在写前面的章节时,我自己不断地思考,“我不能再等了,我要弄清楚在哪里可把(工作流中的)真实数据返回到宿主应用程序中!”为什么?做了这么多的活动和工作流的演示,但都没有实际返回某些感兴趣的东西给宿主应用程序。我不知写过多少我们感兴趣的工作流的实例和演示,但至多只是仅仅处理过数据的初始化(就像第一章-WF简介中你看过的邮政编码的例子)。但事情变得更加有趣,坦率地说,当我们启动工作流,然后从外部源中寻找并处理数据、返回处理后的数据给我们的主应用程序要更加接近现实。
为什么不这样呢?公开一个对象,来从执行的工作流中传给宿主应用程序,或者从宿主应用程序传给工作流不就行了吗?其实,使用现有的串行化技术,如.NET Remoting或者XML Web服务,就可完成这些事。串行化,也叫序列化,它可把数据从原有的形式转换成合适的形式,以在不同进程甚至不同计算机之间进行传输。
为什么谈到序列化呢?因为你的工作流是在你的宿主进程中的不同线程上执行,不同线程之间传送数据,如不进行适当的序列化,将会引发灾难,具体原因超出了本书的讨论范围。其实,你的工作流能在一个持久化的状态下发送它的数据。这并没有在不同线程上,甚至它不在执行中。
但我们想在我们的工作流和正控制该工作流的宿主进程间传送数据时,使用.NET Remoting或者XML Web服务这样的技术为什么并没有认为是多余的呢?其实这绝对有必要!我们将创建local通信,本章将以此出发。我们将搭建必须的体系来满足线程数据序列化,以进行计算机之间或进程之间的数据传输。
创建ExternalDataService服务
当工作流和它的宿主进行通信时,在它发送和接收数据的时候,工作流要使用队列和消息。WF为我们做的越多,我们就可把重点更多的放到应用中特定任务的解决上。
工作流内部进程通信
对于简单的通信任务,WF使用“abstraction layer”来在工作流和宿主之间进行缓冲。抽象层像一个黑盒,你为它提供输入,它会执行一些神奇的任务,然后信息流出到另一边。但我们不用知道它是如何工作的。
在这种情形下,该黑盒就是一个知名的“local communication”服务。和WF术语中的任何一种服务一样,它也是另一种可插拔服务。区别是它不像WF中的那些已预先创建好的服务,你需要写出这个服务的一部分。为什么呢?因为你在宿主应用程序和你的工作流之间传递的数据有一定的特殊性。更进一步说,你可创建各种各样的数据传输方法,你可使用你设计的各种方法从宿主应用程序发送数据,然后在工作流中接收数据。
备注:这里有些事情你需要进行关注,那就是对象或集合的共享问题。因为宿主应用程序和工作流运行时在同一个应用程序域执行,因此引用类型的对象和集合就是通过引用而不是值进行传递。这意味着宿主应用程序和工作流实例在同一时间会访问和使用同一个对象,多线程环境下这会产生bug,出现数据并发访问错误。因此,对于可能要进行并发访问的对象或集合,你可考虑传递一个对象或集合的副本,或许这可通过实现ICloneable接口,或者考虑亲自序列化该对象或集合并传递序列化后的版本。
你可写这种local service,把它插进工作流,然后打开连接,发送数据。这些数据可以是字符串,DataSet对象,甚至可以是你设计的任何可被序列化的自定义对象。通信可以是双向的,尽管在本章我没有演示它。(这里,我仅仅是把数据从工作流中传回给宿主应用程序。)从工作流的角度来说,我们使用工具生成活动的目的是发送和接收数据。从宿主应用程序的角度来说,接收数据等同于一个事件,而发送数据就是在一个服务对象上的方法的简单调用。
备注:我们在后面几章看到更多的活动后还会重温该双向数据传输的概念。工作流活动从宿主应用程序中接收数据基于一个HandleExternalEvent活动,我们将在第10章“Event活动”中看到。我们也需要更深入地了解这些概念间的相互关系,这在第17章“宿主通信”中将进行介绍。对于当前,我们只是在工作流实例完成它的任务后,简单地返回复合数据给宿主。
我们需要做的还不仅仅是这一点,我们最终需要添加ExternalDataService服务到我们的工作流运行时中。ExternalDataService是一个可插拔的服务,它方便了工作流实例和宿主应用程序之间进行序列化数据的传输。在紧接下来的一节我们将写出的该服务的代码将做很多事(包括序列化数据的传输)。让我们来看看大体的开发过程。
设计并实现工作流内部进程通信
我们先决定将传送些什么数据。它是一个DataSet吗?是一个像整形数字或字符串之类的系统直接支持的对象吗?或者是一个由我们自己设计的自定义对象吗?无论它是什么,我们都将设计一个ExternalDataService能够绑定的接口。这个接口将包含我们设计的一些方法,这些方法能分别从工作流实例的角度上及宿主的角度上来发送数据和接收数据。使用该接口中的方法,我们就可来回传送数据。
我们然后需要写一些代码:外部数据服务的一部分。它表述了连接或者称作桥接代码,宿主和工作流将使用它来和WF提供的ExternalDataService进行交互。假如我们正涉及一个XML Web服务,Visual Studio会为我们自动地创建代理代码。但对于工作流来说没有这样的工具,因此我们需要亲自设计这个桥接代码。我们这里使用的“桥”实际上由两个类组成:一个connector类和一个service类。你可用你喜欢的名称来命名它们,但我推荐使用这样的名字来命名它们。connector类管理数据管道(状态维护),而service类被宿主和工作流用来直接进行数据交换。
在创建好接口后,我们将使用一个工具:wca.exe,它的位置通常是在你的“Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v6.0A\Bin”目录下。该工具叫做Workflow communications Activity generator utility,该工具的作用是,给出一个接口,它将生成两个活动,你能使用它们去把该接口和你的工作流实例进行绑定。一个用来发送数据,为invoker,另一个用来接收数据,为sink。一旦它们创建好后,你就能从Visual Studio工具箱中把它们拖拽到工作流视图设计器上,它们也和任何其它工作流活动一样进行工作。但前面我已经提到过,我们没有一个工具创建连接桥代码,这样的工具在工作流方面一定很有用。
提示:从项目的角度考虑,我倾向于为宿主应用程序创建一个或一组项目,为前面提到的接口和连接桥创建另一个项目,为工作流代码再单独创建一个项目。这可让我方便地从宿主应用程序和工作流中添加对该接口和桥接类的引用,做到了在程序集之间进行简洁的功能隔离。
我们有了这些程序集后,我们需要连通我们的工作流和宿主应用程序之间的通信。在执行时,通过使用ExternalDataService整个过程被简化了。我们先快速看看本章中的最基本的应用程序实例(就它而言,它比我们目前看到过的例子都有复杂),然后开使创建我们需要的工作流外部数据通信代码。
机动车数据检查应用程序
本示例应用程序是一个Windows Forms应用程序,它提供了一个用户界面,上面集中了指定驾驶员的机动车数据。该应用程序本身已是很有意义的,我不想再重复创建它的每一个细节。相反,你将使用这个已经提供好了的样本代码来作为本章的起点。但是,我将展示怎样把它们绑进工作流组件中。
主用户界面窗体见图8-1。下拉列表框控件包含了三个驾驶员的姓名,选择其中一个的姓名都会生成一个新的设计好的工作流的实例来对该驾驶员的机动车信息进行检索,并返回一个完整的DataSet。该DataSet然后被绑定到两个ListView控件,一个是违规信息。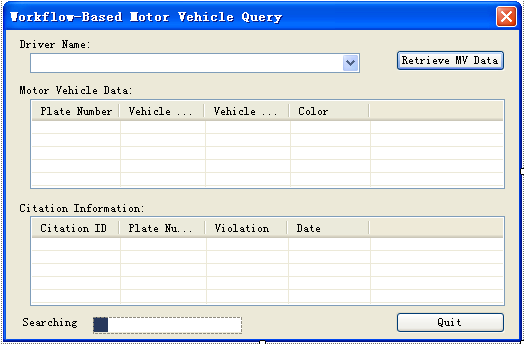
图8-1 MVDataChecker窗体的主用户界面
当你点击“Recrieve MV Data”按钮时,你就会初始化一个新的工作流实例,用户界面会禁用该检索按钮及驾驶员下拉列表框控件并显示一个“searching”通知,如图8-2所示。你在该窗体底部看到的picture box控件是一个动画图片文件。该应用程序根据情况对其中的label控件和picture box控件进行隐藏或显示。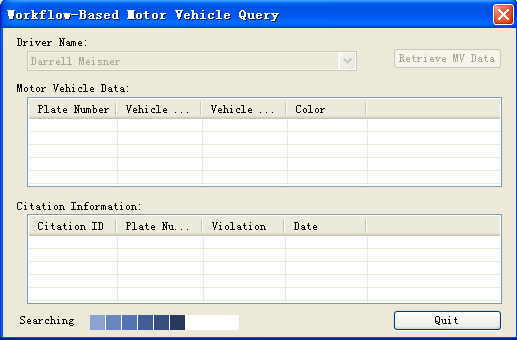
图8-2 MVDataChecker窗体的“searching”用户界面
当工作流实例来完成了它的工作后,它会使用我们将要创建的一个活动来激发一个事件,宿主应用程序会截获该事件,该事件把数据已准备好的消息通告该宿主应用程序。因为Windows窗体的ListView控件不能直接绑定到DataTable对象,因此我们从工作流中检索到数据后将一行一行地把数据插入到该控件中,如图8-3所示。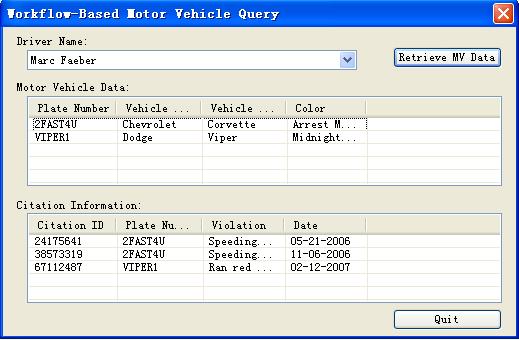
图8-3 MVDataChecker窗体检索数据后的用户界面
在应用程序执行到此时,你可选择是检索另一个驾驶员的信息还是退出程序。假如你在查询过程中退出该应用程序,正执行的工作流实例会被异常终止。
然后我们来看看需要添写完成所有这些任务的代码,首先我们需要为WF提供一个接口,以便它能激发我提过的“数据已准备好”的事件。
创建服务接口
该服务接口完全要由你创建,它应基于你想在你的工作流实例和你的宿主应用程序之间进行通信的数据之上。对于本示例,想像你需要设计一个工作流来从各个源数据中检索驾驶员的信息,然后你想把这些信息整理为一个单一的数据结构:带多个表的DataSet,一个表是车辆标识信息,一个表是驾驶员违规信息。我们将简单地使用虚拟的数据,以便更侧重于把焦点放到工作流自身上。在宿主应用程序中,我们将在两个ListView控件中显示这些(伪造的)数据。
你要把驾驶员的名字传入工作流实例中,该工作流实例使用它来查找驾驶员和车辆的信息。在获取了这些数据后,工作流实例通知宿主应用程序数据已经准备好了,然后宿主应用程序读取并显示这些信息。
因此实际上在我们的接口只需要一个单一的方法:MVDataUpdate。我们知道需要发送一个DataSet,因此我们把这个DataSet作为方法的参数传入到MVDataUpdate中。
创建一个工作流数据通信接口
1.该MVDataChecker示例应用程序,同前面的例子一样,包含两个版本:练习版本(MVDataChecker目录中)和完整版本(MVDataChecker Completed目录中),它们可在本章的源代码中进行下载。我们现在就使用Visual Studio打开练习项目中的解决方案。
2.在该解决方案中包含三个项目。在Visual Studio解决方案浏览器中展开MVDataServic项目,然后打开IMVDataService.cs文件。
3.在MVDataService名称空间中添加下面的代码并进行保存。
 public interface IMVDataService
public interface IMVDataService {
{ void MVDataUpdate (DataSet mvData);
void MVDataUpdate (DataSet mvData); }
}这样就大功告成了!这就是所有你需要为创建一个接口所要做的工作。不过,我们需要添加一个属性,以使这个接口适合于WF的使用,我们将在下面的一节介绍。
使用ExternalDataExchange特性
尽管有了接口:IMVDataService,但我们仍不能把该接口提供给WF,以让WF真正使用它来进行数据通信。为此,我们需要添加ExternalDataExchange特性。
ExternalDataExchange特性是一个简单的标记,WF使用它来指明接口可适合于本地通信服务使用。记得我提到的wca.exe工具吗?它和Visual Studio都使用这个特性来指明接口可被你的工作流实例使用。我们就来添加ExternalDataExchange特性。
备注:不要让词语“特性标记”所欺骗,你不要认为该ExternalDataExchage特性不是一个关键组成部分。它相当重要。当工作流运行时试图进行外部数据传送时会寻找该特性。没有它,工作流和宿主之间进行数据传输就不可能。
创建一个工作流数据通信接口
在Visual Studio中打开IMVDataService.cs文件,为前面定义的接口添加下面的代码:
[ExternalDataExchange]
IMVDataService接口的完整代码在下面的清单8-1中。此时不要担心该应用程序编译出错。在编译无错之前,我们还需要添加更多的代码。
 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
using System.Text; using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities; using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Runtime; using System.Data;
using System.Data;
 namespace MVDataService
namespace MVDataService {
{ [ExternalDataExchange]
[ExternalDataExchange] public interface IMVDataService
public interface IMVDataService {
