原文: https://blog.csdn.net/u012658346/article/details/50917068
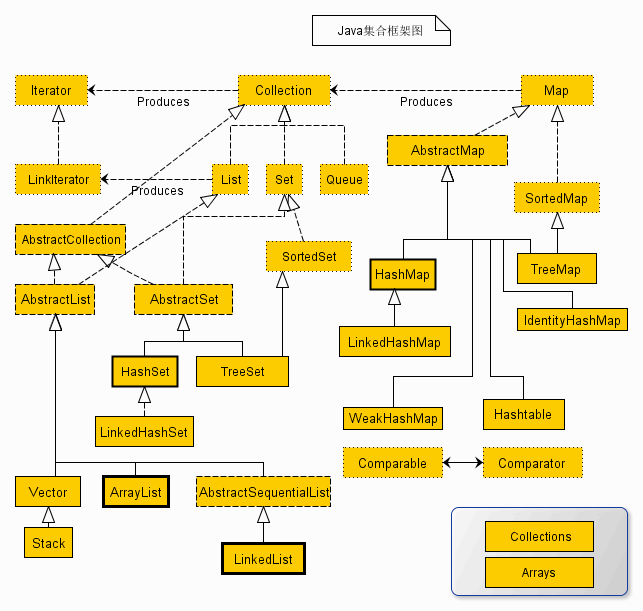
一.java集合类图如下所示:
上述类图中,实线边框的是实现类,比如ArrayList,LinkedList,HashMap等,折线边框的是抽象类,比如AbstractCollection,AbstractList,AbstractMap等,而点线边框的是接口,比如Collection,Iterator,List等。
Java集合都在java.util包中实现。
二.List(基于JDK7)
List是有序的collection,当加入一个元素时,会以特定的顺序加入到集合中来保证元素是有序的。因此元素加入的顺序和取出的顺序可能不同。
List中元素是可以重复加入的,并且能够加入null元素,还可以通过索引来访问元素。
实现了List接口的有Vector、Stack、ArrayList、LinkedList这几个类,List接口为这些类提供了同一的方法。(Vector和Stack已基本很少使用)
List接口的源代码非常简单:
package java.util;
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
void add(int index, E element);
E remove(int index);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
二.ArrayList
1、ArrayList的属性
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
private transient Object[] elementData; //存储元素的数组
private int size; // 数组中已存储的元素个数
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; //数组最大容量
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
ArrayList也就是动态数组,可以看到ArrayList的实现是基于数组的,因此ArrayList也拥有数组的一些特性:
1)通过索引index随机访问的速度非常快,eg:get(index)
2)当元素个数超过数组容量时,需要进行内存的重新分配并复制原有元素,这会非常影响性能,因此最好在使用前就创建足够容量的ArrayList对象
2、构造
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray(); //直接调用toArray()方法
size = elementData.length;
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) //当类型不匹配时,则要重新构造
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
可以看到ArrayList有三种构造方式:
1)传递一个容量参数
2)不传递任何参数,则默认构造一个容量为10的ArrayList
3)以一个集合为参数进行构造,最后会生成一个size为集合大小,元素为集合中的所有元素的ArrayList
3、清除
在Java中,由于可以不用考虑内存释放,很多问题都变得非常简单。
如clear()方法,只需要依次将所有元素置为null即可,对象的释放会有JVM的GC机制自动完成。注意最后还要将size置为0.
