/**
* Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations.
* For example,
* [1,2,3]have the following permutations:
* [1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2], and[3,2,1].
*
* 给定一组数字,返回所有可能的排列。
* 例如,
* [1,2,3]有以下排列:
* [1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[2,1,3]、[2,3,1]、[3,1,2]和[3,2,1]。
*
*/
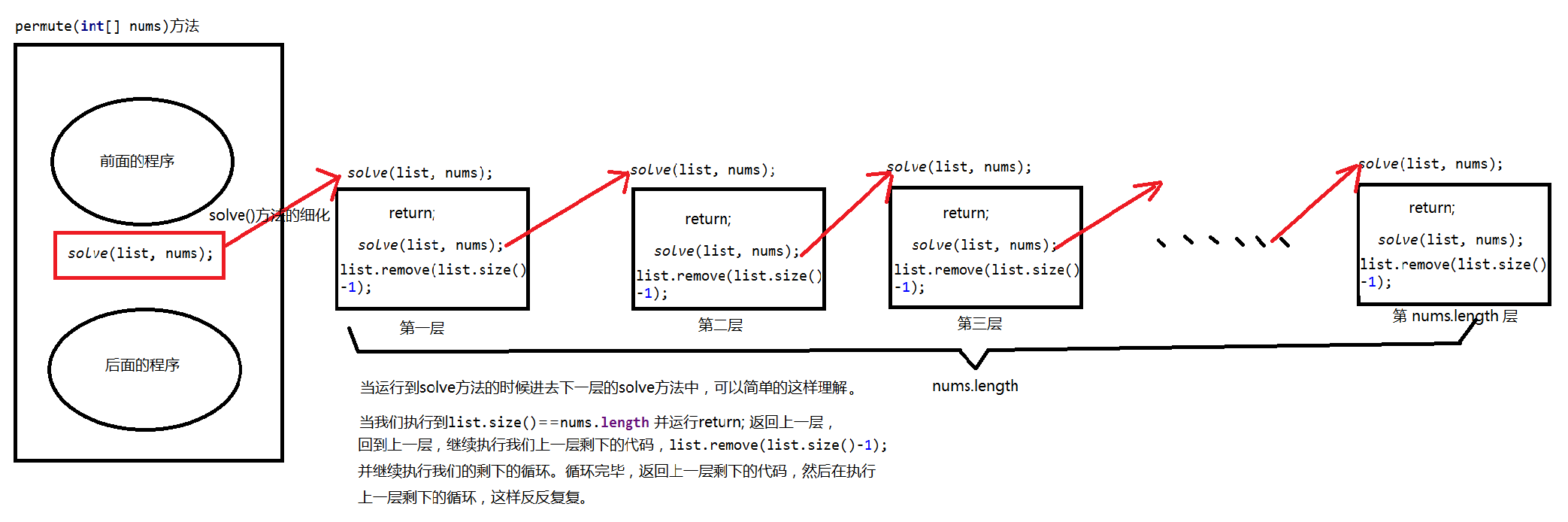
经过自己dubug一步一步的看下来,目前知道了一些步骤,并将它整理了一下。这是我自己对下方代码的理解,一步套一步,又根据nums.length的长度和list.size()的长度来进行判断是否返回上一层。返回上一层又需执行上一层剩下的代码和剩下的循环。
/**
* Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations.
* For example,
* [1,2,3]have the following permutations:
* [1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2], and[3,2,1].
*
* 给定一组数字,返回所有可能的排列。
* 例如,
* [1,2,3]有以下排列:
* [1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[2,1,3]、[2,3,1]、[3,1,2]和[3,2,1]。
*
* 这道题意思理解起来比较简单但是实现的我不是很会。
*/
public class Main39 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,2,3,4 };
System.out.println(Main39.permute(nums));
}
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res;
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 1)
return res;
//对数组元素进行从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
solve(list, nums);
return res;
}
private static void solve(ArrayList<Integer> list, int[] nums) {
if (list.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!list.contains(nums[i])) {
list.add(nums[i]);
solve(list, nums);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
