★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(let_us_code)
➤博主域名:https://www.zengqiang.org
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/12185599.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
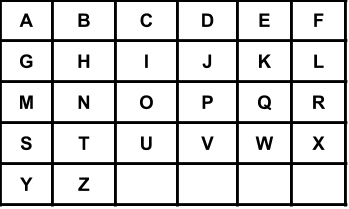
You have a keyboard layout as shown above in the XY plane, where each English uppercase letter is located at some coordinate, for example, the letter A is located at coordinate (0,0), the letter B is located at coordinate (0,1), the letter P is located at coordinate (2,3) and the letter Z is located at coordinate (4,1).
Given the string word, return the minimum total distance to type such string using only two fingers. The distance between coordinates (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|.
Note that the initial positions of your two fingers are considered free so don't count towards your total distance, also your two fingers do not have to start at the first letter or the first two letters.
Example 1:
Input: word = "CAKE"
Output: 3
Explanation:
Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "CAKE" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'C' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'C' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'K' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'E' -> cost = Distance from letter 'K' to letter 'E' = 1
Total distance = 3
Example 2:
Input: word = "HAPPY"
Output: 6
Explanation:
Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "HAPPY" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'H' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'H' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = Distance from letter 'P' to letter 'P' = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'Y' -> cost = Distance from letter 'A' to letter 'Y' = 4
Total distance = 6
Example 3:
Input: word = "NEW"
Output: 3
Example 4:
Input: word = "YEAR"
Output: 7
Constraints:
2 <= word.length <= 300
Each word[i] is an English uppercase letter.

二指输入法定制键盘在 XY 平面上的布局如上图所示,其中每个大写英文字母都位于某个坐标处,例如字母 A 位于坐标 (0,0),字母 B 位于坐标 (0,1),字母 P 位于坐标 (2,3) 且字母 Z 位于坐标 (4,1)。
给你一个待输入字符串 word,请你计算并返回在仅使用两根手指的情况下,键入该字符串需要的最小移动总距离。坐标 (x1,y1) 和 (x2,y2) 之间的距离是 |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|。
注意,两根手指的起始位置是零代价的,不计入移动总距离。你的两根手指的起始位置也不必从首字母或者前两个字母开始。
示例 1:
输入:word = "CAKE"
输出:3
解释:
使用两根手指输入 "CAKE" 的最佳方案之一是:
手指 1 在字母 'C' 上 -> 移动距离 = 0
手指 1 在字母 'A' 上 -> 移动距离 = 从字母 'C' 到字母 'A' 的距离 = 2
手指 2 在字母 'K' 上 -> 移动距离 = 0
手指 2 在字母 'E' 上 -> 移动距离 = 从字母 'K' 到字母 'E' 的距离 = 1
总距离 = 3
示例 2:
输入:word = "HAPPY"
输出:6
解释:
使用两根手指输入 "HAPPY" 的最佳方案之一是:
手指 1 在字母 'H' 上 -> 移动距离 = 0
手指 1 在字母 'A' 上 -> 移动距离 = 从字母 'H' 到字母 'A' 的距离 = 2
手指 2 在字母 'P' 上 -> 移动距离 = 0
手指 2 在字母 'P' 上 -> 移动距离 = 从字母 'P' 到字母 'P' 的距离 = 0
手指 1 在字母 'Y' 上 -> 移动距离 = 从字母 'A' 到字母 'Y' 的距离 = 4
总距离 = 6
示例 3:
输入:word = "NEW"
输出:3
示例 4:
输入:word = "YEAR"
输出:7
提示:
2 <= word.length <= 300
每个 word[i] 都是一个大写英文字母。
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumDistance(_ word: String) -> Int { 3 let word = Array(word) 4 var dp:[Int] = [Int](repeating: 0, count: 26) 5 var res:Int = 0 6 var save:Int = 0 7 let n:Int = word.count 8 for i in 0..<(n - 1) 9 { 10 //A:65 11 let b:Int = Int(word[i].asciiValue! - 65) 12 let c:Int = Int(word[i + 1].asciiValue! - 65) 13 for a in 0..<26 14 { 15 dp[b] = max(dp[b], dp[a] + d(b, c) - d(a, c)) 16 } 17 save = max(save, dp[b]) 18 res += d(b, c) 19 } 20 return res - save 21 } 22 23 func d(_ a:Int,_ b:Int) -> Int 24 { 25 return abs(a / 6 - b / 6) + abs(a % 6 - b % 6) 26 } 27 }
132ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumDistance(_ word: String) -> Int { 3 4 let array = Array(word).compactMap{ $0.asciiValue }.map{ Int($0 - 65) } 5 6 var record = [[[Int]]](repeating:[[Int]](repeating:[Int](repeating:0, count:27), count:27), count:word.count) 7 8 return helper(0,array,26,26,&record) 9 } 10 11 func helper(_ index:Int,_ array:[Int],_ left:Int,_ right:Int,_ record:inout [[[Int]]]) -> Int { 12 if index == array.count { 13 return 0 14 } 15 16 if record[index][left][right] != 0 { 17 return record[index][left][right] 18 } 19 20 let next = array[index] 21 22 record[index][left][right] = min( 23 helper(index+1,array,next,right,&record) + distance(left,next), 24 helper(index+1,array,left,next,&record) + distance(right,next) 25 ) 26 27 return record[index][left][right] 28 } 29 30 func distance(_ a:Int, _ b:Int) -> Int { 31 if a == 26 { 32 return 0 33 } 34 35 return abs(a/6 - b/6) + abs(a%6 - b%6) 36 } 37 }
380ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumDistance(_ word: String) -> Int { 3 var dp = [[[Int]]](repeating: 4 [[Int]](repeating: 5 [Int](repeating: -1, count: 27), 6 count: 27), 7 count: word.count) 8 let ans = minimumDistance(word, 26, 26, word.count-1, &dp) 9 return ans 10 } 11 func minimumDistance(_ word: String, 12 _ lf: Int, 13 _ rf: Int, 14 _ pos: Int, 15 _ dp: inout [[[Int]]]) -> Int { 16 guard pos > -1 else { 17 return 0 18 } 19 guard dp[pos][lf][rf] == -1 else { 20 return dp[pos][lf][rf] 21 } 22 let ch = word[word.index(word.startIndex, offsetBy: pos)] 23 let code = asc(ch)-asc("A") 24 let left = minimumDistance(word, code, rf, pos-1, &dp) + getDist(code, lf) 25 let right = minimumDistance(word, lf, code, pos-1, &dp) + getDist(code, rf) 26 let ans = min(left,right) 27 dp[pos][lf][rf] = ans 28 return ans 29 } 30 31 func getDist(_ f: Int, _ s: Int) -> Int { 32 guard s != 26 else { return 0 } 33 return abs(f/6 - s/6) + abs(f%6 - s%6) 34 } 35 func asc(_ ch: Character) -> Int { 36 return Int(ch.unicodeScalars.first!.value) 37 } 38 }
480ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumDistance(_ word: String) -> Int { 3 let word:[Character] = Array(word) 4 var dict = [String:Int]() // key: index-last1-last2 5 return findRec(word, 0, Character("a"), Character("a"), &dict) 6 } 7 8 func findRec(_ word:[Character], _ index:Int, _ last1:Character, _ last2:Character, _ dict:inout [String:Int]) -> Int { 9 if word.count == index { 10 return 0 11 } 12 if let v = dict["(index)-(last1)-(last2)"] { 13 return v 14 } 15 let dif1 = getRealDif(word[index], last1) 16 let dif2 = getRealDif(word[index], last2) 17 var res1 = Int.max 18 var res2 = Int.max 19 if last1 == Character("a") { 20 res1 = findRec(word, index+1, word[index], last2, &dict) 21 } else { 22 res1 = findRec(word, index+1, word[index], last2, &dict) + dif1 23 } 24 if last2 == Character("a") { 25 res2 = findRec(word, index+1, last1, word[index], &dict) 26 } else { 27 res2 = findRec(word, index+1, last1, word[index], &dict) + dif2 28 } 29 dict["(index)-(last1)-(last2)"] = Swift.min(res1, res2) 30 return Swift.min(res1, res2) 31 } 32 33 func getRealDif(_ a:Character, _ b: Character) -> Int { 34 let rc1 = getrc(getValue(a)) 35 let rc2 = getrc(getValue(b)) 36 return getDif(rc1, rc2) 37 } 38 39 func getDif(_ a:(Int,Int), _ b:(Int, Int)) -> Int { 40 return Swift.abs(a.0-b.0) + Swift.abs(a.1-b.1) 41 42 } 43 func getrc(_ a:Int) -> (Int, Int) { 44 let r = a/6 45 let c = a%6 46 return (r,c) 47 } 48 func getValue (_ char:Character) -> Int { 49 return Int(char.unicodeScalars.first!.value - Character("A").unicodeScalars.first!.value) 50 } 51 }