前言:撸基础篇系列,避免每次都要从头开始看,写个自己的知识体系树
NIO 核心就是异步, 比如,复制文件,让操作系统去处理,等通知
BIO核心类
一,BIO
NIO基本操作类
Bytebuffer
构建:
用JVM的内存构建:
ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferSize)
用JVM的直接内存构建:
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(bufferSize)
内存结构:
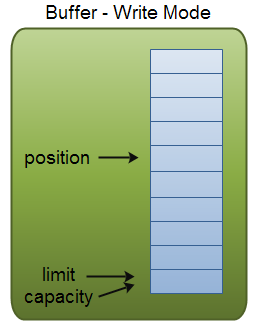 flip()后-->
flip()后-->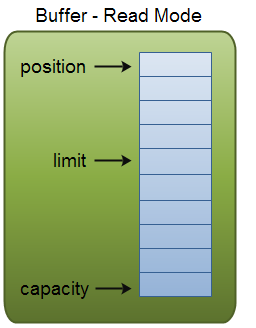
postion, limit,和captain的处理工具类
flip() 如上, postion=0, limit = wirtCont, captian不变
mark()与reset()方法连用,mark一个postion后,可以通过reset方法返回到原来的订单
缓存的数据处理类
clear() 方法会清空整个缓冲区。
compact()方法只会清除已经读过的数据(0到posstion)
CharSet
用于构建String 和ByteBuffer,以及编码的的一个转换类
构建:
Charset charSet = Charset.forName("gbk");
charSet.decode(butBf) , 用于byteBuffer to String
charSet.encode("测试下") 用于String to byteBuffer
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream finput = new FileInputStream("E://test.txt");
FileChannel fchannel = finput.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
fchannel.read(byteBf);
Charset charSet = Charset.forName("utf-8");
byteBf.flip();
System.out.println(charSet.decode(byteBf));
}
网络NIO基本操作
selector
一个轮询,实现了 SelectableChannel 接口的都可以在select上添加感兴趣的事件
NBlocking IO,网络服务
/**
* selector 只是一个通知,具体各个部分自行处理
*
* NIO , 不阻塞,当有东西来了就开始通知处理,不然能一直select到·
*
* @author hejb
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 阻塞为false
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 绑定IP和端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("0.0.0.0", 8080));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 注册感兴趣事件到selector
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (selector.select() != 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// 循选中事件
SelectionKey selecttionKey = iterator.next();
// 删除已经处理
iterator.remove();
if (selecttionKey.isAcceptable()) {
// 返回注册该事件时的channel ,即SelectableChannel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) selecttionKey.channel();
// 有连接事件来了, 可以处理接收请求了,注意如果不进行accept,select.select()一直能轮询到东西
// 接收后返回了个socketchannel,开始配置
SocketChannel socketChannel = channel.accept();
// 也配置成非阻塞处理
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 复用同一个selector上注册感兴趣的事件,并注册感兴趣的可读事件
socketChannel.register(selector, selecttionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 如果来可以可读事件
if (selecttionKey.isReadable()) {
// 返回注册该事件时的channel ,即实现了SelectableChannel的
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selecttionKey.channel();
// 后面就都是通过byteBuffer和channel来读操作了
ByteBuffer byteBf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(byteBf);
Charset charset = Charset.forName("utf-8");
byteBf.flip();
System.out.println("clinet :" + charset.decode(byteBf));
// socket是双通道,故也可以直接返回东西了
socketChannel.write(charset.encode("test only"));
}
}
}
}
// 有个疑问,NIO的链接什么时候关闭呢,有文章说是在finalize方法里,待我去找找
}
那么什么时候用IO,什么时候用NIO呢?