{ void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData);
void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData); }
} }
}使用ExternalDataEventArgs
我在前面提到过,宿主应用程序和正执行的工作流之间使用事件进行通信。宿主应用程序无法事先准确地知道工作流实例准备好数据的时间,对该数据进行轮询效率又低得可怕。因此WF使用异步模式,当数据准备好了的时候激发一些事件。宿主应用程序捕获这些事件然后读出数据。
因为我们想把信息发送给事件的接收者,因此我们需要创建一个自定义事件参数的类。假如你在前面的工作中已创建过一个自定义事件类,你或许就是使用System.EventArgs作为基类。
但是,WF外部数据事件需要带一个(和上述)不同的参数作为基类,以便该事件能承载工作流实例的实例ID。我们应使用的基类是ExternalDataEventArgs,它从System.EventArgs类派生,这样我们就熟悉了它的背景。另外,还有两点要求:我们需要提供一个以该实例ID(一个Guid)作为参数的基本的构造器,该构造器又把实例ID传给基类构造器,第二点是我们必须使用Serializable特性来标记我们的类,以表明我们的类是可序列化的。
我们现在就来创建我们所需要的外部数据事件参数类。
创建工作流数据事件参数类
1.使用Visual Studio打开MVDataService项目,定位在MVDataAvailableArgs.cs文件上,打开该文件准备进行编辑。
2.在该文件所定义的名称空间中,添加下面的代码:
 [Serializable]
[Serializable] public class MVDataAvailableArgs : ExternalDataEventArgs
public class MVDataAvailableArgs : ExternalDataEventArgs {
{ }
}3.最后我们需要添加一个构造器,以便把工作流实例ID传给基类:
 public MVDataAvailableArgs(Guid instanceId)
public MVDataAvailableArgs(Guid instanceId) : base(instanceId)
: base(instanceId) {
{ }
}完整的事件参数类如清单8-2所示。
清单8-2 完整的MVDataAvailableArgs.cs源文件 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
using System.Text; using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities; using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
 namespace MVDataService
namespace MVDataService {
{ [Serializable]
[Serializable] public class MVDataAvailableArgs : ExternalDataEventArgs
public class MVDataAvailableArgs : ExternalDataEventArgs {
{ public MVDataAvailableArgs(Guid instanceId)
public MVDataAvailableArgs(Guid instanceId) : base(instanceId)
: base(instanceId) {
{ }
} }
} }
}创建外部数据服务
我们现在来到了更加复杂的一节,我们的任务是为外部数据服务创建桥接代码。宿主必须有这些代码,它才能访问到工作流实例试图传递过来的数据。我们将使用工具来为工作流创建活动(这在下一节介绍),但对于宿主这边的通信连接来说,却没有现成的工具。
在这里,我们将创建一个稍微简化的连接桥版本(这是对于完整的连接桥架构来说)。该版本仅仅支持工作流到宿主的通信。(当我们学到17章时,我们将会创建一个可重用的通用双向连接桥。)我们在此将创建的连接桥被分成了两个部分:一是connector,它实现了我们前面已经开发好了的接口;二是service,除了别的事情外,它有一个职责是激发“data available”事件以及提供一个“read”方法,使用该方法来把数据从工作流中取出。
提示:该代码应由你而不是WF来提供。我在写本地数据交换服务时提供了该代码,但你要写的代码可以有所不同。唯一要求是本地数据交换服务实现了通信接口并提供一种机制,用于检索需要交换的数据。
为什么如此复杂?和传统的.NET对象不同,工作流实例在工作流运行时的范围内执行。因此进出工作流实例的事件都由工作流运行时进行代理。工作流运行时必须做这些工作,因为你的宿主应用程序不能把数据发送给已经被持久化或不处在执行状态下的工作流实例。
回到我们的连接桥上,该连接类包含一个字段,工作流将使用要被传回的数据来填充该字段。对于我们正在创建的本示例应用程序来说,我们不允许并发执行工作流实例,但这仅仅是出于方便。通常情况下,并没有阻止我们执行并发执行的工作流实例,这些我们将在第17章看到。
当然,每一个工作流实例可能会返回不同的数据,至少它传递的驾驶员会和另一个工作流实例不同。连接类的职责是实现我们开发的在宿主这边接口,以及不间断地保持这些数据。当宿主请求该数据时,连接类根据工作流实例ID来确定应正确返回的DataSet是否已经到达。
该服务类为你处理一些任务。首先,它使用工作流运行时注册该ExternalDataService,以便我们可在宿主和工作流实例间进行通信。它维护一个连接类的单例副本,并把它自己作为服务提供者绑定到该连接类。该服务类也充当了工厂(设计模式)的角色,确保我们有一个且仅有一个连接类(实例)。(假如我们实现了双向的接口,该服务类也会提供一个“write”方法。)我们现在就来创建这些类。
创建桥接器(bridge connector)类
1.在Visual Studio中打开MVDataService项目,定位到MVDataCnnector.cs文件,最后打开该文件。
2.在所定义的名称空间中添加下面的代码:
 public sealed class MVDataConnector : IMVDataService
public sealed class MVDataConnector : IMVDataService {
{ private DataSet _dataValue = null;
private DataSet _dataValue = null; private static WorkflowMVDataService _service = null;
private static WorkflowMVDataService _service = null; private static object _syncLock = new object();
private static object _syncLock = new object();  }
} 字段_dataValue用来容纳工作流实例产生的数据。字段_service用来容纳数据服务对象的单一实例。_syncLock对象仅仅用来进行线程的同步。
3.下面,我们添加一个static属性来访问该服务对象的单一实例。代码如下:
 public static WorkflowMVDataService MVDataService
public static WorkflowMVDataService MVDataService {
{ get { return _service; }
get { return _service; } set
set {
{ if (value != null)
if (value != null) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ // Re-verify the service isn't null
// Re-verify the service isn't null // now that we're locked
// now that we're locked if (value != null)
if (value != null) {
{ _service = value;
_service = value; } // if
} // if else
else {
{ throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance."); } // else
} // else } // lock
} // lock } // if
} // if else
else {
{ throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance."); } // else
} // else }
} }
}4.我们需要添加一个属性来访问该DataSet,代码如下:
 public DataSet MVData
public DataSet MVData {
{ get { return _dataValue; }
get { return _dataValue; } }
}5.因为连接器类从IMVDataService派生,因此我们必须实现MVDataUpdate方法:
 public void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData)
public void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData) {
{ // Assign the field for later recall
// Assign the field for later recall _dataValue = mvData;
_dataValue = mvData;
 // Raise the event to trigger host read
// Raise the event to trigger host read _service.RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent();
_service.RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent(); }
}工作流使用这个方法来把DataSet保存到_dataValue字段中。它激发事件以通知宿主数据已经准备好了。该桥接器类的完整代码参见清单8-3。注意我们这时并没准备去编译整个应用程序,我们还有更多的代码需要添加。
清单8-3 完整的MVDataconnector.cs源文件 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
using System.Text; using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities; using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Runtime; using System.Data;
using System.Data;
 namespace MVDataService
namespace MVDataService {
{ public sealed class MVDataConnector : IMVDataService
public sealed class MVDataConnector : IMVDataService  {
{ private DataSet _dataValue = null;
private DataSet _dataValue = null; private static WorkflowMVDataService _service = null;
private static WorkflowMVDataService _service = null; private static object _syncLock = new object();
private static object _syncLock = new object();
 public static WorkflowMVDataService MVDataService
public static WorkflowMVDataService MVDataService {
{ get { return _service; }
get { return _service; } set
set {
{ if (value != null)
if (value != null) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ // Re-verify the service isn't null
