目录(Content):
一.内存
- 计算机的作用:对数据进行存储和运算。首先我们需要知道我们目前使用的计算机都是二进制的计算机,就以为着计算机只可以存储和运算二进制的数据。例如下载好的一部电影,该电影可以存储到计算机中,计算机中存储的是基于二进制的电影数据,然后我们可以通过相关的视频播放软件结合相关的硬件对电影的二进制数据进行相关的运算操作,所产生的结果就是我们可以看到电影的画面和听到音频的声音。
- 问题:阐述计算机如何计算1+2的结果?
- 阐述:简单理解为,首先可以将1和2输入到计算机中,然后计算机会将1和2转换成二进制的数据进行数据存储,然后通过加法器进行两个二进制数值的计算并返回结果。
- 分析:上述的阐述中提到,计算机首先需要存储1和2这两个数值,那么计算机如何进行数据的存储呢?那么毫无疑问,计算机可以将数据直接存储到内存中。
- 变量:我们在编程世界中,可以将某个数值直接赋值给一个变量,但是最终数值会被存储到计算机的内存中,因此我们可以理解为,变量表示的就是计算机中进行数据存储的某一块内存。
- 如何形象化的理解计算机的内存?
- 举例:将计算机的内存空间映射到我们现实生活中的话,内存就好比是我们在现实生活中三维立体的空间。生活在北京的北漂们,几乎都居住的是一个独立的公寓或者合租在一个几居室的某一个房间中,那么北漂甲就好比是数据,而他所居住的房间则就是存储数据的一块内存空间。
- 分析:从上述案例中,我们可以得知北漂甲居住的房间会有两个基本的属性,其一就是房间空间的大小,其二就是房间的一个位置标识(门牌号)。那么计算机中存储数据的内存空间也会有这两个最基本的属性:内存空间大小和内存空间的地址。内存空间的大小可以表示该空间可以存储数据值的大小范围,内存空间的地址(用十六进制数值表示)可以用来通过寻址定位、查找到该内存空间中所存储的数据值。
- 如何理解 a = 10 这条赋值语句对应的内存图呢?
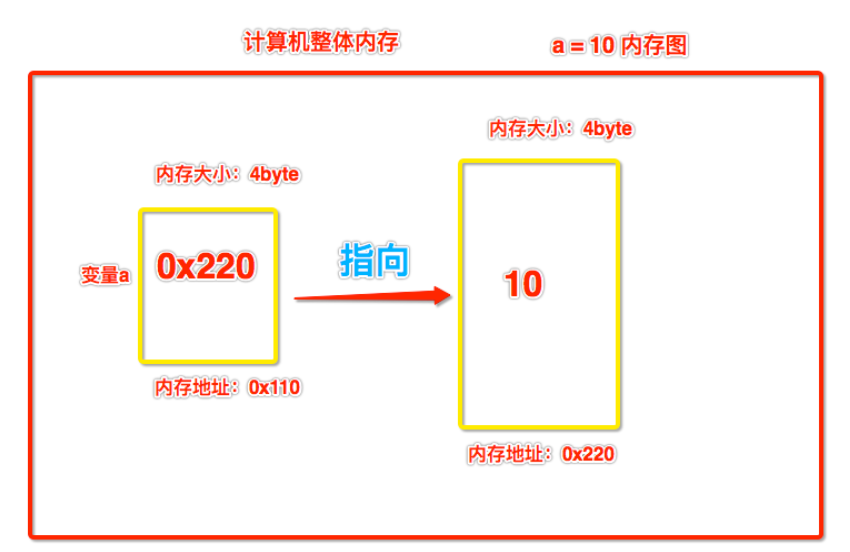
指向:如果一个变量存储了某一块内存空间的地址,则表示该变量指向该块内存
引用(变量):如果一个变量存储了某一刻内存空间的地址,则该变量可以称为该内存的一个引用
- 引用:当一个变量中存储的是某一块内存空间的地址,则该变量即可成为那块内存空间的引用。a=10,a就是10所在内存空间的一个引用。
- 指向:当一个变量中存储了一块内存空间的地址,则称该变量(引用)指向了那块内存。
- 不同类型数据占用内存空间的大小:整形(4字节),浮点型(8字节),字符型(1字节)
二.顺序表:集合中存储的元素是有顺序的。顺序表的结构可以分为两种形式:单数据类型和多数据类型。
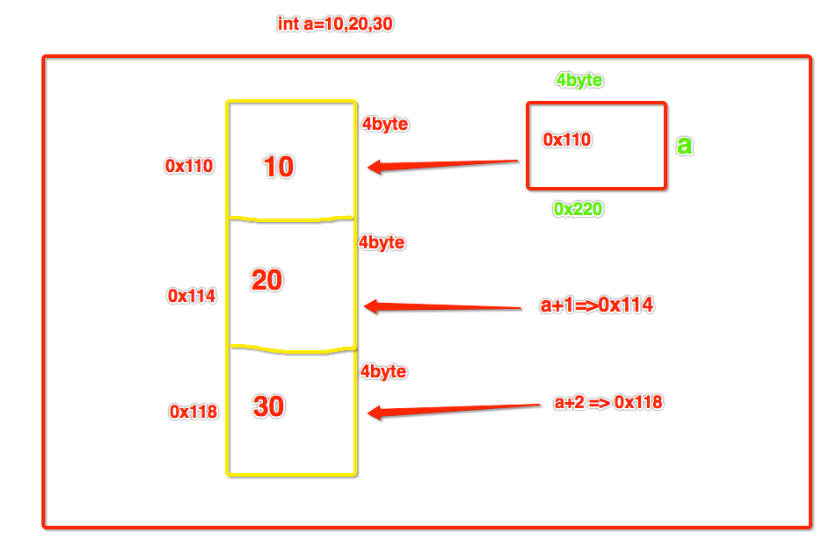
- 单数据类型:在内存中如何存储 int a = 10,20,30,如何取得每一个数据值呢?
