1. FileInputStream
FileInputStream是一个文件输入节点流,它是一个字节流,它的作用是将磁盘文件的内容读取到内存中。
FileInputStream的父类是InputStream。
该类的源码感觉不用细看,因为它是节点流,已经是相对底层的了,读源码没法读出来它是怎么实现的。
下面是该类的两种简单用法,分别是使用read()和read(byte[] buf)方法来读取流数据。
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class FileInputStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("一个一个字节地读取的效果:"); test1(); System.out.println(" 通过字节数组读取的效果:"); test2(); } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** * 使用read()方法,一个字节一个字节地读取 */ private static void test1() { FileInputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("./src/res/1.txt"); int value = 0; while(-1 != (value = fis.read())) { System.out.print((char)value);//转换为字符并打印出来 } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fis) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** * 使用read(byte b[])方法,一次最多读取b.length个字节到b字节数组中 */ private static void test2() { FileInputStream fis= null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("./src/res/1.txt"); int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; while(-1 != (len = fis.read(buf))) { System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len)); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fis) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
代码运行效果:
一个一个字节地读取的效果: hello java hello hello ???ú 通过字节数组读取的效果: hello java hello hello 中国
由上面的运行效果可以看到,当读取的文件中存在中文时,若使用read()方法一个字节一个字节地读取,并且每取到一个字节就打印出来,这个时候就会出现乱码,这是因为中文字符一般都不止占用一个字节(GBK编码时占用2个字节,UTF-8编码时占用3个字节),当取到一个字节时,有可能该字节只是一个中文字符的一部分,将中文截断了,这时打印出来肯定就是乱码的了。而第2种方法先将数据读取到字节数组,再用String的String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length)构造方法还原成字符串,则可以一定程度上避免了中文被截断的隐患,所以该方法可以正确的读取到文件内容,并且咩有出现乱码。
在上面的示例中,文件1.txt使用的是GBK编码,而使用方法2中的String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length)方法使用的也是平台的默认字符集GBK来进行解码的,因此可以正确地读取出文件内容,不会有乱码。倘若将1.txt的编码修改为UTF-8编码,此时还用方法2去读取,则会出现如下所示的乱码情况:
通过字节数组读取的效果:
hello java hello hello 涓�浗
这种情况也很好理解,源文件1.txt是使用GBK编码的,我们使用UTF-8去解码,编码和解码使用的字符集不一致,得到的结果自然是乱码了。这时如果还想将源文件中的内容正确打印到控制台,可以将方法2修改下面所示的方法3:
private static void test3() { FileInputStream fis= null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("./src/res/1.txt"); int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; while(-1 != (len = fis.read(buf))) { System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len, "utf-8")); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fis) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
上面代码中,我们通过String的String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName)构造方法,以显式指定字符集的方式来解码字节数组。如此,同样可以正确读出文件中的内容。综上,可知还原字符串的时候,必须保证编码的统一!
2. FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream是文件输出节点流,同样它也是个字节流。根据API文档可知,FileOutputStream文件输出流是用于将数据写入 File 或 FileDescriptor 的输出流。
首先该类的几个构造方法需要注意一下:
FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException
该方法创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的输出文件流,事实上该方法的底层会调用重载的构造方法来创建指向文件的输出流。由源码可以看出它的实现思路:
public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException { this(name != null ? new File(name) : null, false); }
另外,需要注意的是,使用该方法指向的文件,若文件已存在,则通过该输出流写入时会覆盖文件中的原有内容;若文件不存在,则会先创建文件,再向文件中写入数据。即便如此,该方法还是有可能会抛出FileNotFoundException,这是因为,假如你传入的是一个根本不存在的文件路径(如:suhaha/xxx…/2.txt),那么jvm无法在一个不存在的路径上创建文件,这个时候就会报FileNotFoundException异常。
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException
该方法的功能跟上面的差不多一样,只不过它可以通过第二个参数append,来决定是追加还是覆盖目标文件中的内容,若传入true,则是追加,若传入false,则是覆盖。