// Re-verify the service isn't null // now that we're locked
// now that we're locked
 if (value != null)
if (value != null) {
{ _service = value;
_service = value; } // if
} // if else
else {
{ throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance."); } // else
} // else } // lock
} // lock } // if
} // if else
else {
{ throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance."); } // else
} // else }
} }
}
 public DataSet MVData
public DataSet MVData {
{ get { return _dataValue; }
get { return _dataValue; } }
}
 // Workflow to host communication method
// Workflow to host communication method public void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData)
public void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData) {
{ // Assign the field for later recall
// Assign the field for later recall _dataValue = mvData;
_dataValue = mvData;
 // Raise the event to trigger host read
// Raise the event to trigger host read _service.RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent();
_service.RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent(); }
} }
} }
} 创建桥接服务(bridge service)类
1.再次在Visual Studio中打开MVDataService项目,定位到WorkflowMVDataService.cs文件,打开该文件准备进行编辑。
2.我们创建好了MVDataConnector类,我们还要把下面的代码复制到WorkflowMVDataService.cs文件中:
 public class WorkflowMVDataService
public class WorkflowMVDataService {
{ static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null;
static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null; static ExternalDataExchangeService _dataExchangeService = null;
static ExternalDataExchangeService _dataExchangeService = null; static MVDataConnector _dataConnector = null;
static MVDataConnector _dataConnector = null; static object _syncLock = new object();
static object _syncLock = new object();
 public event EventHandler<MVDataAvailableArgs> MVDataUpdate;
public event EventHandler<MVDataAvailableArgs> MVDataUpdate;
 private Guid _instanceID = Guid.Empty;
private Guid _instanceID = Guid.Empty;
 }
}3.我们需要具有从类的外部访问_instanceID的能力,因此添加下面的属性:
 public Guid InstanceID
public Guid InstanceID {
{ get { return _instanceID; }
get { return _instanceID; } set { _instanceID = value; }
set { _instanceID = value; } }
}4.我们现在要添加一个静态的工厂方法,我们将用它去创建本类的实例。我们这样做是为了确保在我们创建本桥接服务的时候,所有重要的事情都已完成。例如,我们需要确保ExternalDataService服务已被插入到了工作流运行时中。我们也将添加刚才已经创建好了的桥接器类,并把它作为一个可插拔服务以便工作流能访问到该数据连接器类。因此,我们在上面一步所添加的属性下面还要添加下面的方法:
 public static WorkflowMVDataService CreateDataService(Guid instanceID, WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime)
public static WorkflowMVDataService CreateDataService(Guid instanceID, WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ // If we're just starting, save a copy of the workflow runtime reference
// If we're just starting, save a copy of the workflow runtime reference if (_workflowRuntime == null)
if (_workflowRuntime == null) {
{ // Save instance of the workflow runtime.
// Save instance of the workflow runtime. _workflowRuntime = workflowRuntime;
_workflowRuntime = workflowRuntime; } // if
} // if
 // If we're just starting, plug in ExternalDataExchange service
// If we're just starting, plug in ExternalDataExchange service if (_dataExchangeService == null)
if (_dataExchangeService == null) {
{ // Data exchange service not registered, so create an
// Data exchange service not registered, so create an  // instance and register.
// instance and register. _dataExchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService();
_dataExchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService(); _workflowRuntime.AddService(_dataExchangeService);
_workflowRuntime.AddService(_dataExchangeService); } // if
} // if
 // Check to see if we have already added this data exchange service
// Check to see if we have already added this data exchange service MVDataConnector dataConnector = (MVDataConnector)workflowRuntime.
MVDataConnector dataConnector = (MVDataConnector)workflowRuntime. GetService(typeof(MVDataConnector));
GetService(typeof(MVDataConnector)); if (dataConnector == null)
if (dataConnector == null) {
{ // First time through, so create the connector and
// First time through, so create the connector and  // register as a service with the workflow runtime.
// register as a service with the workflow runtime. _dataConnector = new MVDataConnector();
_dataConnector = new MVDataConnector(); _dataExchangeService.AddService(_dataConnector);
_dataExchangeService.AddService(_dataConnector); } // if
} // if else
else {
{ // Use the retrieved data connector.
// Use the retrieved data connector. _dataConnector = dataConnector;
_dataConnector = dataConnector; } // else
} // else
 // Pull the service instance we registered with the connection object
// Pull the service instance we registered with the connection object WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService; if (workflowDataService == null)
if (workflowDataService == null) {
{ // First time through, so create the data service and
// First time through, so create the data service and // hand it to the connector.
// hand it to the connector. workflowDataService = new WorkflowMVDataService(instanceID);
workflowDataService = new WorkflowMVDataService(instanceID); MVDataConnector.MVDataService = workflowDataService;
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = workflowDataService; } // if
} // if else
else {
{ // The data service is static and already registered with
// The data service is static and already registered with // the workflow runtime. The instance ID present when it
// the workflow runtime. The instance ID present when it  // was registered is invalid for this iteration and must be
// was registered is invalid for this iteration and must be // updated.
// updated. workflowDataService.InstanceID = instanceID;
workflowDataService.InstanceID = instanceID; } // else
} // else
 return workflowDataService;
return workflowDataService; } // lock
} // lock }
}5.在前面一节(“创建桥接器类”)我们创建的连接器对象中保存有我们在第4步中创建的该桥接器对象。我们现在将添加一个静态方法,使用该方法可返回该桥接服务实例。尽管这些现在看来没有太大必要,但稍后会讲讲我们这样做的理由。代码如下:
 public static WorkflowMVDataService GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(Guid instanceID)
public static WorkflowMVDataService GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(Guid instanceID) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
 if (workflowDataService == null)
if (workflowDataService == null) {
{ throw new Exception("Error configuring data service
throw new Exception("Error configuring data service service cannot be null.");
service cannot be null."); } // if
} // if
 return workflowDataService;
return workflowDataService; } // lock
} // lock }
}6.下面我们将添加我们(私有属性)的构造器和析构器。有了桥接器类后,我们需要确保在桥接器对象和桥接服务对象间不会造成循环的引用。你需要添加下面的代码:
 private WorkflowMVDataService(Guid instanceID)
private WorkflowMVDataService(Guid instanceID) {
{ _instanceID = instanceID;
_instanceID = instanceID; MVDataConnector.MVDataService = this;
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = this; }
}
 ~WorkflowMVDataService()
~WorkflowMVDataService() {
{ // Clean up
// Clean up _workflowRuntime = null;
_workflowRuntime = null; _dataExchangeService = null;
_dataExchangeService = null; _dataConnector = null;
_dataConnector = null; }
}7.尽管我们为桥接服务类添加了一些重要的东西,但还没有把ExternalDataService引入工作流运行时中,我们仍然要添加一些代码,以使工作流运行时具有读取数据并返回给宿主应用程序的能力。桥接器对象实际上是维持该连接状态,但宿主使用这个服务来获得要访问的数据。下面是我们要添加的read方法:
 public DataSet Read()
public DataSet Read() {
{ return _dataConnector.MVData;
return _dataConnector.MVData; }
}8.要为我们的桥接服务添加的最后的功能块是一个方法,它激发“机动车数据更新(motor vehicle data update)”事件。工作流使用这个方法来为宿主发送一个通知,告知要挑选的数据已经获取完了。代码如下:
 public void RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent()
public void RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent() {
{ if (_workflowRuntime == null)
if (_workflowRuntime == null) _workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
_workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
 _workflowRuntime.GetWorkflow(_instanceID); // loads persisted workflow instances
_workflowRuntime.GetWorkflow(_instanceID); // loads persisted workflow instances if (MVDataUpdate != null)
if (MVDataUpdate != null) {
{ MVDataUpdate(this, new MVDataAvailableArgs(_instanceID));
MVDataUpdate(this, new MVDataAvailableArgs(_instanceID)); } // if
} // if }
}完整的桥接服务代码参见清单8-4:
清单8-4 完整的WorkflowMVDataService.cs源文件 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
using System.Text; using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities; using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Runtime; using System.Data;
using System.Data;
 namespace MVDataService
namespace MVDataService {
{ public class WorkflowMVDataService
public class WorkflowMVDataService {
{ static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null;
static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null; static ExternalDataExchangeService _dataExchangeService = null;
static ExternalDataExchangeService _dataExchangeService = null; static MVDataConnector _dataConnector = null;
static MVDataConnector _dataConnector = null; static object _syncLock = new object();
static object _syncLock = new object();
 public event EventHandler<MVDataAvailableArgs> MVDataUpdate;
public event EventHandler<MVDataAvailableArgs> MVDataUpdate;
 private Guid _instanceID = Guid.Empty;
private Guid _instanceID = Guid.Empty;
 public Guid InstanceID
public Guid InstanceID {
{ get { return _instanceID; }
get { return _instanceID; } set { _instanceID = value; }
set { _instanceID = value; } }
}
 public static WorkflowMVDataService CreateDataService(Guid instanceID, WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime)
public static WorkflowMVDataService CreateDataService(Guid instanceID, WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ // If we're just starting, save a copy of the workflow runtime reference
// If we're just starting, save a copy of the workflow runtime reference if (_workflowRuntime == null)
if (_workflowRuntime == null) {
{ // Save instance of the workflow runtime.
// Save instance of the workflow runtime. _workflowRuntime = workflowRuntime;
_workflowRuntime = workflowRuntime; } // if
} // if
 // If we're just starting, plug in ExternalDataExchange service
// If we're just starting, plug in ExternalDataExchange service if (_dataExchangeService == null)
if (_dataExchangeService == null) {
{ // Data exchange service not registered, so create an
// Data exchange service not registered, so create an  // instance and register.
// instance and register. _dataExchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService();
_dataExchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService(); _workflowRuntime.AddService(_dataExchangeService);
_workflowRuntime.AddService(_dataExchangeService); } // if
} // if
 // Check to see if we have already added this data exchange service
// Check to see if we have already added this data exchange service MVDataConnector dataConnector = (MVDataConnector)workflowRuntime.
MVDataConnector dataConnector = (MVDataConnector)workflowRuntime. GetService(typeof(MVDataConnector));
GetService(typeof(MVDataConnector)); if (dataConnector == null)
if (dataConnector == null) {
{ // First time through, so create the connector and
// First time through, so create the connector and  // register as a service with the workflow runtime.
// register as a service with the workflow runtime. _dataConnector = new MVDataConnector();
_dataConnector = new MVDataConnector(); _dataExchangeService.AddService(_dataConnector);
_dataExchangeService.AddService(_dataConnector); } // if
} // if else
else {
{ // Use the retrieved data connector.
// Use the retrieved data connector. _dataConnector = dataConnector;
_dataConnector = dataConnector; } // else
} // else
 // Pull the service instance we registered with the connection object
// Pull the service instance we registered with the connection object WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService; if (workflowDataService == null)
if (workflowDataService == null) {
{ // First time through, so create the data service and
// First time through, so create the data service and // hand it to the connector.
// hand it to the connector. workflowDataService = new WorkflowMVDataService(instanceID);
workflowDataService = new WorkflowMVDataService(instanceID); MVDataConnector.MVDataService = workflowDataService;
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = workflowDataService; } // if
} // if else
else {
{ // The data service is static and already registered with
// The data service is static and already registered with // the workflow runtime. The instance ID present when it
// the workflow runtime. The instance ID present when it  // was registered is invalid for this iteration and must be
// was registered is invalid for this iteration and must be // updated.
// updated. workflowDataService.InstanceID = instanceID;
workflowDataService.InstanceID = instanceID; } // else
} // else
 return workflowDataService;
return workflowDataService; } // lock
} // lock }
}
 public static WorkflowMVDataService GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(Guid instanceID)
public static WorkflowMVDataService GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(Guid instanceID) {
{ lock (_syncLock)
lock (_syncLock) {
{ WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
 if (workflowDataService == null)
if (workflowDataService == null) {
{ throw new Exception("Error configuring data service
throw new Exception("Error configuring data service service cannot be null.");
service cannot be null."); } // if
} // if
 return workflowDataService;
return workflowDataService; } // lock
} // lock }
}
 private WorkflowMVDataService(Guid instanceID)
private WorkflowMVDataService(Guid instanceID) {
{ _instanceID = instanceID;
_instanceID = instanceID; MVDataConnector.MVDataService = this;
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = this; }
}
 ~WorkflowMVDataService()
~WorkflowMVDataService() {
{ // Clean up
// Clean up _workflowRuntime = null;
_workflowRuntime = null; _dataExchangeService = null;
_dataExchangeService = null; _dataConnector = null;
_dataConnector = null; }
}
 public DataSet Read()
public DataSet Read() {
{ return _dataConnector.MVData;
return _dataConnector.MVData; }
}
 public void RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent()
public void RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent() {
{ if (_workflowRuntime == null)
if (_workflowRuntime == null) _workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
_workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
 _workflowRuntime.GetWorkflow(_instanceID); // loads persisted workflow instances
_workflowRuntime.GetWorkflow(_instanceID); // loads persisted workflow instances if (MVDataUpdate != null)
if (MVDataUpdate != null) {
{ MVDataUpdate(this, new MVDataAvailableArgs(_instanceID));
MVDataUpdate(this, new MVDataAvailableArgs(_instanceID)); } // if
} // if }
} }
} }
}CallExternalMethod活动
你目前在本章看到过的所有代码都已支持一个特殊的WF活动:CallExternalMethod活动。CallExternalMethod活动的作用是可以接受一个接口及该接口所支持的方法,并来调用这个方法。现在的问题是,由谁来实现这个方法?
