比较忙,很长世间没空看openstack源码,抽时间看了一下cinder的源码,贴下学习心得。本文简单写一下cinder的三个服务的启动,cinder-api, cinder-scheduler, 以及cinder-volume,三者启动都差不多
1、cinder-api
入口文件为/usr/bin/cinder-api,由此可知,入口为cinder.cmd.api文件中的main函数
1 #!/usr/bin/python2 2 # PBR Generated from u'console_scripts' 3 4 import sys 5 6 from cinder.cmd.api import main 7 8 9 if __name__ == "__main__": 10 sys.exit(main())
main函数如下,主要关注14-16行即可
1 def main(): 2 objects.register_all() 3 gmr_opts.set_defaults(CONF) 4 CONF(sys.argv[1:], project='cinder', 5 version=version.version_string()) 6 config.set_middleware_defaults() 7 logging.setup(CONF, "cinder") 8 python_logging.captureWarnings(True) 9 utils.monkey_patch() 10 11 gmr.TextGuruMeditation.setup_autorun(version, conf=CONF) 12 13 rpc.init(CONF) 14 launcher = service.process_launcher() 15 server = service.WSGIService('osapi_volume') 16 launcher.launch_service(server, workers=server.workers) 17 launcher.wait()
14行创建一个 ProcessLauncher 对象,以便后续对app进行launch
15行创建 WSGIService 对象,名称为 osapi_volume
16行,launch对象调用launch_service方法对server进行处理,通过查看源码,是调用了ProcessLauncher对象的_start_child对服务进行处理
1 def launch_service(self, service, workers=1): 2 """Launch a service with a given number of workers. 3 4 :param service: a service to launch, must be an instance of 5 :class:`oslo_service.service.ServiceBase` 6 :param workers: a number of processes in which a service 7 will be running 8 """ 9 _check_service_base(service) #对象类型校验 10 wrap = ServiceWrapper(service, workers) #对象包装 11 12 # Hide existing objects from the garbage collector, so that most 13 # existing pages will remain in shared memory rather than being 14 # duplicated between subprocesses in the GC mark-and-sweep. (Requires 15 # Python 3.7 or later.) 16 if hasattr(gc, 'freeze'): 17 gc.freeze() 18 19 LOG.info('Starting %d workers', wrap.workers) 20 while self.running and len(wrap.children) < wrap.workers: 21 self._start_child(wrap)
_start_child方法很简单,调用了os.fork()创建了一个子进程,如果创建子进程成功,再次调用_child_process方法
1 def _start_child(self, wrap): 2 if len(wrap.forktimes) > wrap.workers: 3 # Limit ourselves to one process a second (over the period of 4 # number of workers * 1 second). This will allow workers to 5 # start up quickly but ensure we don't fork off children that 6 # die instantly too quickly. 7 if time.time() - wrap.forktimes[0] < wrap.workers: 8 LOG.info('Forking too fast, sleeping') 9 time.sleep(1) 10 11 wrap.forktimes.pop(0) 12 13 wrap.forktimes.append(time.time()) 14 15 pid = os.fork() 16 if pid == 0: 17 self.launcher = self._child_process(wrap.service) 18 while True: 19 self._child_process_handle_signal() 20 status, signo = self._child_wait_for_exit_or_signal( 21 self.launcher) 22 if not _is_sighup_and_daemon(signo): 23 self.launcher.wait() 24 break 25 self.launcher.restart() 26 27 os._exit(status) 28 29 LOG.debug('Started child %d', pid) 30 31 wrap.children.add(pid) 32 self.children[pid] = wrap 33 34 return pid