示例代码:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class FileOutputStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { FileOutputStream fos = null; try { fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/res/2.txt"); //路径正确时,若文件不存在,则自动创建 // fos = new FileOutputStream("suhaha/xxx"); //如果是随便乱写一个压根不存在的路径,则会报FileNotFoundException异常 String str1 = "hello java"; String str2 = "中国"; //将字符串转换为字节数组 byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes(); byte[] bytes2 = str2.getBytes(); fos.write(bytes1[0]); //将单个字节写入输出流中,写入:h fos.write(bytes2); //将整个字节数组写入,写入:中国 fos.write(bytes1, 6, 4);//将字节数组bytes1中从索引6开始的4个字节写入输出流中,写入:java } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fos) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
代码运行效果:
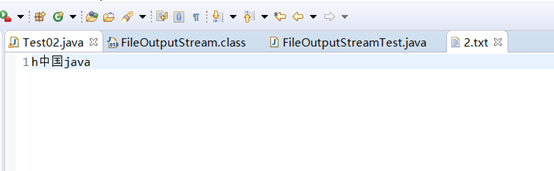
同样,在通过FileOutputStream将数据写入目标文件时,也有可能存在由编码引起的乱码问题。
在上面的示例中,在使用str1.getBytes()方法将字符串转换为字节数组时,由getBytes()方法的源码可以看出,它使用的是平台默认的字符集进行编码,我在windows平台上默认是使用GBK字符集。然后,最后通过输出流写入的文件也是使用GBK进行编码的,因此最后写入的数据没有出现乱码,倘若目标文件2.txt是UTF-8编码,则使用上面的代码进行写入就会出现如下所示的乱码:
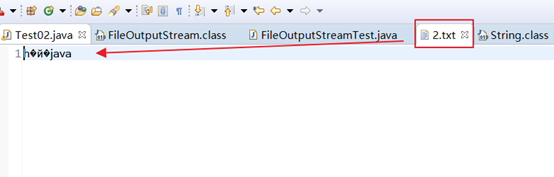
此时可以通过手动将2.txt文件的编码由UTF-8改为GBK,来将数据正确显式出来。
然而,如果我们的需求就是需要将数据写入一个用UTF-8编码的目标文件中,则可用通过使用String类的byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)方法显式指定字符集来将字符串转换为字节数组,这样就可以将数据正确写入一个UTF-8目标文件中。示例代码如下所示:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class FileOutputStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { FileOutputStream fos = null; try { fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/res/2.txt"); //路径正确时,若文件不存在,则自动创建 // fos = new FileOutputStream("suhaha/xxx"); //如果是随便乱写一个压根不存在的路径,则会报FileNotFoundException异常 String str1 = "hello java"; String str2 = "中国"; //将字符串转换为字节数组 byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes(); byte[] bytes2 = str2.getBytes("utf-8"); fos.write(bytes1[0]); //将单个字节写入输出流中,写入:h fos.write(bytes2); //将整个字节数组写入,写入:中国 fos.write(bytes1, 6, 4);//将字节数组bytes1中从索引6开始的4个字节写入输出流中,写入:java } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fos) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
3. FileInputStream和FileOutputStream综合使用示例
下面的代码中定义了两个方法,test1()和test2(),test1()方法从一个GBK编码的源文件中读取数据,复制到一个以UTF-8编码的目标文件中;test2()则正好反之,它从一个UTF-8编码的源文件中读取数据,复制到一个以GBK编码的目标文件中。
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class FileInOutStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // test1(); test2(); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** * 从1.txt文件中读取数据,复制到2.txt文件中 * 其中,1.txt是用GBK编码的,2.txt使用UTF-8编码的 */ private static void test1() { FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("./src/res/1.txt"); fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/res/2.txt"); int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; while(-1 != (len = fis.read(buf))) { //从源文件1.txt读取到字节数组中的数据是GBK编码的 String str = new String(buf, 0, len); //先转为字符串,这里默认使用GBK进行解码 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes("utf-8"); //再显式指定以utf-8字符集进行编码 fos.write(bytes); //将字节数组数据写入到以utf-8编码的目标文件2.txt中 fos.flush(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fos) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(null != fis) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** * 从2.txt文件中读取数据,复制到1.txt文件中 * 其中,1.txt是用GBK编码的,2.txt使用UTF-8编码的 */ private static void test2() { FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("./src/res/2.txt"); fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/res/1.txt"); int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; while(-1 != (len = fis.read(buf))) { //从源文件2.txt读取到字节数组中的数据是utf-8编码的 String str = new String(buf, 0, len, "utf-8"); //先转为字符串,这里显式指定使用utf-8进行解码 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); //再以默认字符集GBK进行编码 fos.write(bytes); //将字节数组数据写入到以GBK编码的目标文件1.txt中 fos.flush(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(null != fos) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(null != fis) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
注:上面演示的方法可能比较low,但是如果只使用目前的这两个文件输入输出流的话,这是我能想到的一个解决办法。
通过转换流InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter也可以实现该功能,可以参考J07-Java IO流总结七 《 InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter 》