★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)
➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/11014400.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
In an N by N square grid, each cell is either empty (0) or blocked (1).
A clear path from top-left to bottom-right has length k if and only if it is composed of cells C_1, C_2, ..., C_k such that:
- Adjacent cells
C_iandC_{i+1}are connected 8-directionally (ie., they are different and share an edge or corner) C_1is at location(0, 0)(ie. has valuegrid[0][0])C_kis at location(N-1, N-1)(ie. has valuegrid[N-1][N-1])- If
C_iis located at(r, c), thengrid[r][c]is empty (ie.grid[r][c] == 0).
Return the length of the shortest such clear path from top-left to bottom-right. If such a path does not exist, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: [[0,1],[1,0]]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
Output: 4
Note:
1 <= grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100grid[i][j]is0or1
在一个 N × N 的方形网格中,每个单元格有两种状态:空(0)或者阻塞(1)。
一条从左上角到右下角、长度为 k 的畅通路径,由满足下述条件的单元格 C_1, C_2, ..., C_k 组成:
- 相邻单元格
C_i和C_{i+1}在八个方向之一上连通(此时,C_i和C_{i+1}不同且共享边或角) C_1位于(0, 0)(即,值为grid[0][0])C_k位于(N-1, N-1)(即,值为grid[N-1][N-1])- 如果
C_i位于(r, c),则grid[r][c]为空(即,grid[r][c] == 0)
返回这条从左上角到右下角的最短畅通路径的长度。如果不存在这样的路径,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:[[0,1],[1,0]]

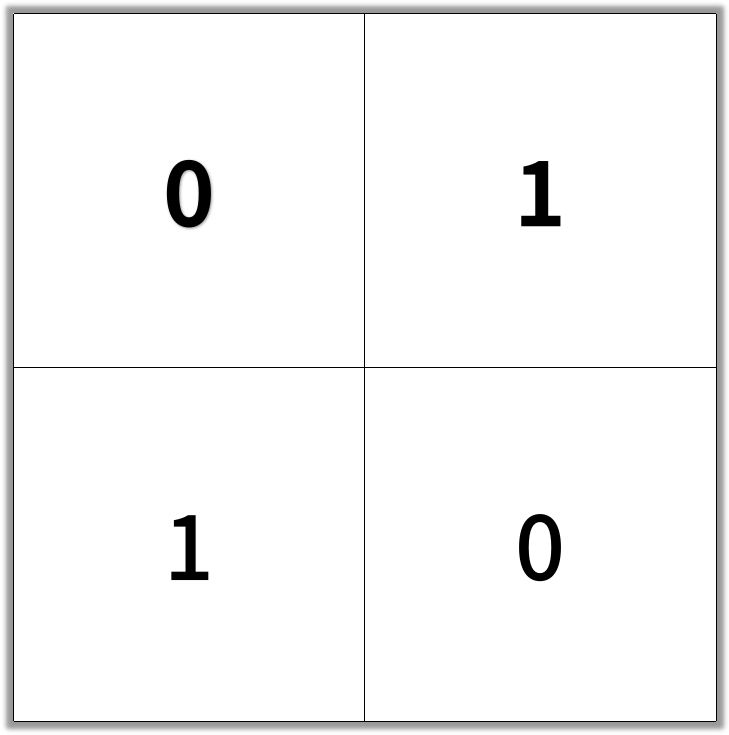
输出:2

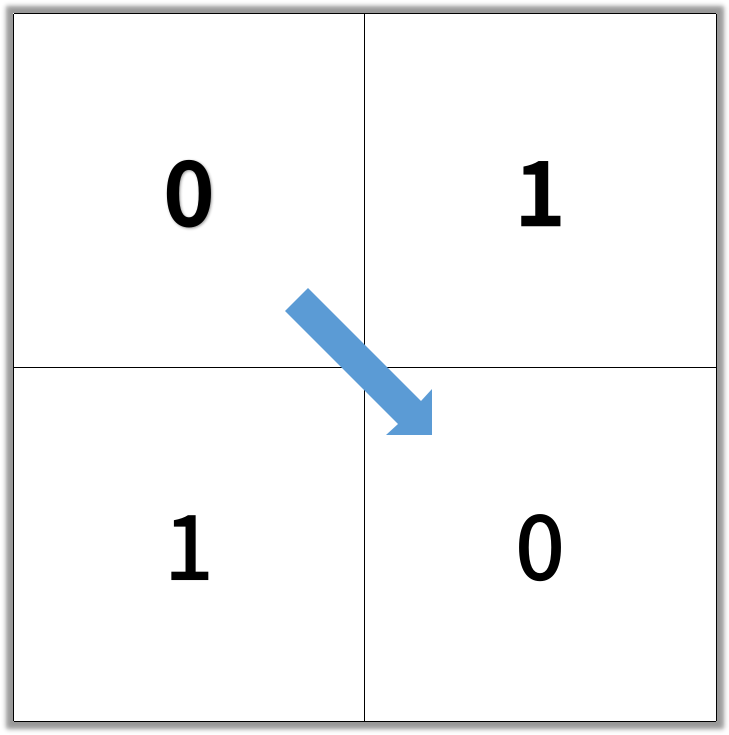
示例 2:
输入:[[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]