- 多数据类型:在内存中如何存储 li = 10,'a',96.5,如何获取每一个数据值呢?
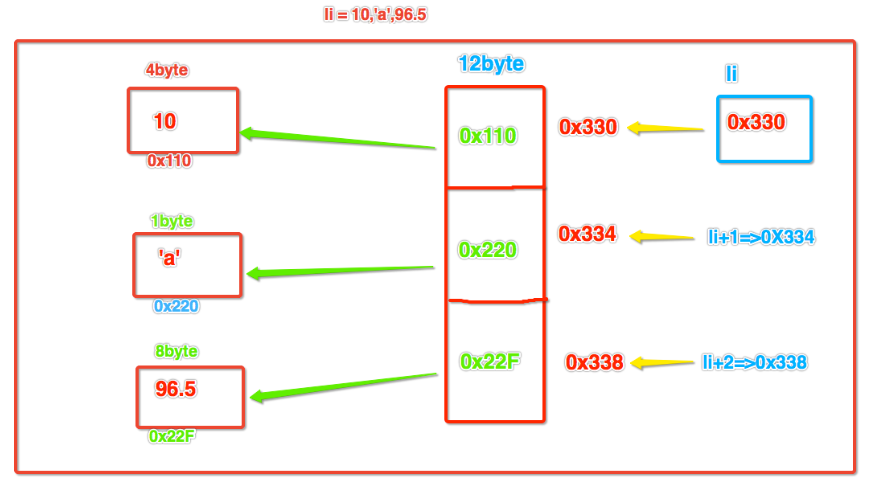
- 顺序表的弊端:顺序表的结构需要预先知道数据大小来申请连续的存储空间,而在进行扩充时又需要进行数据的搬迁。
- Python中的 list 和 tuple 两种类型采用了顺序表的实现技术。
数组是单类型顺序表numpy(数组只能存储单类型的数据结构)


单数据类型顺序表的内存图(内存连续开启)
多数据类型顺序表的内存图(内存连续开辟)
顺序表的弊端:顺序表的结构需要预先知道数据大小来申请连续的存储空间,而在进行扩充时又需要进行数据的搬迁
列表为什么索引从0开始?如果不是0就会乱了,就是通过下面的计算公式进行计算的
a+0=0x110==>0x110+(0*4)
a+1=0x114==>0x110+(1*4)
a+2=0x118==>0x110+(2*4)
三.链表
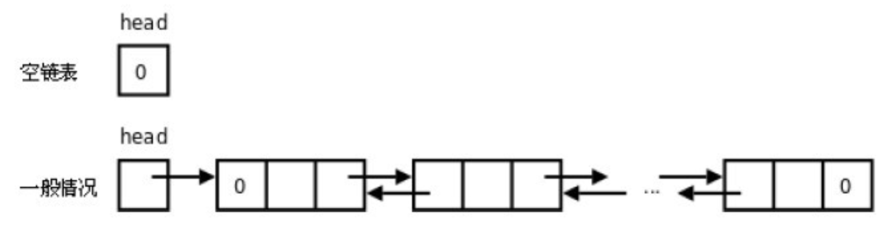
定义:相对于顺序表,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。
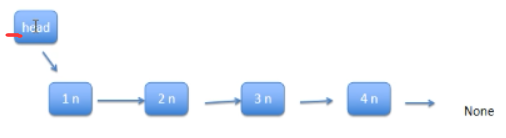
- 链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是不像顺序表一样连续存储数据,而是每一个结点(数据存储单元)里存放下一个结点的信息(即地址

- 1、单向链表
单向链表也叫单链表,是表中最简单的一种形式,它的每个节点包含两个域,一个信息域(元素域)和一个链接域。这个链接指向链表中的下一个节点,而最后一个节点的链接域则指向一个空值。
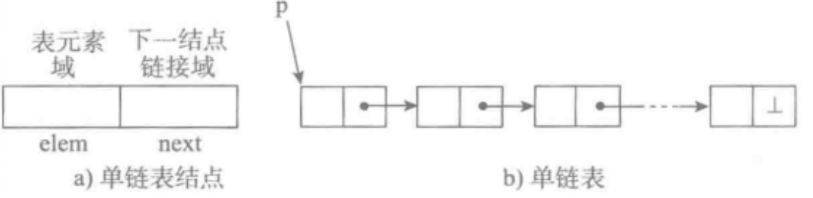
- 表中元素elem用来存放具体的数据。
- 链接域next用来存放下一个节点的位置。
- 变量p指向链表的头节点(首节点)的位置,从p出发能找到表中的任意节点。
- 单向链表的抽象数据类型定义:
is_empty():链表是否为空
length():链表长度
travel():遍历整个链表
add(item):链表头部添加元素
append(item):链表尾部添加元素
insert(pos, item):指定位置添加元素
remove(item):删除节点
search(item):查找节点是否存在
兵马未动粮草先行,先了解下魔术方法__str__
代码实现:
最重要的是,第一个节点的地址
class Node(): def __init__(self,item): self.item = item self.next = None #存储的是链表中下一个节点的地址 def __str__(self): return str(self.item) class Link(): def __init__(self): #永远指向链表中第一个节点地址或者None(空) self._head = None def isEmpty(self): return self._head is None def add(self,item): #1. node = Node(item) node.next = self._head self._head = node
def length(self): count = 0 if self.isEmpty(): return count else: cur = self._head while cur is not None: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): #2遍历函数
# cur存储的就是第一个节点的地址 cur = self._head while cur is not None: print(cur) cur = cur.next
def append(self,item): node = Node(item) cur = self._head if self.isEmpty(): self._head = node else: while cur is not None: #因为循环遍历结束后cur会指向空并非最后一个节点 pre_cur = cur cur = cur.next pre_cur.next = node def search(self,item): ex = False cur = self._head while cur is not None: if cur.item == item: ex = True break cur = cur.next return ex def insertTo(self,item,index): cur = self._head ex = 0 node = Node(item) #插入到第一个节点位置 if index <= 0: self.add(item) #插入到最后一个节点位置 elif index >= self.length(): self.append(item) else: while cur is not None: pre = cur cur = cur.next #此处插入的一定不是第一个节点和最后一个节点位置,因此index要减1 if ex == index-1: node.next = cur pre.next = node break ex += 1 def remove(self,item): pre = None cur = self._head #删除的是第一个节点 if cur.item == item: self._head = cur.next else: while cur is not None: pre = cur cur = cur.next if cur.item == item: pre.next = cur.next cur.next = None cur = cur.next #测试代码 link = Link() link.add('bobo') link.add('jay') link.add('tom') link.add('jerry') # print(link.search('tom')) # link.insertTo('haha',1) link.remove('bobo') link.travel()