1 def _child_process(self, service): 2 self._child_process_handle_signal() 3 4 # Reopen the eventlet hub to make sure we don't share an epoll 5 # fd with parent and/or siblings, which would be bad 6 eventlet.hubs.use_hub() 7 8 # Close write to ensure only parent has it open 9 os.close(self.writepipe) 10 # Create greenthread to watch for parent to close pipe 11 eventlet.spawn_n(self._pipe_watcher) 12 13 # Reseed random number generator 14 random.seed() 15 16 launcher = Launcher(self.conf, restart_method=self.restart_method) 17 launcher.launch_service(service) 18 return launcher
_child_process方法中调用了eventlet,获取hub,并且创建一个线程,对进程进行观察,同时创建一个Launcher对象,对服务进行lanch,launch_service
1 def launch_service(self, service, workers=1): 2 """Load and start the given service. 3 4 :param service: The service you would like to start, must be an 5 instance of :class:`oslo_service.service.ServiceBase` 6 :param workers: This param makes this method compatible with 7 ProcessLauncher.launch_service. It must be None, 1 or 8 omitted. 9 :returns: None 10 11 """ 12 if workers is not None and workers != 1: 13 raise ValueError(_("Launcher asked to start multiple workers")) 14 _check_service_base(service) 15 service.backdoor_port = self.backdoor_port 16 self.services.add(service) #关键
Launcher 对象的关键在于这个add方法,它将所有调用其进行launch的服务添加到Service()的service列表中,最终调用了添加的service的start()方法
1 def add(self, service): 2 """Add a service to a list and create a thread to run it. 3 4 :param service: service to run 5 """ 6 self.services.append(service) 7 self.tg.add_thread(self.run_service, service, self.done) 8 9 @staticmethod 10 def run_service(service, done): 11 """Service start wrapper. 12 13 :param service: service to run 14 :param done: event to wait on until a shutdown is triggered 15 :returns: None 16 17 """ 18 try: 19 service.start() 20 except Exception: 21 LOG.exception('Error starting thread.') 22 raise SystemExit(1) 23 else: 24 done.wait()
这个service即最初提到的WSGIService 对象,查看一下其start方法
1 def start(self): 2 """Start serving this service using loaded configuration. 3 4 Also, retrieve updated port number in case '0' was passed in, which 5 indicates a random port should be used. 6 7 :returns: None 8 9 """ 10 if self.manager: 11 self.manager.init_host() 12 self.server.start() 13 self.port = self.server.port
此时self.manager为None,关键执行步骤为self.server.start(),这个server为WSGIService 进行init的时候构造的对象
1 class WSGIService(service.ServiceBase): 2 """Provides ability to launch API from a 'paste' configuration.""" 3 4 def __init__(self, name, loader=None): 5 """Initialize, but do not start the WSGI server. 6 7 :param name: The name of the WSGI server given to the loader. 8 :param loader: Loads the WSGI application using the given name. 9 :returns: None 10 11 """ 12 self.name = name 13 self.manager = self._get_manager() 14 self.loader = loader or wsgi.Loader(CONF) 15 self.app = self.loader.load_app(name) 16 self.host = getattr(CONF, '%s_listen' % name, "0.0.0.0") 17 self.port = getattr(CONF, '%s_listen_port' % name, 0) 18 self.use_ssl = getattr(CONF, '%s_use_ssl' % name, False) 19 self.workers = (getattr(CONF, '%s_workers' % name, None) or 20 processutils.get_worker_count()) 21 if self.workers and self.workers < 1: 22 worker_name = '%s_workers' % name 23 msg = (_("%(worker_name)s value of %(workers)d is invalid, " 24 "must be greater than 0.") % 25 {'worker_name': worker_name, 26 'workers': self.workers}) 27 raise exception.InvalidConfigurationValue(msg) 28 setup_profiler(name, self.host) 29 30 self.server = wsgi.Server(CONF, 31 name, 32 self.app, 33 host=self.host, 34 port=self.port, 35 use_ssl=self.use_ssl) # 这里