public void clear() {
modCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4、增
当要向集合中加入一个元素时,首先都是保证安全性(数组容量和索引大小,容量不足时就会重新分配内存,以原有元素重新构造),然后再加入一个元素。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
当直接向数组中加入一个元素时,直接在数组末尾加入。
当在索引index处加入时,则需要将index处及以后的元素全部向后移动一个,再将index处元素置为待插入的新元素
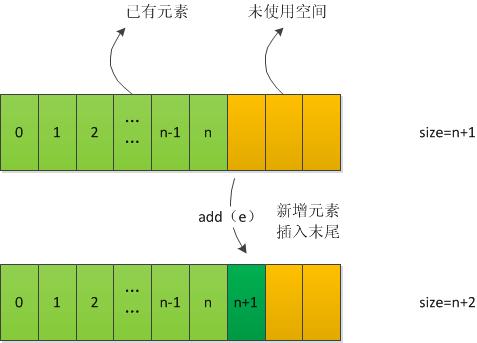
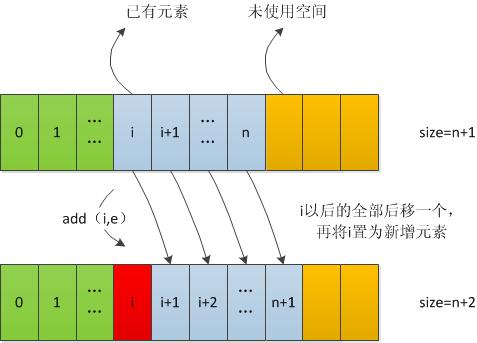
5、删
从集合中删除一个元素的主要步骤是:
1)首先找到待删除元素的位置index
2)然后将index之后的所有元素向前移动一个
3)将size-1
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
6、查&改
set()和get()方法的实现非常简单,首先检查安全性(index位置是否合法),然后再直接用index索引数组元素并返回或修改
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
7、iterator
ArrayList通过一个下标cursor属性来实现迭代器。
cursor可访问的范围为[0,size],当cursor=0时,hasPrevious()返回false;当cursor=size时,hasNext()为false。
这是一个双向索引的迭代器,以next操作为例(prev侧实现类似):
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1; //cursor+1
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; //再将元素返回
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
8、遍历
ArrayList的遍历方式主要有如下几种:
1)通过索引及get()访问(与原始的数组访问方式类似)
Integer value = null;
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)list.get(i);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2)for循环遍历
Integer value = null;
for (Integer integ:list) {
value = integ;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3)通过iterator访问
Integer value = null;
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
三.LinkedList
与ArrayList不同,LinkedList是基于链表的,因此随机插入和删除的操作非常快,不需要像ArrayList那样可能需要大量copy,同时也不担心容量不足带来的效率问题,但是LinkedList随机访问的速度较差。
LinkedList中每个节点都包含prev和next索引,形成双向链表。LinkedList则通过first和last两个属性分别保存双向链表的头节点和尾部节点。
基本结构如下所示(部分连线未画出):
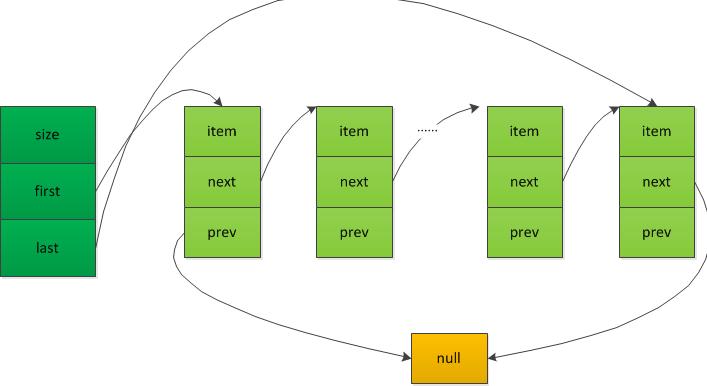
1、基本辅助操作
创建一个节点Node对象
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
向链表中加入、移除一个节点
向链表中加入一个节点对应的主要是对各个相关节点的操作,与C中修改指针的操作非常相似。
主要步骤是:
1)首先找到待插入位置的前后节点
2)然后以前后节点分别作为prev和next创建一个新节点
3)再对前后节点的prev和next属性进行更改
4)更新LinkedList的first、last引用
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
从链表中移除一个节点的各个操作与上面的各个操作基本类似,对应的几个方法分别是:
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { }
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { }
E unlink(Node<E> x) { }- 1
- 2
- 3
LinkedList的很多方法都是基于上述这些操作的,因此在对上述基本操作有了一定的了解之后,就可以开始开始对LinkedList的学习了。
2、构造
LinkedList只提供了两种构造方法:构造一个空的LinkedList或者一个集合来构造
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3、增加、移除一个元素
当向集合中加入一个元素时,可以在链表头部、尾部加入,也可以在index之前加入,当不传递位置信息时,默认在链表尾部加入。
可以发现add()最终的操作都是link相关方法,即以新增元素为参数创建一个节点,再在恰当的位置与链表link在一起,即将元素加入到集合中了。
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e); //默认在链表尾部加入
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
由上面增加一个元素的操作可以知道移除一个元素的操作也与之类似:首先找到待移除元素节点,然后调用unlink()方法解除该节点与链表直接的联系,即从链表中移除了。
4、查、改
get()与set()方法非常简单,与ArrayList基本相同:首先进行index合法性检查,再返回相应的value。
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
5、根据index索引一个元素
首先进行简单的二分,判断index是链表的前半部还是后半部,然后再分别从链表头或链表尾部进行查找,使得效率有了一定程度的提升
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
通过对List、ArrayList、LinkedList的源码分析可以发现,其实他们的内部实现非常简单。
ArrayList、LinkedList的特点也与基本的数组、双向链表类似。
简单的总结如下:
List:有序、元素可重复、可以加入null元素、可通过索引index访问元素
ArrayList:基于动态数组,随机访问效率很高,插入或删除一个元素时效率较低(可能需要扩容、内存重分配、拷贝)
LinkedList:基于双向链表,随机访问效率较低,插入或删除一个元素时效率较高