> {
private Array<T> array;
public ArrayQueue() {
array = new Array<>();
}
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(T t) {
array.insertToLast(t);
}
@Override
public T dequeue() {
return array.removeHead();
}
@Override
public T getFront() {
return array.getHead();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return array.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Queue: ");
builder.append("front [");
for(int i=0; i<array.getSize(); i++){
builder.append(array.getElement(i));
if(i!=array.getSize()-1){
builder.append(", ");
}
}
builder.append("] tail");
return builder.toString();
}
}
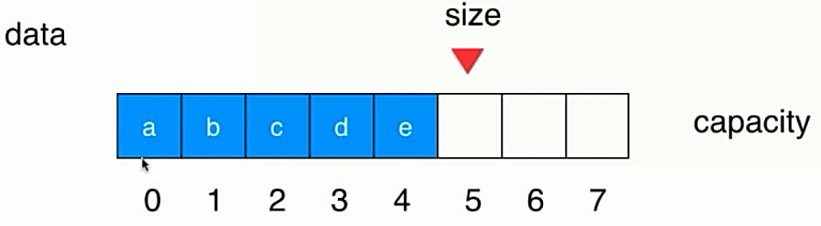
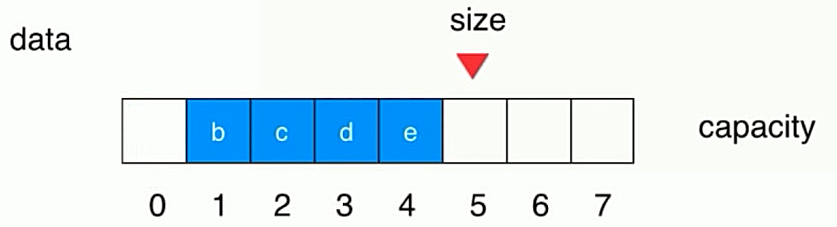
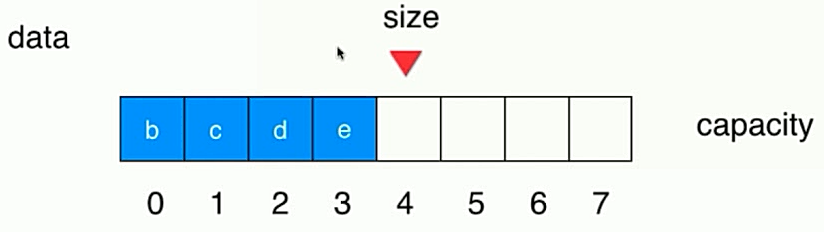
3.3、数组队列的弊端
- 出队操作,其后的元素都要向前移动一个位置,复杂度为O(n);
4、循环队列:数组队列的升级
4.1、循环队列简介
循环数组是数组队列优化,把循环队列想象为一个环。出对的复杂的降为O(1)

-
定义两个"指针"变量front、tail:front指向队列的第一个元素,tail指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置
(因为是一个环,所以规定顺逆时针方向来看,tail可能在front前面)
-
队列容量 = 数组长度 - 1,规定浪费一个数组空间
-
队列空条件:front == tail
-
队列满条件:(tail + 1)% 数组长度 == front (这样规定,会有意识地空置一个数组空间)
-
循环队列中,tail如何变化:tail = (队列最后一个元素的索引值 + 1) % 数组长度
4.2、相应的操作
- 循环队列初始化
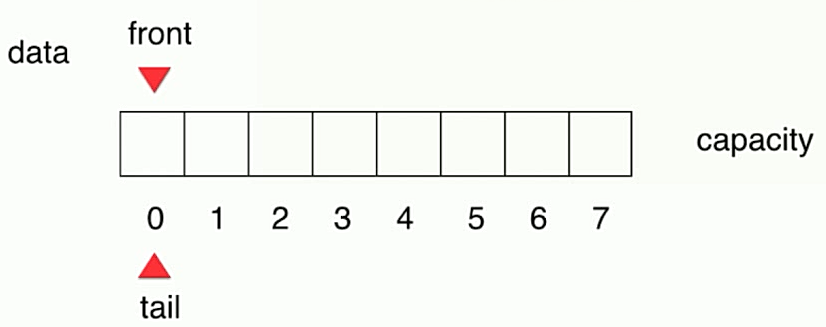
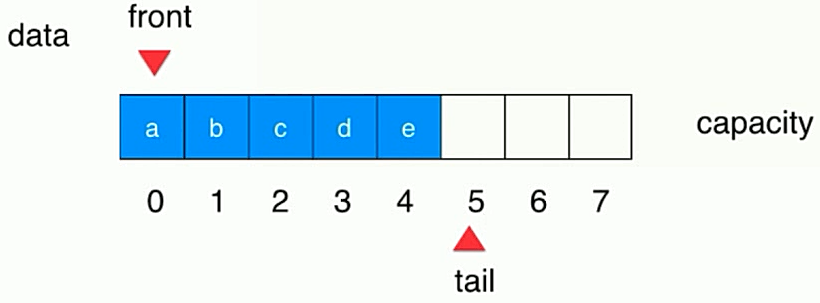
- 入队,tail移位,tail = (数组最后一个元素的索引值 + 1) / 数组的长度
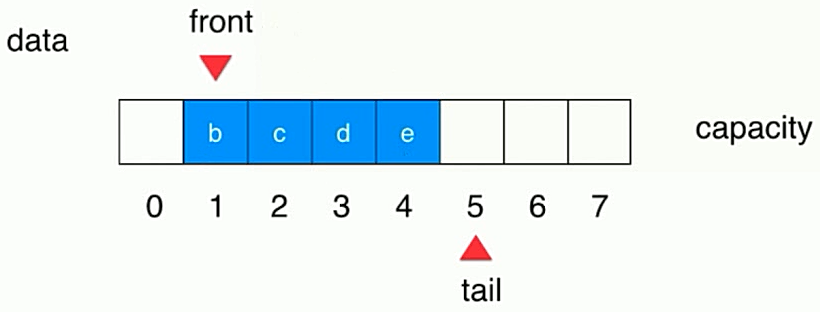
- 出队,front移位
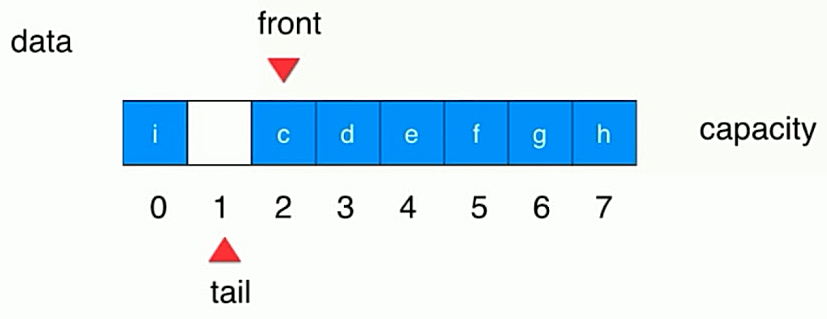
-
当数组空间的最后一个位置存入值后,此时 tail = (最大的索引值 + 1) % 数组长度 =0
此时如果数组前面有剩余空间:front>0,tail != front,还可以继续存入值

-
继续存入值,此时 tail+1 == front,队列满,但是这样会浪费一个数组空间
只要满足(tail+1) % 数组长度 == front 就可以说明队列已满
4.3、循环队列代码
注:这里是从右侧入队,左侧出队
package queue.loopQueue;
import queue.Queue;
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front, tail;
// 队列中元素的个数
private int size;
public LoopQueue(int capacity) {
data = (E[])new Object[capacity+1];
front = tail =0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue() {
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length - 1;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
if((tail+1)%data.length == front){
resize(getCapacity()*2);
}
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size++;
}
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity+1];
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
newData[i] = data[(i+front) % data.length];
}
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空");
}
E e = data[front];
data[front] = null;
front = (front+1) % data.length;
size--;
if(size == getCapacity()/4 && getCapacity()/2 != 0){
resize(getCapacity()/2);
}
return e;
}
@Override
public E getFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空");
}
return data[front];
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front==tail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Queue: size = %d, capacity = %d
", size, getCapacity());
builder.append("front [");
for(int i=front; i!=tail; i=(i+1)%data.length){
builder.append(data[i]);
if((i+1)%data.length != tail){
builder.append(", ");
}
}
builder.append("] tail");
return builder.toString();
}
}
4.4测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopQueue<Integer> integerLoopQueue = new LoopQueue<>(3);
System.out.println("当前队列的容量"+integerLoopQueue.getCapacity());
System.out.println("队列是否为空:"+integerLoopQueue.isEmpty());
System.out.println("当前队列的大小:"+integerLoopQueue.getSize());
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(10);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(20);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(40);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(5);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(25);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(36);
integerLoopQueue.enqueue(77);
System.out.println(integerLoopQueue);
System.out.println("队列是否为空:"+integerLoopQueue.isEmpty());
System.out.println("当前队列的大小:"+integerLoopQueue.getSize());
System.out.println("当前队列的容量"+integerLoopQueue.getCapacity());
System.out.println("队首元素:"+integerLoopQueue.getFront());
integerLoopQueue.dequeue();
integerLoopQueue.dequeue();
integerLoopQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("出队后的队列:");
System.out.println(integerLoopQueue);
}
5、测试比对
这里测试一下数组队列和循环队列:它们执行同样次数的入队出队操作。
执行时间相差很大,主要表现在出队操作上。循环队列不要快太多
package loopQueue;
import org.junit.Test;
import arrayQueue.ArrayQueue;
import arrayQueue.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
public class LoopQueueTest {
@Test
public void ArrayVsLoop(){
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>();
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
int arrayTime = getRunTime(1000000, arrayQueue);
int loopTime = getRunTime(1000000, loopQueue);
System.out.printf("顺序队列的执行时间是:%d毫秒
",arrayTime);
System.out.printf("循环队列的执行时间是:%d毫秒
",loopTime);
}
//毫秒级计时
private int getRunTime(int times, Queue<Integer> queue){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i=0; i<times; i++){
queue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for(int i=0; i<times; i++){
queue.dequeue();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long time = endTime - startTime;
return (int)time;
}
}
6、Java中的Queue
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。