2.单向循环链表:单链表的一个变形是单向循环链表,链表中最后一个节点的next域不再为None,而是指向链表的头结点。
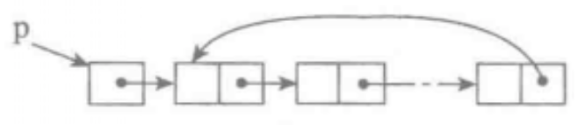
- 基本操作和单链表基本一样,实现代码如下:
# coding=utf-8 # 单向循环链表 class Node: """节点""" def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.next = None def __str__(self): return str(self.item) class SinCycLinkedList: """单向循环链表""" def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self._head is None def length(self): """链表长度""" if self.is_empty(): return 0 count = 1 cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: # print("cur", cur.item) count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历""" if self.is_empty(): return cur = self._head print(cur.item) while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next print(cur.item) def add(self, item): """在头部添加一个节点""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node node.next = self._head else: node.next = self._head cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next cur.next = node self._head = node def append(self, item): """在尾部添加一个节点""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node node.next = self._head else: cur = self._head # print(type(cur), cur.item, cur.next) while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next # print(cur.item) cur.next = node node.next = self._head def insert(self, pos, item): """指定位置pos添加节点""" if pos <= 0: self.add(item) elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) else: node = Node(item) cur = self._head cur_pos = 0 while cur.next != self._head: if (pos - 1) == cur_pos: node.next = cur.next cur.next = node break cur_pos += 1 cur = cur.next def remove(self, item): """删除一个节点""" if self.is_empty(): return pre = self._head # 删除首节点 if pre.item == item: cur = pre while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next cur.next = pre.next # 删除首节点(跳过该节点) self._head = pre.next # 重新指定首节点 # 删除其他的节点 else: cur = pre while cur.next != self._head: if cur.next.item == item: cur.next = cur.next.next cur = cur.next def search(self, item): """查找节点是否存在""" if self.is_empty(): return -1 cur_pos = 0 cur = self._head if cur.item == item: return cur_pos while cur.next != self._head: if cur.item == item: return cur_pos cur_pos += 1 cur = cur.next if cur_pos == self.length() - 1: return -1 if __name__ == "__main__": ll = SinCycLinkedList() ll.add(1) # 1 ll.add(2) # 2 1 # ll.travel() ll.append(3) # 2 1 3 ll.insert(2, 4) # 2 1 4 3 ll.insert(4, 5) # 2 1 4 3 5 ll.insert(0, 6) # 6 2 1 4 3 5 print("length:", ll.length()) # 6 ll.travel() # 6 2 1 4 3 5 print("search(3)", ll.search(3)) # 4 print("search(7)", ll.search(7)) # -1 print("search(6)", ll.search(6)) # 0 print("remove(1)") ll.remove(1) print("length:", ll.length()) # 6 2 4 3 5 print("remove(6)") ll.remove(6) ll.travel()
3.双向链表:一种更复杂的链表是 "双向链表" 或 "双面链表"。每个节点有两个链接:一个指向前一个节点,当次节点为第一个节点时,指向空值;而另一个指向下一个节点,当此节点为最后一个节点时,指向空值。