1 def start(self): 2 """Start serving a WSGI application. 3 4 :returns: None 5 """ 6 # The server socket object will be closed after server exits, 7 # but the underlying file descriptor will remain open, and will 8 # give bad file descriptor error. So duplicating the socket object, 9 # to keep file descriptor usable. 10 11 self.dup_socket = self.socket.dup() 12 13 if self._use_ssl: 14 self.dup_socket = sslutils.wrap(self.conf, self.dup_socket) 15 16 wsgi_kwargs = { 17 'func': eventlet.wsgi.server, 18 'sock': self.dup_socket, 19 'site': self.app, 20 'protocol': self._protocol, 21 'custom_pool': self._pool, 22 'log': self._logger, 23 'log_format': self.conf.wsgi_log_format, 24 'debug': False, 25 'keepalive': self.conf.wsgi_keep_alive, 26 'socket_timeout': self.client_socket_timeout 27 } 28 29 if self._max_url_len: 30 wsgi_kwargs['url_length_limit'] = self._max_url_len 31 32 self._server = eventlet.spawn(**wsgi_kwargs)
至此,cinder-api启动顺利启动
2、cinder-scheduler
入口文件为/usr/bin/cinder-scheduler,则实际调用文件为cinder/cmd/scheduler.py下的main
1 #!/usr/bin/python2 2 # PBR Generated from u'console_scripts' 3 4 import sys 5 6 from cinder.cmd.scheduler import main 7 8 9 if __name__ == "__main__": 10 sys.exit(main())
1 def main(): 2 objects.register_all() 3 gmr_opts.set_defaults(CONF) 4 CONF(sys.argv[1:], project='cinder', 5 version=version.version_string()) 6 logging.setup(CONF, "cinder") 7 python_logging.captureWarnings(True) 8 utils.monkey_patch() 9 gmr.TextGuruMeditation.setup_autorun(version, conf=CONF) 10 server = service.Service.create(binary='cinder-scheduler') 11 service.serve(server) 12 service.wait()
实际启动服务的只有10,11,12行,通过Service对象的类方法create创建一个名server的service,然后用serve方法(实际调用launch对service进行处理),launch方法通过判断serve传进的worker参数来判断,传入的对象是process还是service,但是不管是service还是process,都是调用了launch_service这个接口,此处,同上述api所述,Launcher 对象的关键在于这个add方法,它将所有调用其进行launch的服务添加到Service()的service列表中,最终调用了添加的Service的start()方法。
1 @classmethod 2 def create(cls, host=None, binary=None, topic=None, manager=None, 3 report_interval=None, periodic_interval=None, 4 periodic_fuzzy_delay=None, service_name=None, 5 coordination=False, cluster=None, **kwargs): 6 if not host: 7 host = CONF.host 8 if not binary: 9 binary = os.path.basename(inspect.stack()[-1][1]) 10 if not topic: 11 topic = binary 12 if not manager: 13 subtopic = topic.rpartition('cinder-')[2] 14 manager = CONF.get('%s_manager' % subtopic, None) 15 if report_interval is None: 16 report_interval = CONF.report_interval 17 if periodic_interval is None: 18 periodic_interval = CONF.periodic_interval 19 if periodic_fuzzy_delay is None: 20 periodic_fuzzy_delay = CONF.periodic_fuzzy_delay 21 service_obj = cls(host, binary, topic, manager, 22 report_interval=report_interval, 23 periodic_interval=periodic_interval, 24 periodic_fuzzy_delay=periodic_fuzzy_delay, 25 service_name=service_name, 26 coordination=coordination, 27 cluster=cluster, **kwargs) 28 29 return service_obj
1 def serve(server, workers=None): 2 global _launcher 3 if _launcher: 4 raise RuntimeError(_('serve() can only be called once')) 5 6 _launcher = service.launch(CONF, server, workers=workers)
1 def launch(conf, service, workers=1, restart_method='reload'): 2 """Launch a service with a given number of workers. 3 4 :param conf: an instance of ConfigOpts 5 :param service: a service to launch, must be an instance of 6 :class:`oslo_service.service.ServiceBase` 7 :param workers: a number of processes in which a service will be running 8 :param restart_method: Passed to the constructed launcher. If 'reload', the 9 launcher will call reload_config_files on SIGHUP. If 'mutate', it will 10 call mutate_config_files on SIGHUP. Other values produce a ValueError. 11 :returns: instance of a launcher that was used to launch the service 12 """ 13 14 if workers is not None and workers <= 0: 15 raise ValueError(_("Number of workers should be positive!")) 16 17 if workers is None or workers == 1: 18 launcher = ServiceLauncher(conf, restart_method=restart_method) 19 else: 20 launcher = ProcessLauncher(conf, restart_method=restart_method) 21 launcher.launch_service(service, workers=workers) 22 23 return launcher
至此,cinder-scheduler启动完成
3、cinder-volume
cinder-volume的入口文件为/usr/bin/cinder-volume,由此可知真正的入口函数为cinder/cmd/volume.py中的main函数
1 #!/usr/bin/python2 2 # PBR Generated from u'console_scripts' 3 4 import sys 5 6 from cinder.cmd.volume import main 7 8 9 if __name__ == "__main__": 10 sys.exit(main())
1 def _launch_services_win32(): 2 if CONF.backend_name and CONF.backend_name not in CONF.enabled_backends: 3 msg = _('The explicitly passed backend name "%(backend_name)s" is not ' 4 'among the enabled backends: %(enabled_backends)s.') 5 raise exception.InvalidInput( 6 reason=msg % dict(backend_name=CONF.backend_name, 7 enabled_backends=CONF.enabled_backends)) 8 9 # We'll avoid spawning a subprocess if a single backend is requested. 10 single_backend_name = (CONF.enabled_backends[0] 11 if len(CONF.enabled_backends) == 1 12 else CONF.backend_name) 13 if single_backend_name: 14 launcher = service.get_launcher() 15 _launch_service(launcher, single_backend_name) 16 elif CONF.enabled_backends: 17 # We're using the 'backend_name' argument, requesting a certain backend 18 # and constructing the service object within the child process. 19 launcher = service.WindowsProcessLauncher() 20 py_script_re = re.compile(r'.*.pyw?$') 21 for backend in filter(None, CONF.enabled_backends): 22 cmd = sys.argv + ['--backend_name=%s' % backend] 23 # Recent setuptools versions will trim '-script.py' and '.exe' 24 # extensions from sys.argv[0]. 