一、接口
接口的定义格式:
interface 接口名{
}
接口要注意的事项 :
1. 接口是一个特殊的类。
2. 接口的成员变量默认的修饰符为: public static final 。那么也就是说接口中的成员变量都是常量(必须初始化)。
3. 接口中 的方法都是抽象的方法,默认的修饰符为: public abstract。
4. 接口不能创建对象。
5. 接口是没有构造方法的。
6. 接口是给类去实现使用的,非抽象类实现一个接口的时候,必须要把接口中所有方法全部实现。
实现接口的格式:
class 类名 implements 接口名{
}
接口的作用:
1. 程序的解耦。 (低耦合)
2. 定义约束规范。
3. 拓展功能。
//普通的铅笔类
class Pencil{
String name;
public Pencil(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void write(){
System.out.println(name+"沙沙的写...");
}
}
//橡皮接口
interface Eraser{
public void remove();
}
//带橡皮的铅笔
class PencilWithEraser extends Pencil implements Eraser {
public PencilWithEraser(String name){
super(name);
}
public void remove(){
System.out.println("涂改,涂改....");
}
}
class Demo8
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//System.out.println("Hello World!");
PencilWithEraser p = new PencilWithEraser("2B铅笔");
p.write();
p.remove();
}
}
二、类与接口、接口与接口
(一)类与接口的关系
类与接口之间关系: 实现关系。
类与接口要注意的事项:
1. 非抽象类实现一个接口时,必须要把接口中所有方法全部实现。
2. 抽象类实现一个接口时,可以实现也可以不实现接口中的 方法。
3. 一个类可以实现多个接口 。
疑问: java为什么不支持多继承,而支持了多实现呢?
class A{
public void print(){
System.out.println("AAAAAA");
}
}
class B{
public void print(){
System.out.println("BBBBBB");
}
}
class C extends A ,B{
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new C().print(); //存在同名的方法
}
(二)接口与接口的关系
接口与接口之间关系: 继承关系。
接口与接口之间要注意事项:一个接口是可以继承多个接口的。
三、多态
(一)
多态:一个对象具备多种形态。(父类的引用类型变量指向了子类的对象)或者是接口 的引用类型变量指向了接口实现类的对象)
多态的前提:必须存在继承或者实现 关系。
动物 a = new 狗();
多态要注意 的细节:
1. 多态情况下,子父类存在同名的成员变量时,访问的是父类的成员变量。
2. 多态情况下,子父类存在同名的非静态的成员函数时,访问的是子类的成员函数。
3. 多态情况下,子父类存在同名的静态的成员函数时,访问的是父类的成员函数。
4. 多态情况下,不能访问子类特有的成员。
总结:多态情况下,子父类存在同名的成员时,访问的都是父类的成员,除了在同名非静态函数时才是访问子类的。
编译看左边,运行不一定看右边。
编译看左边:java编译器在编译的时候,会检查引用类型变量所属的类是否具备指定的成员,如果不具备马上编译报错。
//老鼠
class Mouse extends Animal{
String color = "黑色";
public Mouse(String name){
super(name);
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(name+"四条腿慢慢的走!");
}
public static void eat(){
System.out.println("老鼠在偷吃..");
}
//老鼠特有方法---打洞
public void dig(){
System.out.println("老鼠在打洞..");
}
}
class Fish extends Animal {
public Fish(String name){
super(name);
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(name+"摇摇尾巴游..");
}
}
class Demo11
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
Mouse m = new Mouse("老鼠");
System.out.println(m.color);
//多态: 父类的引用类型变量指向子类的对象
*/
Animal a = new Mouse("老鼠");
a.dig();
//a.eat();
}
}
(二)多态的应用
1. 多态用于形参类型的时候,可以接收更多类型的数据 。
2. 多态用于返回值类型的时候,可以返回更多类型的数据。
多态的好处: 提高了代码的拓展性。
//图形类
abstract class MyShape{
public abstract void getArea();
public abstract void getLength();
}
class Circle extends MyShape{
public static final double PI = 3.14;
double r;
public Circle(double r){
this.r =r ;
}
public void getArea(){
System.out.println("圆形的面积:"+ PI*r*r);
}
public void getLength(){
System.out.println("圆形的周长:"+ 2*PI*r);
}
}
class Rect extends MyShape{
int width;
int height;
public Rect(int width , int height){
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void getArea(){
System.out.println("矩形的面积:"+ width*height);
}
public void getLength(){
System.out.println("矩形的周长:"+ 2*(width+height));
}
}
class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
//System.out.println("Hello World!");
Circle c = new Circle(4.0);
print(c);
Rect r = new Rect(3,4);
print(r);
*/
MyShape m = getShape(0); //调用了使用多态的方法,定义的变量类型要与返回值类型一致。
m.getArea();
m.getLength();
}
//需求1: 定义一个函数可以接收任意类型的图形对象,并且打印图形面积与周长。
public static void print(MyShape s){ // MyShpe s = new Circle(4.0);
s.getArea();
s.getLength();
}
// 需求2: 定义一个函数可以返回任意类型的图形对象。
public static MyShape getShape(int i){
if (i==0){
return new Circle(4.0);
}else{
return new Rect(3,4);
}
}
}
(三)目前多态情况下不能访问子类特有的成员。
如果需要访问子类特有的成员,那么需要进行类型强制转换.