代码实现:
# coding=utf-8 # 双向链表 class Node: """节点""" def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.prev = None self.next = None class DLinkList: """双向链表""" def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self._head is None def length(self): """获取链表长度""" if self.is_empty(): return 0 else: cur = self._head count = 1 while cur.next is not None: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历链表""" print("↓↓" * 10) if self.is_empty(): print("") else: cur = self._head print(cur.item) while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next print(cur.item) print("↑↑" * 10) def add(self, item): """链表头部添加节点""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node else: cur = self._head node.next = cur cur.prev = node self._head = node def append(self, item): """链表尾部添加节点""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node else: cur = self._head # 遍历找到最后一个节点 while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next # 在尾节点添加新的节点 cur.next = node node.prev = cur def insert(self, pos, item): """指定位置添加""" # 头部添加 if pos <= 0: self.add(item) # 尾部添加 elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) # 其他位置添加 else: node = Node(item) cur = self._head cur_pos = 0 while cur.next is not None: if cur_pos == (pos - 1): # 与下一个节点互相指向 node.next = cur.next cur.next.prev = node # 与上一个节点互相指向 cur.next = node node.prev = cur cur_pos += 1 cur = cur.next def remove(self, item): """删除节点""" if self.is_empty(): return else: cur = self._head # 删除首节点 if cur.item == item: self._head = cur.next cur.next.prev = None # 删除其他节点 else: while cur.next is not None: if cur.item == item: # 删除之前:1 ←→ [2] ←→ 3 # 删除之后:1 ←→ 3 cur.prev.next = cur.next cur.next.prev = cur.prev cur = cur.next # 删除尾节点 if cur.item == item: cur.prev.next = None def search(self, item): """查找节点是否存在""" if self.is_empty(): return -1 else: cur = self._head cur_pos = 0 while cur.next is not None: if cur.item == item: return cur_pos cur_pos += 1 cur = cur.next if cur_pos == (self.length() - 1): return -1 if __name__ == "__main__": ll = DLinkList() ll.add(1) # 1 ll.add(2) # 2 1 ll.append(3) # 2 1 3 ll.insert(2, 4) # 2 1 4 3 ll.insert(4, 5) # 2 1 4 3 5 ll.insert(0, 6) # 6 2 1 4 3 5 print("length:", ll.length()) # 6 ll.travel() # 6 2 1 4 3 5 print("search(3)", ll.search(3)) print("search(4)", ll.search(4)) print("search(10)", ll.search(10)) ll.remove(1) print("length:", ll.length()) ll.travel() print("删除首节点 remove(6):") ll.remove(6) ll.travel() print("删除尾节点 remove(5):") ll.remove(5) ll.travel()