25 if py_script_re.match(sys.argv[0]): 26 cmd = [sys.executable] + cmd 27 launcher.add_process(cmd) 28 _notify_service_started() 29 30 _ensure_service_started() 31 32 launcher.wait() 33 34 35 def _launch_services_posix(): 36 launcher = service.get_launcher() 37 38 for backend in filter(None, CONF.enabled_backends): 39 _launch_service(launcher, backend) 40 41 _ensure_service_started() 42 43 launcher.wait() 44 45 46 def main(): 47 objects.register_all() 48 gmr_opts.set_defaults(CONF) 49 CONF(sys.argv[1:], project='cinder', 50 version=version.version_string()) 51 logging.setup(CONF, "cinder") 52 python_logging.captureWarnings(True) 53 priv_context.init(root_helper=shlex.split(utils.get_root_helper())) 54 utils.monkey_patch() 55 gmr.TextGuruMeditation.setup_autorun(version, conf=CONF) 56 global LOG 57 LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__) 58 59 if not CONF.enabled_backends: 60 LOG.error('Configuration for cinder-volume does not specify ' 61 '"enabled_backends". Using DEFAULT section to configure ' 62 'drivers is not supported since Ocata.') 63 sys.exit(1) 64 65 if os.name == 'nt': 66 # We cannot use oslo.service to spawn multiple services on Windows. 67 # It relies on forking, which is not available on Windows. 68 # Furthermore, service objects are unmarshallable objects that are 69 # passed to subprocesses. 70 _launch_services_win32() 71 else: 72 _launch_services_posix()
根据平台是windows还是linux,进行不同的调用,因为是在linux上部署,所有调用的函数为_launch_services_posix(),其中调用了_launch_service(launcher, backend)创建Service对象
1 @classmethod 2 def create(cls, host=None, binary=None, topic=None, manager=None, 3 report_interval=None, periodic_interval=None, 4 periodic_fuzzy_delay=None, service_name=None, 5 coordination=False, cluster=None, **kwargs): 6 """Instantiates class and passes back application object. 7 8 :param host: defaults to CONF.host 9 :param binary: defaults to basename of executable 10 :param topic: defaults to bin_name - 'cinder-' part 11 :param manager: defaults to CONF.<topic>_manager 12 :param report_interval: defaults to CONF.report_interval 13 :param periodic_interval: defaults to CONF.periodic_interval 14 :param periodic_fuzzy_delay: defaults to CONF.periodic_fuzzy_delay 15 :param cluster: Defaults to None, as only some services will have it 16 17 """ 18 if not host: 19 host = CONF.host 20 if not binary: 21 binary = os.path.basename(inspect.stack()[-1][1]) 22 if not topic: 23 topic = binary 24 if not manager: 25 subtopic = topic.rpartition('cinder-')[2] 26 manager = CONF.get('%s_manager' % subtopic, None) 27 if report_interval is None: 28 report_interval = CONF.report_interval 29 if periodic_interval is None: 30 periodic_interval = CONF.periodic_interval 31 if periodic_fuzzy_delay is None: 32 periodic_fuzzy_delay = CONF.periodic_fuzzy_delay 33 service_obj = cls(host, binary, topic, manager, 34 report_interval=report_interval, 35 periodic_interval=periodic_interval, 36 periodic_fuzzy_delay=periodic_fuzzy_delay, 37 service_name=service_name, 38 coordination=coordination, 39 cluster=cluster, **kwargs) 40 41 return service_obj
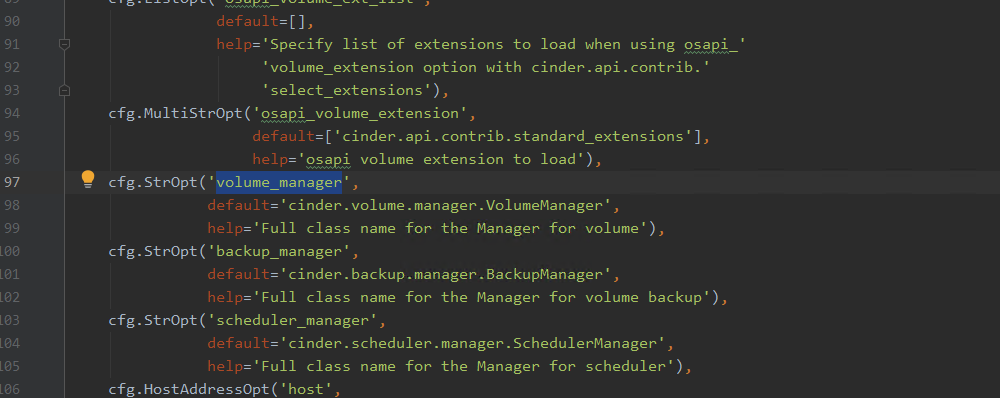
此处manager被初始化为volume_manager,并在service初始化时,相关类被导入
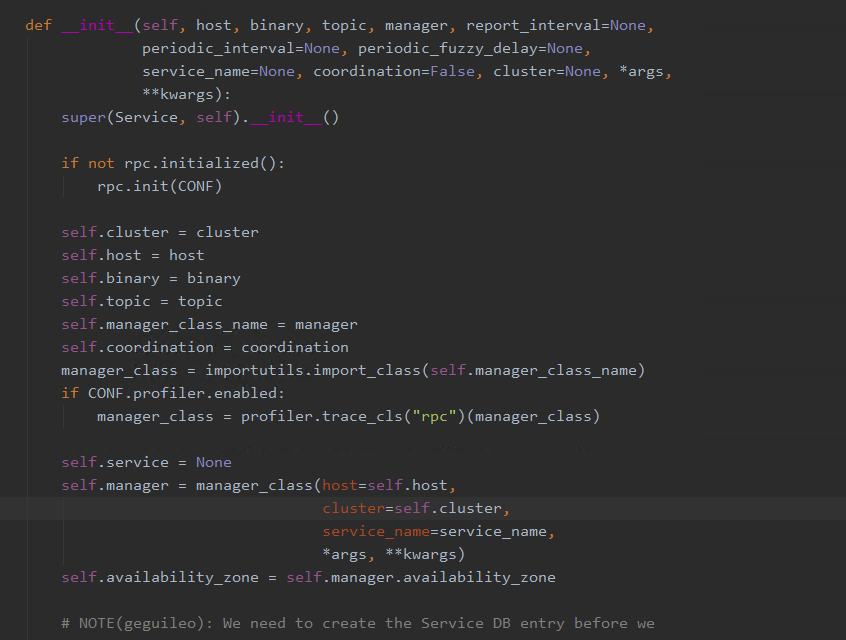
在Service的start方法中有self.manager.init_host
