前文中笔者介绍了管道,本文接着介绍命名管道。文中演示所用环境为 Ubuntu 18.04 desktop。
命名管道(named pipe)又被称为先进先出队列(FIFO),是一种特殊的管道,存在于文件系统中。命名管道与管道非常类似,但是又有自身的显著特征:
- 命名管道可以用于任何两个进程间的通信,而不限于同源的两个进程。
- 命名管道作为一种特殊的文件存放在文件系统中,而不是像管道那样存放在内核中。当进程对命名管道的使用结束后,命名管道依然存在于文件系统中,除非对其进行删除操作,否则该命名管道不会自行消失。
和管道一样,命名管道也只能用于数据的单向传输,如果要用命名管道实现两个进程间数据的双向传输,建议使用两个单向的命名管道。
创建命名管道
在命令行上创建命名管道
可以通过命令行命令 mkfifo 或 mknod 创建命名管道:
$ mkfifo /tmp/testp $ mknod /tmp/testp p
可以通过 ls 命令查看命名管道的文件属性:

输出中的第一个字符为 p,表示这个文件的类型为管道。最后的 | 符号是有 ls 命令的 -F 选项添加的,也表示这个一个管道。
在程序中创建命名管道
在程序中创建命名管道,可以使用 mkfifo 函数,其签名如下:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
参数 pathname 是一个字符串指针,用于存放命名管道的文件路径。参数 mode 用于表示指定所创建文件的权限。该函数调用成功时返回 0;调用失败时返回 -1。
mkfifo 函数是一个专门用来创建命名管道的函数,而另外一个函数 mknod 却可以兼职创建命名文件,其函数签名如下:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int mknod(char *pathname, mode_t mode, dev_t dev);
创建命名管道只是 mknod 函数的功能之一,它的前两个参数和 mkfifo 函数相同。在创建命名管道时,为第三个参数 dev 传递 0 就可以了。该函数调用成功时返回 0;调用失败时返回 -1。
在程序中使用命名管道
下面的 demo 模拟一个生产者进程和消费者进程,二者通过命名管道传输数据。生产者的代码如下:
#include <limits.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/testp" #define BUFFER_SIZE 4096 #define TEN_MEG (1024 * 1024 * 10) int main(void) { int pipe_fd; int res; int open_mode = O_WRONLY; int bytes_sent = 0; char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1]; if(access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) == -1) { res = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0777); if(res != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not create fifo %s ", FIFO_NAME); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } } printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_WRONLY ", getpid()); pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode); printf("Process %d opened fd %d ", getpid(), pipe_fd); if(pipe_fd != -1) { while(bytes_sent < TEN_MEG) { res = write(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); if(res == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Write error on pipe "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } bytes_sent += res; } (void)close(pipe_fd); } else { exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("Process %d finished ", getpid()); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
把上面的代码保存到文件 namedpipedemo.c 中。
消费者的代码如下:
#include <limits.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/testp" #define BUFFER_SIZE 4096 int main(void) { int pipe_fd; int res; int open_mode = O_RDONLY; int bytes_read = 0; char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1]; memset(buffer, '�', sizeof(buffer)); printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_RDONLY ", getpid()); pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode); printf("Process %d opened fd %d ", getpid(), pipe_fd); if(pipe_fd != -1) { do { res = read(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); bytes_read += res; } while (res > 0); (void)close(pipe_fd); } else { exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read ", getpid(), bytes_read); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
把上面的代码保存到文件 namedpipedemo2.c 中。并分别编译这两个程序:
$ gcc -Wall namedpipedemo.c -o pipe1 $ gcc -Wall namedpipedemo2.c -o pipe2
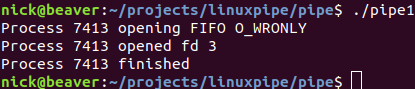
先在一个终端中执行生产者:

然后在另一个终端中执行消费者:
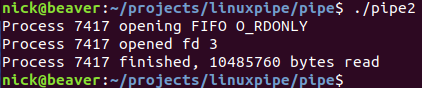
结果是二者完成数据传输后都返回了:
删除命名管道
删除命名管道和删除一个普通文件没有什么区别:
$ rm /tmp/testp
这就可以了!
参考:
《Linux 程序设计》
《Linux 环境下 C 编程指南》