//动物类 abstract class Animal{ String name; public Animal(String name){ this.name = name; } public abstract void run(); } //老鼠 class Mouse extends Animal{ public Mouse(String name){ super(name); } public void run(){ System.out.println(name+"四条腿慢慢的走!"); } //老鼠特有方法---打洞 public void dig(){ System.out.println("老鼠在打洞.."); } } //鱼 class Fish extends Animal{ public Fish(String name){ super(name); } public void run(){ System.out.println(name+"摇摇尾巴游啊游 !"); } //吹泡泡 public void bubble(){ System.out.println(name+"吹泡泡...!"); } } class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* Animal a = new Mouse("老鼠"); //多态 //调用子类特有的方法 Mouse m = (Mouse)a; //强制类型转换 m.dig(); */ Mouse m = new Mouse("米老鼠"); Fish f = new Fish("草鱼"); print(f); } //需求: 定义一个函数可以接收任意类型的动物对象,在函数内部要调用到动物特有的方法。 public static void print(Animal a){ // Animal a = new Mouse("米老鼠"); if(a instanceof Fish){ Fish f = (Fish)a; f.bubble(); }else if(a instanceof Mouse){ Mouse m = (Mouse)a; m.dig(); } } }
类型转换最常见的异常: java.lang.ClassCastException。 强制类型转换失败。
(四)接口关系下的多态
实现关系下的多态:接口 变量 = new 接口实现类的对象。
interface Dao{ //接口的方法全部都是非静态的方法。 public void add(); public void delete(); } //接口的实现类 class UserDao implements Dao{ public void add(){ System.out.println("添加员工成功!!"); } public void delete(){ System.out.println("删除员工成功!!"); } } class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //实现关系下的多态 Dao d = new UserDao(); //接口的引用类型变量指向了接口实现类的对象。 d.add(); } }