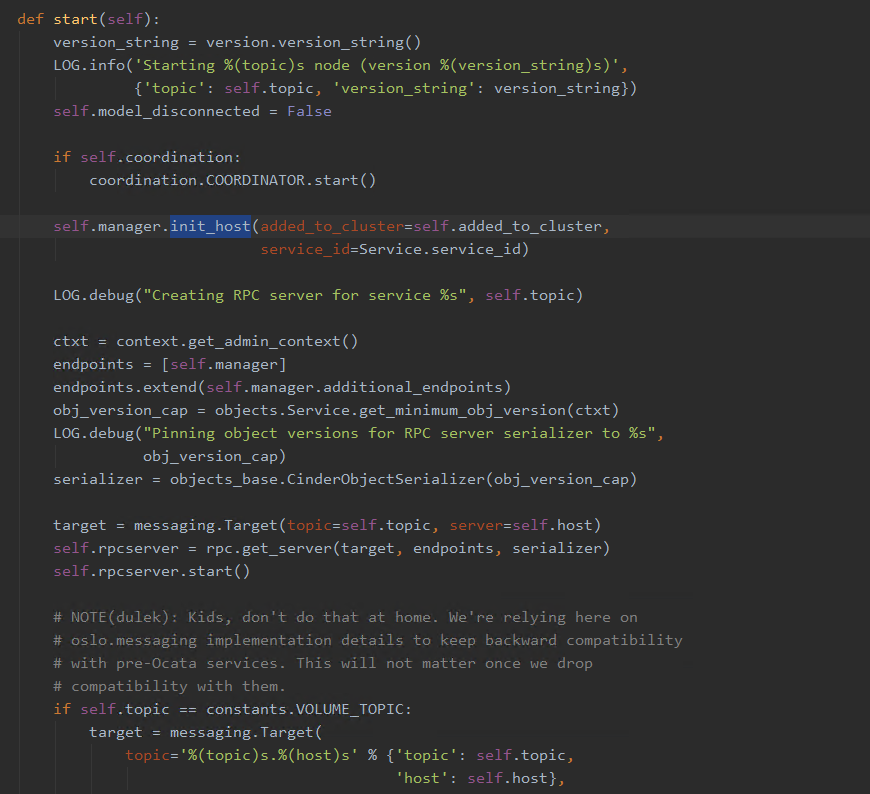
对cinder-volume采用的driver进行初始化
1 def init_host(self, added_to_cluster=None, **kwargs): 2 """Perform any required initialization.""" 3 ctxt = context.get_admin_context() 4 if not self.driver.supported: 5 utils.log_unsupported_driver_warning(self.driver) 6 7 if not self.configuration.enable_unsupported_driver: 8 LOG.error("Unsupported drivers are disabled." 9 " You can re-enable by adding " 10 "enable_unsupported_driver=True to the " 11 "driver section in cinder.conf", 12 resource={'type': 'driver', 13 'id': self.__class__.__name__}) 14 return 15 16 # If we have just added this host to a cluster we have to include all 17 # our resources in that cluster. 18 if added_to_cluster: 19 self._include_resources_in_cluster(ctxt) 20 21 LOG.info("Starting volume driver %(driver_name)s (%(version)s)", 22 {'driver_name': self.driver.__class__.__name__, 23 'version': self.driver.get_version()}) 24 try: 25 self.driver.do_setup(ctxt) 26 self.driver.check_for_setup_error() 27 except Exception: 28 LOG.exception("Failed to initialize driver.", 29 resource={'type': 'driver', 30 'id': self.__class__.__name__}) 31 # we don't want to continue since we failed 32 # to initialize the driver correctly. 33 return 34 35 # Initialize backend capabilities list 36 self.driver.init_capabilities() 37 38 volumes = self._get_my_volumes(ctxt) 39 snapshots = self._get_my_snapshots(ctxt) 40 self._sync_provider_info(ctxt, volumes, snapshots) 41 # FIXME volume count for exporting is wrong 42 43 self.stats['pools'] = {} 44 self.stats.update({'allocated_capacity_gb': 0}) 45 46 try: 47 for volume in volumes: 48 # available volume should also be counted into allocated 49 if volume['status'] in ['in-use', 'available']: 50 # calculate allocated capacity for driver 51 self._count_allocated_capacity(ctxt, volume) 52 53 try: 54 if volume['status'] in ['in-use']: 55 self.driver.ensure_export(ctxt, volume) 56 except Exception: 57 LOG.exception("Failed to re-export volume, " 58 "setting to ERROR.", 59 resource=volume) 60 volume.conditional_update({'status': 'error'}, 61 {'status': 'in-use'}) 62 # All other cleanups are processed by parent class CleanableManager 63 64 except Exception: 65 LOG.exception("Error during re-export on driver init.", 66 resource=volume) 67 return 68 69 self.driver.set_throttle() 70 71 # at this point the driver is considered initialized. 72 # NOTE(jdg): Careful though because that doesn't mean 73 # that an entry exists in the service table 74 self.driver.set_initialized() 75 76 # Keep the image tmp file clean when init host. 77 backend_name = vol_utils.extract_host(self.service_topic_queue) 78 image_utils.cleanup_temporary_file(backend_name) 79 80 # Migrate any ConfKeyManager keys based on fixed_key to the currently 81 # configured key manager. 82 self._add_to_threadpool(key_migration.migrate_fixed_key, 83 volumes=volumes) 84 85 # collect and publish service capabilities 86 self.publish_service_capabilities(ctxt) 87 LOG.info("Driver initialization completed successfully.", 88 resource={'type': 'driver', 89 'id': self.driver.__class__.__name__}) 90 91 # Make sure to call CleanableManager to do the cleanup 92 super(VolumeManager, self).init_host(added_to_cluster=added_to_cluster, 93 **kwargs)