你可能会考虑由你的宿主应用程序来完成,但这不太正确。假如你向前看看前面的一节“创建桥接器类”,你实际上在那里会找到这个方法。数据连接器由ExternalDataService捆住实现了该方法。该数据服务依次把该方法的调用转换成一个宿主应用程序能识别的事件。
直接使用CallExternalMethod活动是允许的,你甚至可以绕开一些服务代码就可把它插入到你的应用程序中。但是绕开这些服务代码对你来说还有一组难题。你的宿主应用程序和你的工作流实例是一对一地联系在一起的。在这里使用数据服务来完成这件事要更适合一些,当你把该数据服务结合起来后,你就能使许多的应用程序实例从许多的工作流实例中进行数据访问,而绕过你创建好的那些数据服务后则不能做到这些。
对于直接使用CallExternalMethod活动,它通常更适合于创建自定义活动来为你调用外部方法。你可使用一个工具来自定义你的数据交换接口和创建派生自CallExternalMethod的活动,更恰当地对其命名,对它们的属性(接口和方法名称)进行配置。接下来我们就来看看该工具的使用方法。
创建和使用自定义外部数据服务活动
回头看看,我们刚刚写下的代码比目前整本书已写过的代码还要多。原因是WF事先不知道我们的工作流将和我们的宿主应用程序之间交换些什么信息。因此在二者之间毫无疑问必须做一些工作,以便对它们之间的差距进行填充。
但是,WF知悉所有的工作流活动,我们可愉快地使用一个工具来对我们的数据传送接口进行解释,使用ExternalDataExchange特性(attribute)来进行标记,自动地生成WF活动。
我们本章正生成的应用程序把数据从工作流中发送到宿主应用程序中,也就是说数据传送是单向的。我故意这样做是因为,我们只有积累了足够的知识,才能更好地学习并充分理解双向数据传送。我们将使用的Workflow Communication Activity生成器完全有能力创建那些发送和接受宿主数据的活动。对于本应用程序的特殊性,我们将“扔掉”它的输出部分,因为我们不需要它。(其实,将生成的活动是畸形的,因为我们的接口没有指定宿主到工作流的通信,这些我们将保留到第10章讲解。)
为此,我们就来执行wca.exe并创建一个可用来发送数据到我们的宿主应用程序的活动。
创建通信活动
1.为使wca.exe能生成符合我们要求的代码,我们需要确保有一个接口。因此,确保MVDataService项目生成时无错误(如生成时有错误,请纠正所有的错误)并已生成了MVDataService程序集。
2.点击操作系统的开始按钮,然后点击运行菜单项打开运行对话框。
3.在打开的组合框控件中输入“cmd”,然后点击确定进入命令提示符窗口。
4.更改起始目录以便我们能直接访问到“MVDataService”程序集。通常使用的是“cd”命令。
5.wca.exe文件默认情况下被安装到Program Files目录下的Windows SDK子目录中。(当然,假如你没有使用默认目录进行安装,你在此需要使用你安装Windws SDK的目录。)在命令行提示符下输入下面的命令来执行该工具(包含双引号):
“C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v6.0A\Bin\Wca.exe” MVDataService.dll
按下回车键,该工具的输出结果和下面的类似:
6.在命令提示符中键入dir你可看到wca.exe创建的文件。
7.IMVDataService.Sinks.cs文件不是必须要的,可忽略它甚至是删除它,因为该文件只是包含了一些指示,没有代码。(在我们的通信接口中没有定义事件。)我们在第十章将再使用这个文件。对于另一个生成的文件:IMVDataService.Invokes.cs文件,是我们要保留的文件。它包含我们能使用的一个新活动的源代码,该活动可把数据从工作流中发送给宿主应用程序。因此,我们将重命名该文件以便更加好用。在命令提示符下输入“ren IMVDataService.Invokes.cs MVDataUpdate.cs”,然后按下回车键重命名该文件。
8.因为我们刚刚重命名的这个文件是一个工作流活动,因此我们需要把它从当前目录下移动到MVWorkflow目录下以便编译和使用。在命令提示符下输入“move MVDataUpdate.cs ..\..\..\MVWorkflow”,然后按下回车键。
9.回到Visual Studio,我们需要把这个新创建的MVDataUpdate.cs文件添加我们的工作流项目中。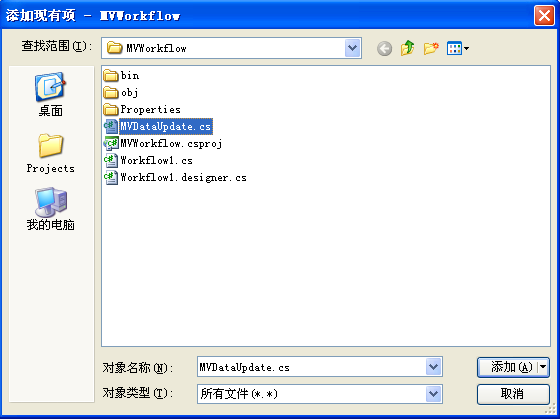
10.编译并生成MVWorkflow项目,假如出现编译错误的话,修正所有的错误。在你成功编译后,在视图设计器界面模式下打开Workflow1.cs文件将会在Visual Studio的工具箱中看到这个MVDataUpdate活动。
备注:假如MVDataUpdate因为某些原因没有添加进Visual Studio工具箱中,请关闭该解决方案,然后再重新打开它。
我们现在就准备好了一个活动,我们可使用它来把数据发送到我们的宿主应用程序中。该活动的基类是CallExternalMethod,它的作用是触发对工作流执行环境的外部调用。
添加并配置该工作流通信活动
1.在Visual Studio中以视图设计器的模式打开MVWorkflow项目中的Workflow1.cs文件。该工作流预先加载了两个活动:一个是Delay活动,用来模拟处理数据的等待时间;一个是Code活动,它创建并填充一个基于驾驶员姓名的DataSet。
2.打开Visual Studio工具箱,定位到MVDataUpdate活动。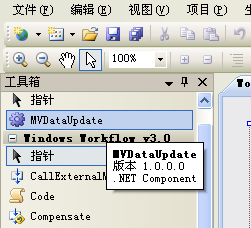
3.把该活动拖拽到工作流视图设计器界面上,放到Code活动的下面使它在Code活动执行后执行。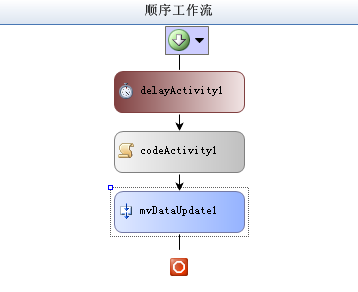
4.我们的工作流在视图设计器上的设计工作这就完成了。现在该写少量代码来进行衔接。因此以代码视图模式打开Workflow1.cs文件。在Workflow1类中找到GenerateMVDData方法。这个方法是codeActivity1所执行的方法,在里面你会看到对GenerateVehicleTable和GenerateViolationTable两个方法的调用,它们创建并填充所要返回的DataSet。(其实,你可用一些外部服务来为驾驶员的信息进行一个调用,但我们在此对这些进行了模拟)。在生成了DataSet后,我们需要添加下面的代码以把DataSet返回给宿主:
 // Assign the DataSet we just created as the host data
// Assign the DataSet we just created as the host data mvDataUpdate1.mvData = ds;
mvDataUpdate1.mvData = ds;指定了我们所返回的DataSet后,我们就完成了工作流的开发,并且使用了工具来把该DataSet传给宿主应用程序。但我们的宿主应用程序需要做些什么才能接收到该数据了?
在宿主应用程序中检索工作流数据
现在让我们返回到我们的主应用程序中。我们现在要做的是修改应用程序,以使用我们在本章的“创建外部数据访问”这一节中创建的桥接类。
备注:尽管这是一个简化的例子,但这个应用程序仍然是一个完全意义上的Windows Form应用程序,它演示了怎样处理工作流及其怎样进行多线程操作(比如updating控制的时候)。
为了让我们的接口可使用工作流返回的数据集,我们需要使用桥接代码中的connector类来对我们的工作流实例进行注册(为了使我们能正确的接收DataSet)。我们也需要勾住(hook)MVDataUpdate事件,以便我们的应用程序知道接收数据的时间。为方便做这些事。我们将为“Retrieve MV Data”按钮的event handler添加一点代码,并为MVDataUpdate添加一个新的event handler。
备注:假如你不熟悉匿名方法(anonymous methods)的话,现在就是简要学习它的一个好机会!
为我们的宿主应用程序添加工作流外部数据服务
1.在Visual Studio解决方案资源管理器中打开Form1.cs文件,并切换到代码视图界面。
2.找到cmdRetrieve_Click方法。在该响应按钮点击的事件方法中已经存在了初始化工作流实例的代码,但我们还需要在创建工作流实例和启动该实例之间的地方插入一些代码,也就是在调用“_workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow”的下面添加如下的代码(为让Visual Studio为我们自动生成事件处理程序的代码,请尽量不要使用复制粘贴的方式,应在=号后使用连续两个Tab键):
 // Hook returned data event.
// Hook returned data event. MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService =
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService = MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.CreateDataService(
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.CreateDataService( _workflowInstance.InstanceId,
_workflowInstance.InstanceId, _workflowRuntime);
_workflowRuntime);
 dataService.MVDataUpdate +=
dataService.MVDataUpdate += new EventHandler<MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs>(
new EventHandler<MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs>( dataService_MVDataUpdate);
dataService_MVDataUpdate);3.在Form1类中,为Visual Studio刚刚创建的dataService_MVDataUpdate事件处理程序添加下面的事件处理代码,并去掉存在的“not implemented”异常。
 IAsyncResult result = this.BeginInvoke(
IAsyncResult result = this.BeginInvoke( new EventHandler(
new EventHandler( delegate
delegate {
{ // Retrieve connection. Note we could simply cast the sender as
// Retrieve connection. Note we could simply cast the sender as // our data service, but we'll instead be sure to retrieve
// our data service, but we'll instead be sure to retrieve // the data meant for this particular workflow instance.
// the data meant for this particular workflow instance. MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService =
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService = MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService. GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(e.InstanceId);
GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(e.InstanceId);
 // Read the motor vehicle data
// Read the motor vehicle data DataSet ds = dataService.Read();
DataSet ds = dataService.Read();
 // Bind the vehicles list to the vehicles table
// Bind the vehicles list to the vehicles table ListViewItem lvi = null;
ListViewItem lvi = null; foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Vehicles"].Rows)
foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Vehicles"].Rows) {
{ // Create the string array
// Create the string array string[] items = new string[4];
string[] items = new string[4]; items[0] = (string)row["Plate"];
items[0] = (string)row["Plate"]; items[1] = (string)row["Make"];
items[1] = (string)row["Make"]; items[2] = (string)row["Model"];
items[2] = (string)row["Model"]; items[3] = (string)row["Color"];
items[3] = (string)row["Color"];
 // Create the list item
// Create the list item lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
 // Add to the list
// Add to the list lvVehicles.Items.Add(lvi);
lvVehicles.Items.Add(lvi); } // foreach
} // foreach
 // Bind the violations list to the violations table
// Bind the violations list to the violations table foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Violations"].Rows)
foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Violations"].Rows) {
{ // Create the string array
// Create the string array string[] items = new string[4];
string[] items = new string[4]; items[0] = (string)row["ID"];
items[0] = (string)row["ID"]; items[1] = (string)row["Plate"];
items[1] = (string)row["Plate"]; items[2] = (string)row["Violation"];
items[2] = (string)row["Violation"]; items[3] = ((DateTime)row["Date"]).ToString("MM/dd/yyyy");
items[3] = ((DateTime)row["Date"]).ToString("MM/dd/yyyy");
 // Create the list item
// Create the list item lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
 // Add to the list
// Add to the list lvViolations.Items.Add(lvi);
lvViolations.Items.Add(lvi); } // foreach
} // foreach } // delegate
} // delegate ), null, null
), null, null ); // BeginInvoke
); // BeginInvoke this.EndInvoke(result);
this.EndInvoke(result);
 // Reset for next request
// Reset for next request WorkflowCompleted();
WorkflowCompleted(); 就这样!我们的应用程序就完成了,编译并执行该应用程序。当你点击“Retrieve MV Data”按钮时,选中的驾驶员姓名就会被传给工作流实例。当DataSet创建好后,该工作流实例就会激发MVDataUpdate事件。宿主应用程序代码会截获该事件进行数据的接收,然后把它绑定到ListView控件。
在最后一步我们需注意一个关键的地方,就是在我们调用WorkflowMVDataService的静态方法GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService来检索数据服务包含的DataSet后,我们使用数据服务的Read方法来把该DataSet拉进我们的宿主应用程序执行环境中以便我们进行数据绑定。
用InvokeWorkflow调用外部工作流
这儿要问你一个问题:假如你有一个正在执行的工作流,该工作流能执行第二个工作流吗?
答案是Yes!有这样一个活动,InvokeWorkflow活动,可用它来启动第二个工作流。我们通过一个例子来简要地看看这个活动。我们将创建一个新的控制台应用程序示例来启动一个工作流,该工作流只是向控制台输出一条信息。在输出该信息后,该工作流实例启动第二个工作流实例,被启动的工作流实例也输出一条信息,这样就生动地为我们展示了两个工作流都执行了。
调用第二个工作流
1.和前面一样,本章的源代码中包含了完整版和练习版两种版本的WorkflowInvoker应用程序。我们现在打开练习版的WorkflowInvoker解决方案。
2.在Visual Studio加载WorkflowInvoker解决方案后,在WorkflowInvoker解决方案中添加一个新的基于顺序工作流库的项目,工作流的名称命名为:Workflow1,保存该项目。
3.下一步,从工具箱中拖拽一个Code活动到工作流视图设计器界面上。在该活动的ExecuteCode属性中键入“SayHello”,然后按下回车键。
4.Visual Studio会自动切换到代码编辑界面。定位到Visual Studio刚刚添加的SayHello方法,在该方法内输入下面的代码:
 // Output text to the console.
// Output text to the console. Console.WriteLine("Hello from Workflow1!");
Console.WriteLine("Hello from Workflow1!"); 5.我们现在需要添加第二个要执行的工作流,因此重复步骤2,但工作流的名称命名为:Workflow2。重复步骤3和4,但把信息“Hello from Workflow1!”替换为“Hello from Workflow2!”,当然工作流源文件的名称也要重命名为workflow2.cs,以避免冲突。
6.我们想在第一个工作流中调用第二个工作流,但这样做,我们还需要添加对第二个工作流的引用。在这之前,我们需要编译并生成Workflow1。
7.回到Visual Studio解决方案资源管理器,为Workflow1项目添加对项目Workflow2的项目级引用。
8.回到Workflow1的工作流视图设计器界面上。这次,拖拽一个InvokeWorkflow活动到你的顺序工作流视图设计器界面上。
9.看看这个新活动的属性,我们会看到它有一个“TargetWorkflow”属性需要我们去设置。点击以激活它的TargetWorkflow属性,然后点击它的浏览(...)按钮(该按钮带三个点)。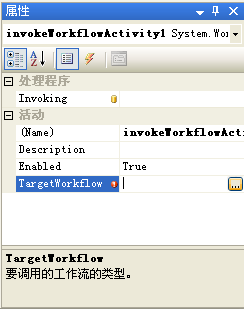
10.这将打开一个“浏览和选择一个.NET类型”对话框。在左边面板中选择Workflow2,这将在右边的面板中显示Workflow2类型。在右边的面板中选择Workflow2类型(Workflow2.Workflow2是它的完全限定名称),然后点击确定。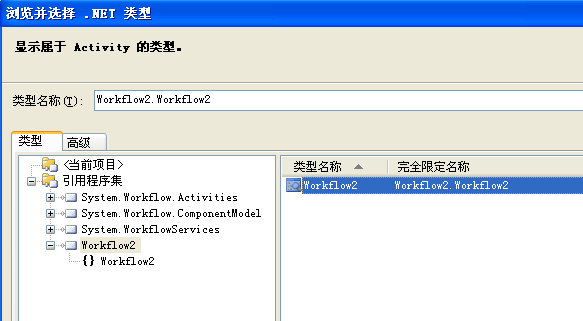
11.然后Visual Studio会检查该Workflow2工作流,并在工作流视图设计器的InvokeWorkflow活动内部展示它的图形界面。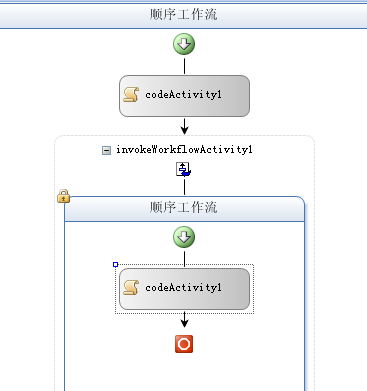
12.工作流现在就完整地实现了,我们现在需要为WorkflowInvoker项目添加对Workflow1和Workflow2的项目引用。
13.接下来在Program.cs文件中定位到下面的代码上:
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for workflow completion.");
14.在上面的代码下添加如下代码:
 // Create the workflow instance.
// Create the workflow instance. WorkflowInstance instance =
WorkflowInstance instance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(Workflow1.Workflow1));
workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(Workflow1.Workflow1));
 // Start the workflow instance.
// Start the workflow instance. instance.Start();
instance.Start();15.我们现在将为宿主应用程序添加少量的代码,以便每个工作流完成后通知我们。在WorkflowCompleted的事件处理程序中插入下面的代码:
 if (e.WorkflowDefinition is Workflow1.Workflow1)
if (e.WorkflowDefinition is Workflow1.Workflow1) Console.WriteLine("Workflow 1 completed.");
Console.WriteLine("Workflow 1 completed."); else
else Console.WriteLine("Workflow 2 completed.");
Console.WriteLine("Workflow 2 completed.");
 waitHandle.Set();
waitHandle.Set(); 第一个完成的工作流设置AutoResetEvent,以便强制应用程序等待工作流完成。我们可添加代码以使应用程序等待所有的工作流,但出于展示的目的这已足够。假如你编译并执行该WorkflowInvoker应用程序,你将在控制台中看到下面图8-4中所展示的输出结果。假如输出信息的顺序有些许的不同,不用吃惊,这是多线程程序的特征。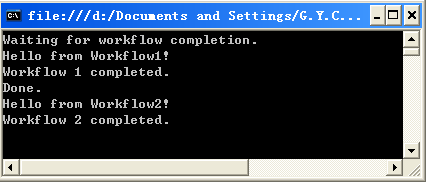
图8-4 WorkflowInvoker应用程序的控制台输出
¥¥¥¥¥¥
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Runtime.Hosting;
namespace MVDataChecker
{
public static class WorkflowFactory
{
// Singleton instance of the workflow runtime
private static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null;
// Lock (sync) object
private static object _syncRoot = new object();
// Factory method
public static WorkflowRuntime GetWorkflowRuntime()
{
// Lock execution thread in case of multi-threaded
// (concurrent) access.
lock (_syncRoot)
{
// Check for startup condition
if (null == _workflowRuntime)
{
// Provide for shutdown
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ProcessExit += new EventHandler(StopWorkflowRuntime);
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.DomainUnload += new EventHandler(StopWorkflowRuntime);
// Not started, so create instance
_workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
// Start the runtime
_workflowRuntime.StartRuntime();
} // if
// Return singleton instance
return _workflowRuntime;
} // lock
}
// Shutdown method
static void StopWorkflowRuntime(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_workflowRuntime != null)
{
if (_workflowRuntime.IsStarted)
{
try
{
// Stop the runtime
_workflowRuntime.StopRuntime();
}
catch (ObjectDisposedException)
{
// Already disposed of, so ignore...
} // catch
} // if
} // if
}
}
}
{
partial class Form1
{
/// <summary>
/// Required designer variable.