大量链接涌入的时候,传的数据比较少,然后处理时间比较长,的时候适合NIO(偏向IO密集型)
如果传入的链接比较少,然后传输数据量大,比如文件上传之类,适合BIO
NIO的网络模型:
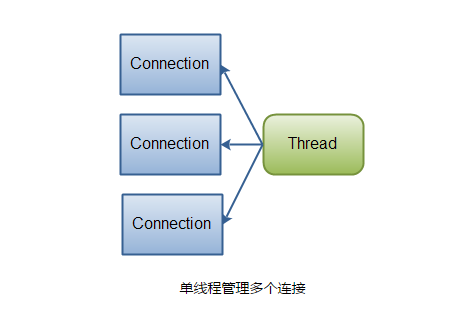
用一个thread(selector)做服务接收,和链接的维持
IO的网路模型
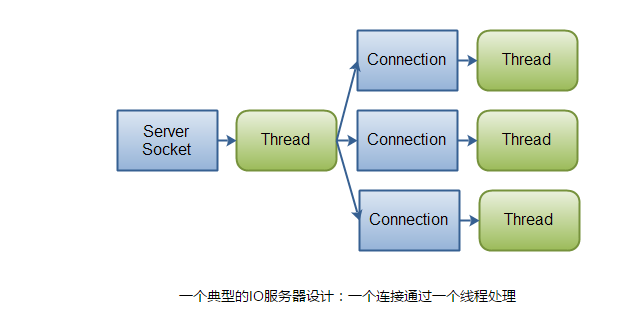
用一个thread做服务接收,其它每个链接都用一条线程保持
文件操作流部分
NIO主要是引入了缓冲区和映射来操作文件
JAVA操作文件的过程
1, JAVA读取-> 2,调用native读取--> 3, 调用系统读取(切换到内核态)-> 4,磁盘读取文件
每一层都有设置缓存, JAVA操作上的分类
先说缓冲区,以前的IO中也有缓冲区,如 BufferedInputStream
传统BIO的缓存操作
BIO流的设计,先看连个读取文件例子
没有缓存的FileInputStream
public static String readFileWithoutBuffer() throws IOException { // BIO inputstream without buffer FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("E://test.txt"); byte[] content = new byte[1024]; int length = input.read(content); input.close(); return new String(content, 0, length); }
读取文件时,read的实现是直接通过调用系统的读取数据(native),就是每次读取时都要调用到系统读取。
带缓存的BufferedInputStream
public static String readFileWithBuffer() throws IOException { // BIO inputstream with buffer FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("E://test.txt"); BufferedInputStream binpt = new BufferedInputStream(input); byte[] bufferContent = new byte[1024]; int length = binpt.read(bufferContent); return new String(bufferContent, 0, length); }
BufferedInputStream是通过内部缓冲区数组实现的缓冲,每次读取时先返回内部数组的数据,默认大小是8192。
具体点用了Decorator模式,继承自FileInputStream ,(覆盖)装饰read方法
代码段:
public synchronized int read() throws IOException { if (pos >= count) { fill(); // 如果读取大于缓存了,填充缓冲buff if (pos >= count) return -1; } return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff; }
结论:
BufferedInputStream 的作用不是减少 磁盘IO操作次数(这个OS已经帮我们做了),而是通过减少系统调用次数来提高性能的。
NIO的文件映射操作
总结下JAVA文件操作
顺序读取
1, InputStream/OutputStream - 直接调用native方法
2, BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream- 在类里维护了个byte[],先缓存读取到byte中(装饰器的模式)
随机读取
3,RandomAccessFile - 直接调用native方法
4,FileChannel -系统的虚拟内存映射文件,讲文件映射到内存中当数组操作
各种文件读取适用场景
--转个实验
在Core Java II中进行了这么一个实验:在同一台机器上,对JDK的jre/lib目录中的37MB的rt.jar文件分别用以上四种操作来计算CRC32校验和,记录下了如下时间
| 方法 | 时间 |
| 普通输入流 | 110s |
| 带缓冲的输入流 | 9.9s |
| 随机访问文件 | 162s |
| 内存映射文件 | 7.2s |
这个小实验也验证了内存映射文件这个方法的可行性,由于具有随机访问的功能(映射在内存数组),所以常用来替代RandomAccessFile。
当然,对于中等尺寸文件的顺序读入则没有必要使用内存映射以避免占用本就有限的I/O资源,这时应当使用带缓冲的输入流。
欢迎关注我的公众号, 一起来构建我们的知识体系