driver是从配置文件中获取

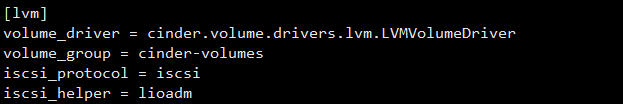
LVMVolumeDriver继承于driver.VolumeDriver
do_setup在LVMVolumeDriver中未再进行实现覆盖
check_for_setup_error代码如下
1 def check_for_setup_error(self): 2 """Verify that requirements are in place to use LVM driver.""" 3 if self.vg is None: 4 root_helper = utils.get_root_helper() 5 6 lvm_conf_file = self.configuration.lvm_conf_file 7 if lvm_conf_file.lower() == 'none': 8 lvm_conf_file = None 9 10 try: 11 lvm_type = self.configuration.lvm_type 12 if lvm_type == 'auto': 13 if volutils.supports_thin_provisioning(): 14 lvm_type = 'thin' 15 else: 16 lvm_type = 'default' 17 self.vg = lvm.LVM( 18 self.configuration.volume_group, 19 root_helper, 20 lvm_type=lvm_type, 21 executor=self._execute, 22 lvm_conf=lvm_conf_file, 23 suppress_fd_warn=( 24 self.configuration.lvm_suppress_fd_warnings)) 25 26 except exception.VolumeGroupNotFound: 27 message = (_("Volume Group %s does not exist") % 28 self.configuration.volume_group) 29 raise exception.VolumeBackendAPIException(data=message) 30 31 vg_list = volutils.get_all_volume_groups( 32 self.configuration.volume_group) 33 vg_dict = 34 next(vg for vg in vg_list if vg['name'] == self.vg.vg_name) 35 if vg_dict is None: 36 message = (_("Volume Group %s does not exist") % 37 self.configuration.volume_group) 38 raise exception.VolumeBackendAPIException(data=message) 39 40 pool_name = "%s-pool" % self.configuration.volume_group 41 42 if self.configuration.lvm_type == 'auto': 43 # Default to thin provisioning if it is supported and 44 # the volume group is empty, or contains a thin pool 45 # for us to use. 46 self.vg.update_volume_group_info() 47 48 self.configuration.lvm_type = 'default' 49 50 if volutils.supports_thin_provisioning(): 51 if self.vg.get_volume(pool_name) is not None: 52 LOG.info('Enabling LVM thin provisioning by default ' 53 'because a thin pool exists.') 54 self.configuration.lvm_type = 'thin' 55 elif len(self.vg.get_volumes()) == 0: 56 LOG.info('Enabling LVM thin provisioning by default ' 57 'because no LVs exist.') 58 self.configuration.lvm_type = 'thin' 59 60 if self.configuration.lvm_type == 'thin': 61 # Specific checks for using Thin provisioned LV's 62 if not volutils.supports_thin_provisioning(): 63 message = _("Thin provisioning not supported " 64 "on this version of LVM.") 65 raise exception.VolumeBackendAPIException(data=message) 66 67 if self.vg.get_volume(pool_name) is None: 68 try: 69 self.vg.create_thin_pool(pool_name) 70 except processutils.ProcessExecutionError as exc: 71 exception_message = (_("Failed to create thin pool, " 72 "error message was: %s") 73 % six.text_type(exc.stderr)) 74 raise exception.VolumeBackendAPIException( 75 data=exception_message) 76 77 # Enable sparse copy since lvm_type is 'thin' 78 self._sparse_copy_volume = True
此处self.vg被初始化为lvm.LVM实例,为真正的driver。
上述即为cinder-volume的启动~