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
/// <summary>
/// Clean up any resources being used.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing">true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.</param>
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && (components != null))
{
components.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
System.ComponentModel.ComponentResourceManager resources = new System.ComponentModel.ComponentResourceManager(typeof(Form1));
this.label1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.cmbDriver = new System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox();
this.cmdRetrieve = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.label2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.lvVehicles = new System.Windows.Forms.ListView();
this.columnHeader1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader2 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader3 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader4 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.label3 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.lvViolations = new System.Windows.Forms.ListView();
this.columnHeader5 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader6 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader7 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.columnHeader8 = new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader();
this.cmdQuit = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.lblSearching = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.pbSearching = new System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.pbSearching)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// label1
//
this.label1.AutoSize = true;
this.label1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(12, 9);
this.label1.Name = "label1";
this.label1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(69, 13);
this.label1.TabIndex = 0;
this.label1.Text = "Driver Name:";
//
// cmbDriver
//
this.cmbDriver.DropDownStyle = System.Windows.Forms.ComboBoxStyle.DropDownList;
this.cmbDriver.FormattingEnabled = true;
this.cmbDriver.Items.AddRange(new object[] {
"Marc Faeber",
"Tracy Tallman",
"Darrell Meisner"});
this.cmbDriver.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(24, 25);
this.cmbDriver.Name = "cmbDriver";
this.cmbDriver.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(330, 21);
this.cmbDriver.TabIndex = 1;
//
// cmdRetrieve
//
this.cmdRetrieve.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(390, 22);
this.cmdRetrieve.Name = "cmdRetrieve";
this.cmdRetrieve.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(109, 23);
this.cmdRetrieve.TabIndex = 2;
this.cmdRetrieve.Text = "Retrieve MV Data";
this.cmdRetrieve.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
this.cmdRetrieve.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.cmdRetrieve_Click);
//
// label2
//
this.label2.AutoSize = true;
this.label2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(12, 59);
this.label2.Name = "label2";
this.label2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(101, 13);
this.label2.TabIndex = 3;
this.label2.Text = "Motor Vehicle Data:";
//
// lvVehicles
//
this.lvVehicles.Columns.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader[] {
this.columnHeader1,
this.columnHeader2,
this.columnHeader3,
this.columnHeader4});
this.lvVehicles.FullRowSelect = true;
this.lvVehicles.GridLines = true;
this.lvVehicles.HeaderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeaderStyle.Nonclickable;
this.lvVehicles.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(24, 75);
this.lvVehicles.Name = "lvVehicles";
this.lvVehicles.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(475, 97);
this.lvVehicles.TabIndex = 4;
this.lvVehicles.UseCompatibleStateImageBehavior = false;
this.lvVehicles.View = System.Windows.Forms.View.Details;
//
// columnHeader1
//
this.columnHeader1.Text = "Plate Number";
this.columnHeader1.Width = 88;
//
// columnHeader2
//
this.columnHeader2.Text = "Vehicle Make";
this.columnHeader2.Width = 85;
//
// columnHeader3
//
this.columnHeader3.Text = "Vehicle Model";
this.columnHeader3.Width = 85;
//
// columnHeader4
//
this.columnHeader4.Text = "Color";
this.columnHeader4.Width = 80;
//
// label3
//
this.label3.AutoSize = true;
this.label3.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(12, 186);
this.label3.Name = "label3";
this.label3.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 13);
this.label3.TabIndex = 5;
this.label3.Text = "Citation Information:";
//
// lvViolations
//
this.lvViolations.Columns.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader[] {
this.columnHeader5,
this.columnHeader6,
this.columnHeader7,
this.columnHeader8});
this.lvViolations.FullRowSelect = true;
this.lvViolations.GridLines = true;
this.lvViolations.HeaderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeaderStyle.Nonclickable;
this.lvViolations.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(24, 202);
this.lvViolations.Name = "lvViolations";
this.lvViolations.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(475, 97);
this.lvViolations.TabIndex = 6;
this.lvViolations.UseCompatibleStateImageBehavior = false;
this.lvViolations.View = System.Windows.Forms.View.Details;
//
// columnHeader5
//
this.columnHeader5.Text = "Citation ID";
this.columnHeader5.Width = 88;
//
// columnHeader6
//
this.columnHeader6.Text = "Plate Number";
this.columnHeader6.Width = 86;
//
// columnHeader7
//
this.columnHeader7.Text = "Violation";
this.columnHeader7.Width = 82;
//
// columnHeader8
//
this.columnHeader8.Text = "Date";
this.columnHeader8.Width = 82;
//
// cmdQuit
//
this.cmdQuit.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(390, 306);
this.cmdQuit.Name = "cmdQuit";
this.cmdQuit.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(109, 23);
this.cmdQuit.TabIndex = 7;
this.cmdQuit.Text = "Quit";
this.cmdQuit.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
this.cmdQuit.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.cmdQuit_Click);
//
// lblSearching
//
this.lblSearching.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(15, 306);
this.lblSearching.Name = "lblSearching";
this.lblSearching.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(66, 23);
this.lblSearching.TabIndex = 8;
this.lblSearching.Text = "Searching";
this.lblSearching.TextAlign = System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleLeft;
this.lblSearching.Visible = false;
//
// pbSearching
//
this.pbSearching.Image = ((System.Drawing.Image)(resources.GetObject("pbSearching.Image")));
this.pbSearching.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(87, 311);
this.pbSearching.Name = "pbSearching";
this.pbSearching.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(149, 18);
this.pbSearching.TabIndex = 9;
this.pbSearching.TabStop = false;
this.pbSearching.Visible = false;
//
// Form1
//
this.AcceptButton = this.cmdRetrieve;
this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F);
this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(513, 335);
this.Controls.Add(this.pbSearching);
this.Controls.Add(this.lblSearching);
this.Controls.Add(this.cmdQuit);
this.Controls.Add(this.lvViolations);
this.Controls.Add(this.label3);
this.Controls.Add(this.lvVehicles);
this.Controls.Add(this.label2);
this.Controls.Add(this.cmdRetrieve);
this.Controls.Add(this.cmbDriver);
this.Controls.Add(this.label1);
this.FormBorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle.FixedDialog;
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.MinimizeBox = false;
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "Workflow-Based Motor Vehicle Query";
this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Load);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.pbSearching)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
this.PerformLayout();
}
#endregion
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label1;
private System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox cmbDriver;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button cmdRetrieve;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label2;
private System.Windows.Forms.ListView lvVehicles;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader1;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader2;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader3;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader4;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label3;
private System.Windows.Forms.ListView lvViolations;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader5;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader6;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader7;
private System.Windows.Forms.ColumnHeader columnHeader8;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button cmdQuit;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label lblSearching;
private System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox pbSearching;
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
namespace MVDataChecker
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// Our workflow runtime instance
WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null;
// Currently executing workflow instance (we'll only have
// one).
WorkflowInstance _workflowInstance = null;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Initialize the driver combobox
cmbDriver.SelectedItem = cmbDriver.Items[0];
// Create an instance of the workflow runtime
_workflowRuntime = WorkflowFactory.GetWorkflowRuntime();
_workflowRuntime.WorkflowTerminated += new EventHandler<WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs>(workflowRuntime_WorkflowTerminated);
_workflowRuntime.WorkflowCompleted += new EventHandler<WorkflowCompletedEventArgs>(workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted);
}
void workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted(object sender, WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e)
{
// Remove the local data service
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService = MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.CreateDataService(_workflowInstance.InstanceId, _workflowRuntime);
dataService.MVDataUpdate -= new EventHandler<MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs>(dataService_MVDataUpdate);
// Clear instance (for application termination purposes)
_workflowInstance = null;
// Update the user interface
WorkflowCompleted();
}
void workflowRuntime_WorkflowTerminated(object sender, WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs e)
{
// Remove the local data service
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService = MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.CreateDataService(_workflowInstance.InstanceId, _workflowRuntime);
dataService.MVDataUpdate -= new EventHandler<MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs>(dataService_MVDataUpdate);
// Clear instance (for application termination purposes)
_workflowInstance = null;
// Some error...
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("Your vehicle record search was terminated! Error: {0}", e.Exception.Message));
// Update the user interface
WorkflowCompleted();
}
private void cmdRetrieve_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Disable the search button
cmdRetrieve.Enabled = false;
// We've selected a driver, so disable the driver selection
// combobox
cmbDriver.Enabled = false;
// Clear the lists
lvVehicles.Items.Clear();
lvViolations.Items.Clear();
// Show the search controls
lblSearching.Visible = true;
pbSearching.Visible = true;
// Set the cursor to "app starting"
Cursor = Cursors.AppStarting;
// Process the request, starting by creating the parameters
Dictionary<string, object> parms = new Dictionary<string, object>();
parms.Add("DriverName", cmbDriver.SelectedItem);
// Create instance.
_workflowInstance = _workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(MVWorkflow.Workflow1), parms);
// Hook returned data event
// Hook returned data event.
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService =
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.CreateDataService(
_workflowInstance.InstanceId,
_workflowRuntime);
dataService.MVDataUpdate += new EventHandler<MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs>(dataService_MVDataUpdate);
// Start instance.
_workflowInstance.Start();
}
void dataService_MVDataUpdate(object sender, MVDataService.MVDataAvailableArgs e)
{
IAsyncResult result = this.BeginInvoke(
new EventHandler(
delegate
{
// Retrieve connection. Note we could simply cast the sender as
// our data service, but we'll instead be sure to retrieve
// the data meant for this particular workflow instance.
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService dataService =
MVDataService.WorkflowMVDataService.
GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(e.InstanceId);
// Read the motor vehicle data
DataSet ds = dataService.Read();
// Bind the vehicles list to the vehicles table
ListViewItem lvi = null;
foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Vehicles"].Rows)
{
// Create the string array
string[] items = new string[4];
items[0] = (string)row["Plate"];
items[1] = (string)row["Make"];
items[2] = (string)row["Model"];
items[3] = (string)row["Color"];
// Create the list item
lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
// Add to the list
lvVehicles.Items.Add(lvi);
} // foreach
// Bind the violations list to the violations table
foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Violations"].Rows)
{
// Create the string array
string[] items = new string[4];
items[0] = (string)row["ID"];
items[1] = (string)row["Plate"];
items[2] = (string)row["Violation"];
items[3] = ((DateTime)row["Date"]).ToString("MM/dd/yyyy");
// Create the list item
lvi = new ListViewItem(items);
// Add to the list
lvViolations.Items.Add(lvi);
} // foreach
} // delegate
), null, null
); // BeginInvoke
this.EndInvoke(result);
// Reset for next request
WorkflowCompleted();
}
private void cmdQuit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Check for executing workflows
if (_workflowInstance != null)
{
// Cease processing
_workflowInstance.Abort();
} // if
// Quit...
Application.Exit();
}
private delegate void WorkflowCompletedDelegate();
private void WorkflowCompleted()
{
if (this.InvokeRequired)
{
// Wrong thread, so switch to the UI thread...
WorkflowCompletedDelegate d = delegate() { WorkflowCompleted(); };
this.Invoke(d);
} // if
else
{
// Hide the search controls
lblSearching.Visible = false;
pbSearching.Visible = false;
// Reset the cursor
Cursor = Cursors.Arrow;
// Enable the driver selection combobox
cmbDriver.Enabled = true;
// Enable the search button
cmdRetrieve.Enabled = true;
} // else
}
}
}
¥¥¥¥¥¥¥
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Data;
namespace MVDataService
{
[ExternalDataExchange]
public interface IMVDataService
{
void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData);
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
namespace MVDataService
{
[Serializable]
public class MVDataAvailableArgs : ExternalDataEventArgs
{
public MVDataAvailableArgs(Guid instanceId)
: base(instanceId)
{
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Data;
namespace MVDataService
{
public sealed class MVDataConnector : IMVDataService
{
private DataSet _dataValue = null;
private static WorkflowMVDataService _service = null;
private static object _syncLock = new object();
public static WorkflowMVDataService MVDataService
{
get { return _service; }
set
{
if (value != null)
{
lock (_syncLock)
{
// Re-verify the service isn't null
// now that we're locked
if (value != null)
{
_service = value;
} // if
else
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
} // else
} // lock
} // if
else
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("You must provide a service instance.");
} // else
}
}
public DataSet MVData
{
get { return _dataValue; }
}
public void MVDataUpdate(DataSet mvData)
{
// Assign the field for later recall
_dataValue = mvData;
// Raise the event to trigger host read
_service.RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent();
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Data;
namespace MVDataService
{
public class WorkflowMVDataService
{
static WorkflowRuntime _workflowRuntime = null;
static ExternalDataExchangeService _dataExchangeService = null;
static MVDataConnector _dataConnector = null;
static object _syncLock = new object();
public event EventHandler<MVDataAvailableArgs> MVDataUpdate;
private Guid _instanceID = Guid.Empty;
public Guid InstanceID
{
get { return _instanceID; }
set { _instanceID = value; }
}
public static WorkflowMVDataService CreateDataService(Guid instanceID, WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime)
{
lock (_syncLock)
{
// If we're just starting, save a copy of the workflow runtime reference
if (_workflowRuntime == null)
{
// Save instance of the workflow runtime.
_workflowRuntime = workflowRuntime;
} // if
// If we're just starting, plug in ExternalDataExchange service
if (_dataExchangeService == null)
{
// Data exchange service not registered, so create an
// instance and register.
_dataExchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService();
_workflowRuntime.AddService(_dataExchangeService);
} // if
// Check to see if we have already added this data exchange service
MVDataConnector dataConnector = (MVDataConnector)workflowRuntime.
GetService(typeof(MVDataConnector));
if (dataConnector == null)
{
// First time through, so create the connector and
// register as a service with the workflow runtime.
_dataConnector = new MVDataConnector();
_dataExchangeService.AddService(_dataConnector);
} // if
else
{
// Use the retrieved data connector.
_dataConnector = dataConnector;
} // else
// Pull the service instance we registered with the connection object
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
if (workflowDataService == null)
{
// First time through, so create the data service and
// hand it to the connector.
workflowDataService = new WorkflowMVDataService(instanceID);
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = workflowDataService;
} // if
else
{
// The data service is static and already registered with
// the workflow runtime. The instance ID present when it
// was registered is invalid for this iteration and must be
// updated.
workflowDataService.InstanceID = instanceID;
} // else
return workflowDataService;
} // lock
}
public static WorkflowMVDataService GetRegisteredWorkflowDataService(Guid instanceID)
{
lock (_syncLock)
{
WorkflowMVDataService workflowDataService = MVDataConnector.MVDataService;
if (workflowDataService == null)
{
throw new Exception("Error configuring data serviceservice cannot be null.");
} // if
return workflowDataService;
} // lock
}
private WorkflowMVDataService(Guid instanceID)
{
_instanceID = instanceID;
MVDataConnector.MVDataService = this;
}
~WorkflowMVDataService()
{
// Clean up
_workflowRuntime = null;
_dataExchangeService = null;
_dataConnector = null;
}
public DataSet Read()
{
return _dataConnector.MVData;
}
public void RaiseMVDataUpdateEvent()
{
if (_workflowRuntime == null)
_workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
_workflowRuntime.GetWorkflow(_instanceID); // loads persisted workflow instances
if (MVDataUpdate != null)
{
MVDataUpdate(this, new MVDataAvailableArgs(_instanceID));
} // if
}
}
}
¥¥¥¥¥¥
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.Design;
using System.Collections;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Compiler;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Serialization;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Design;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities.Rules;
using System.Data;
namespace MVWorkflow
{
public sealed partial class Workflow1: SequentialWorkflowActivity
{
public Workflow1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private string _driver = String.Empty;
public string DriverName
{
get { return _driver; }
set { _driver = value; }
}
private void GenerateMVData(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a blank DataSet to pass back
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
// Pull (create) the vehicle information for the
// assigned driver
ds.Tables.Add(GenerateVehicleTable(DriverName));
// Pull (create) the vehicle information for the
// assigned driver
ds.Tables.Add(GenerateViolationTable(DriverName));
// Assign the DataSet we just created as the host data
mvDataUpdate1.mvData = ds;
}
private DataTable GenerateVehicleTable(string driverName)
{
// Create the empty table
DataTable dt = new DataTable("Vehicles");
// Add the columns for plate number, make, model, and color
// (all strings).
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Plate",typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Make",typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Model",typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Color",typeof(string)));
// Now add the actual data, based on the driver. Normally
// this would be a database or service call of some type,
// but we're just simulating pulling data here. We know
// we have only three drivers...
if (driverName == "Marc Faeber")
{
// Add a vehicle
DataRow row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["Plate"] = "2FAST4U";
row["Make"] = "Chevrolet";
row["Model"] = "Corvette";
row["Color"] = "Arrest Me Red";
row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["Plate"] = "VIPER1";
row["Make"] = "Dodge";
row["Model"] = "Viper";
row["Color"] = "Midnight Black";
} // if
else if (driverName == "Tracy Tallman")
{
// Add a vehicle
DataRow row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["Plate"] = "28ADX55";
row["Make"] = "Buick";
row["Model"] = "LeSabre";
row["Color"] = "Polo White";
} // else if
else if (driverName == "Darrell Meisner")
{
// Add a vehicle
DataRow row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["Plate"] = "42NBR31";
row["Make"] = "Ford";
row["Model"] = "Windstar";
row["Color"] = "Does it matter?";
} // else if
return dt;
}
private DataTable GenerateViolationTable(string driverName)
{
// Create the empty table
DataTable dt = new DataTable("Violations");
// Add the columns for citation ID, plate number, violation,
// and date (all strings but date, which is a date).
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ID", typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Plate", typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Violation", typeof(string)));
dt.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Date", typeof(DateTime)));
// Now add the actual data, based on the driver. Normally
// this would be a database or service call of some type,
// but we're just simulating pulling data here. We know
// we have only three drivers...
if (driverName == "Marc Faeber")
{
// Add a violation
DataRow row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["ID"] = "24175641";
row["Plate"] = "2FAST4U";
row["Violation"] = "Speeding, 55MPH in a 25MPH zone";
row["Date"] = new DateTime(2006, 5, 21);
row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["ID"] = "38573319";
row["Plate"] = "2FAST4U";
row["Violation"] = "Speeding, 85MPH in a 65MPH zone";
row["Date"] = new DateTime(2006, 11, 6);
row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["ID"] = "67112487";
row["Plate"] = "VIPER1";
row["Violation"] = "Ran red light";
row["Date"] = new DateTime(2007, 2, 12);
} // if
else if (driverName == "Tracy Tallman")
{
// You're kidding, right? In a LeSabre?
} // else if
else if (driverName == "Darrell Meisner")
{
// Add a violation
DataRow row = dt.NewRow();
dt.Rows.Add(row);
row["ID"] = "43564217";
row["Plate"] = "42NBR31";
row["Violation"] = "Illegal Parking";
row["Date"] = new DateTime(2006, 10, 3);
} // else if
return dt;
}
}
}