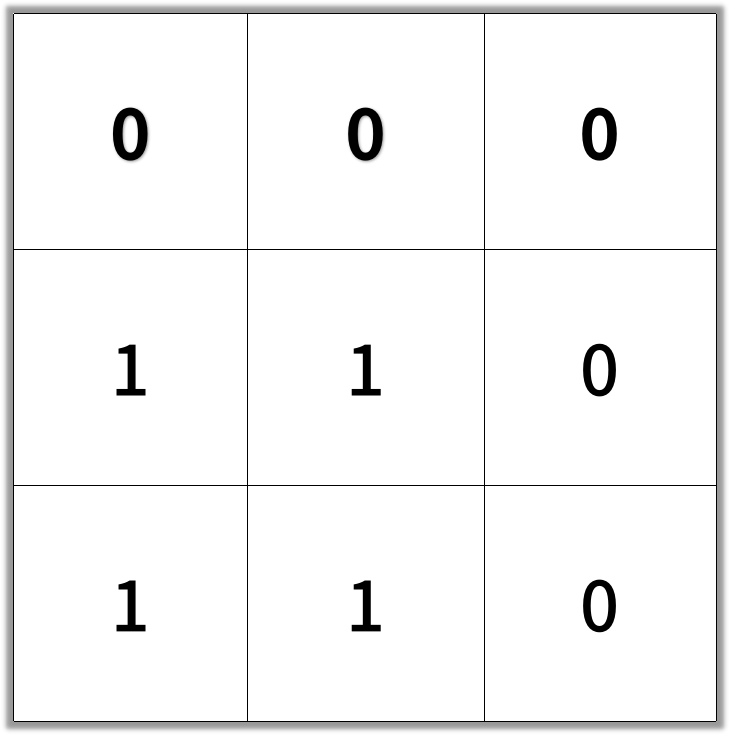
输出:4

提示:
1 <= grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100grid[i][j]为0或1
1 class Solution { 2 let dir:[[Int]] = [[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0],[1,-1],[-1,1],[-1,-1],[1,1]] 3 func shortestPathBinaryMatrix(_ grid: [[Int]]) -> Int { 4 let m:Int = grid.count 5 let n:Int = grid[0].count 6 7 if grid[0][0]==1 || grid[m-1][n-1]==1 8 { 9 return -1 10 } 11 12 var visited:[[Bool]] = [[Bool]](repeating:[Bool](repeating:false,count:n),count:m) 13 visited[0][0] = true 14 var queue:[[Int]] = [[Int]]() 15 queue.append([0,0]) 16 var ans:Int = 0 17 while(!queue.isEmpty) 18 { 19 let size:Int = queue.count 20 for _ in 0..<size 21 { 22 var pop:[Int] = queue.removeFirst() 23 if pop[0] == m-1 && pop[1] == n-1 24 { 25 return ans + 1 26 } 27 for k in 0..<8 28 { 29 let nextX:Int = dir[k][0]+pop[0] 30 let nextY:Int = dir[k][1]+pop[1] 31 if nextX>=0 && nextX<m && nextY>=0 && nextY<n && !visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY]==0 32 { 33 queue.append([nextX,nextY]) 34 visited[nextX][nextY] = true 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 ans += 1 39 } 40 return -1 41 } 42 }
612ms
1 class Solution { 2 func shortestPathBinaryMatrix(_ grid: [[Int]]) -> Int { 3 guard grid.count > 0 && grid[0].count > 0 else { return -1 } 4 guard grid[0][0] == 0 else { return -1 } 5 let R = grid.count 6 let C = grid[0].count 7 let directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1), (-1, -1)] 8 var isVisited = [[Bool]](repeating: [Bool](repeating: false, count: grid[0].count), count: grid.count) 9 var queue = [(0, 0)] 10 isVisited[0][0] = true 11 var steps = 1 12 while queue.count > 0 { 13 14 let size = queue.count 15 steps += 1 16 for i in 0..<size { 17 let curr = queue.removeFirst() 18 for direct in directions { 19 let nextR = curr.0 + direct.0 20 let nextC = curr.1 + direct.1 21 // print((nextR, nextC)) 22 guard nextR < grid.count && nextR >= 0 && nextC < grid[0].count && nextC >= 0 && 23 !isVisited[nextR][nextC] && grid[nextR][nextC] == 0 else { 24 continue 25 } 26 27 // print((R, C)) 28 if nextR == R-1 && nextC == C-1 { return steps } 29 queue.append((nextR, nextC)) 30 isVisited[nextR][nextC] = true; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 return -1 35 } 36 }
868ms
1 class Solution { 2 func shortestPathBinaryMatrix(_ grid: [[Int]]) -> Int { 3 guard !grid.isEmpty, !grid[0].isEmpty else { return -1 } 4 guard grid[0][0] == 0, grid[grid.count - 1][grid.count - 1] == 0 else { return -1 } 5 var grid = grid 6 7 let visiting = Set<[Int]>([[0, 0]]) 8 return bfs(&grid, visiting: visiting, level: 1) 9 } 10 11 private func bfs(_ grid: inout [[Int]], visiting: Set<[Int]>, level: Int) -> Int { 12 guard grid[grid.count - 1][grid.count - 1] == 0 else { return level } 13 14 let dirs: [[Int]] = [ 15 [-1, -1], 16 [-1, 0], 17 [-1, 1], 18 [ 0, 1], 19 [ 0, -1], 20 [ 1, -1], 21 [ 1, 0], 22 [ 1, 1] 23 ] 24 var nextVisiting = Set<[Int]>() 25 for p in visiting { 26 dirs 27 .map { [p[0] + $0[0], p[1] + $0[1]] } 28 .forEach { np in 29 if np[0] >= 0, 30 np[1] >= 0, 31 np[0] < grid.count, 32 np[1] < grid.count, 33 grid[np[0]][np[1]] == 0 { 34 nextVisiting.insert(np) 35 grid[np[0]][np[1]] = 1 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 guard !nextVisiting.isEmpty else { return -1 } 40 return bfs(&grid, visiting: nextVisiting, level: level + 1) 41 } 42 }