四、值交换
需求1:定义一个函数交换两个基本类型变量的值。
class Demo5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
changeValue(a,b);
System.out.println("交换之后的值:a = "+a +" b="+b); // a=3 b=5
}
//需求1:定义一个函数交换两个基本类型变量的值。
public static void changeValue(int a , int b){
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("方法内部交换的值:a = "+a +" b="+b);
}
}
重点:
(1)形式参数是所属函数的局部变量;
(2)不同函数的局部变量之间没有关系,相互独立;
(3)Java函数在传递过程中只能够传值,不能传址。
解决方法:
所以解决之道就是要找到要交换对象的引用。对于普通的值类型,像int或者double这样的可以改传他们的包装类Integer和Double。
public static void changeValue(Integer a ,Integer b){ int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; System.out.println("方法内部交换的值:a = "+a +" b="+b); }

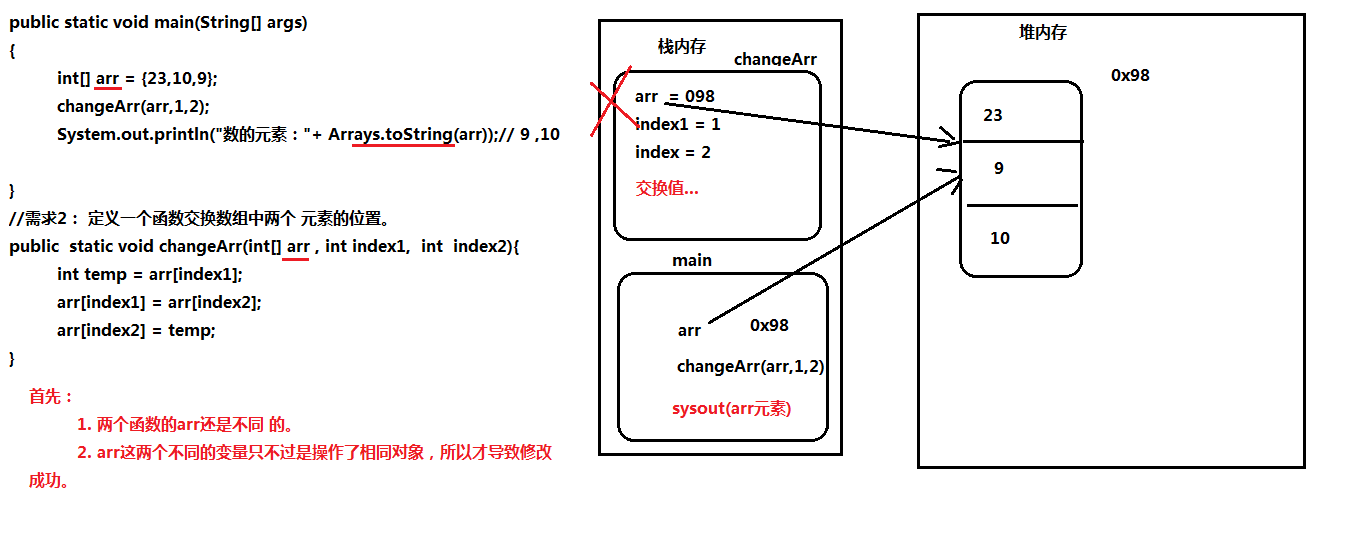
需求2:定义一个函数交换数组中两个 元素的位置。
class Demo5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = {23,10,9};
changeArr(arr,1,2);
System.out.println("数的元素:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));//23 9 10
}
//需求2: 定义一个函数交换数组中两个 元素的位置。
public static void changeArr(int[] arr , int index1, int index2){
int temp = arr[index1];
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
arr[index2] = temp;
}
}
重点:
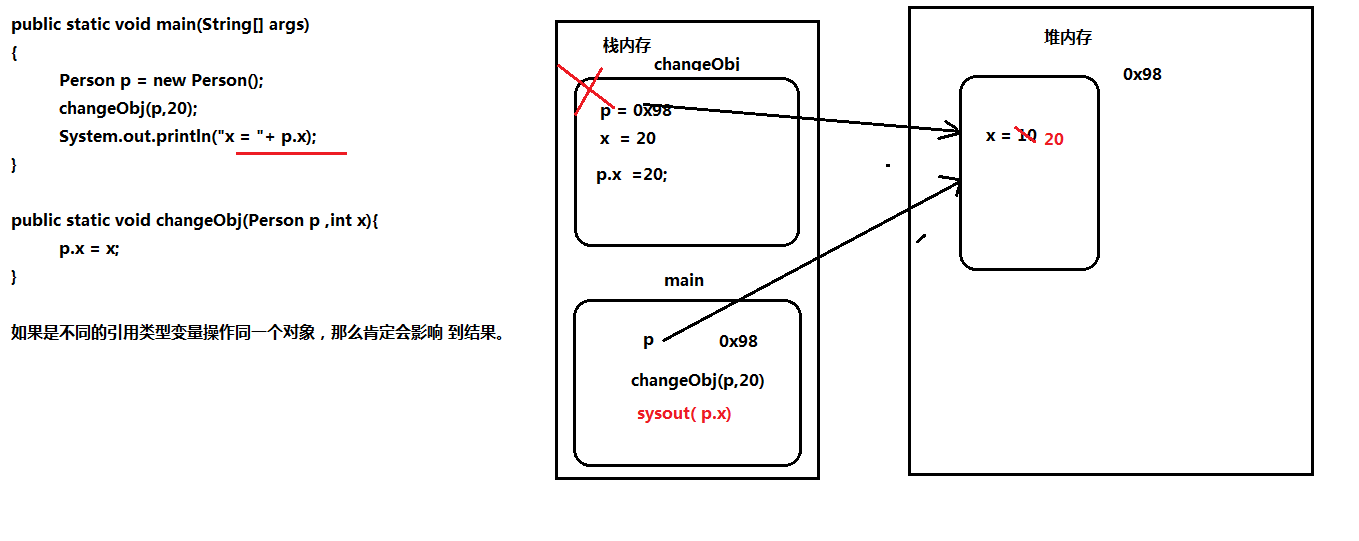
需求3:
import java.util.*;
class Person{
int x =10;
}
class Demo5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Person p = new Person();
changeObj(p,20);
System.out.println("x = "+ p.x); //x=20
}
public static void changeObj(Person p ,int x){
p.x = x;
}
}
重点: