一.图的表示
1.顶点的表示:使用整数0~V-1来表示。即使顶点是字母表示的,也可以利用符号表转换为顶点名字和整数一一对应的关系。
2.图的表示方法:实际中最常用的一种是邻接表数组(Adjaxency-list )
(1)使用数组表示以每一个顶点为索引的列表
(2)数组中的元素表示与该顶点邻接的顶点所构成的集合(这里使用ArrayList/bag来承载邻接元素)
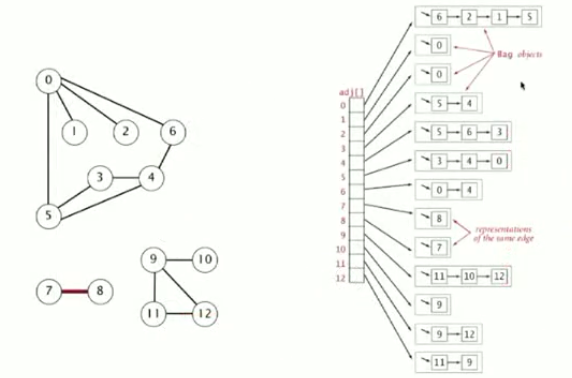
3.代码实现

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; //无向图的表示 public class Graph { private final int V; //邻接表数组,里面的每个元素都是一个集合类 private Bag<Integer>[] adj; //初始化V个顶点的图 public Graph(int V) { this.V=V; adj=(Bag<Integer>[])new Bag[V]; //将每个元素初始化,不然会为null for(int v=0;v<V;v++) { adj[v]=new Bag<Integer>(); } } public void addEdge(int v,int w) { adj[v].add(w); adj[w].add(v); } //顶点v的邻接元素集合 public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){ return adj[v]; } //点的度数 public static int degree(Graph G,int v) { int degree=0; for(int w:G.adj(v)) degree++; return degree; } public int V() {return V;} }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Bag.java * Execution: java Bag < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * * A generic bag or multiset, implemented using a singly-linked list. * * % more tobe.txt * to be or not to - be - - that - - - is * * % java Bag < tobe.txt * size of bag = 14 * is * - * - * - * that * - * - * be * - * to * not * or * be * to * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code Bag} class represents a bag (or multiset) of * generic items. It supports insertion and iterating over the * items in arbitrary order. * <p> * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class Node. * See {@link LinkedBag} for the version from the * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. * The <em>add</em>, <em>isEmpty</em>, and <em>size</em> operations * take constant time. Iteration takes time proportional to the number of items. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this bag */ public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; // beginning of bag private int n; // number of elements in bag // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty bag. */ public Bag() { first = null; n = 0; } /** * Returns true if this bag is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this bag is empty; * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this bag. * * @return the number of items in this bag */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Adds the item to this bag. * * @param item the item to add to this bag */ public void add(Item item) { Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; n++; } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the {@code Bag} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { Bag<String> bag = new Bag<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); bag.add(item); } StdOut.println("size of bag = " + bag.size()); for (String s : bag) { StdOut.println(s); } } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/
4.说明:
(1)在实际中,往往顶点是巨大的,而顶点的平均度数是很小的,即图往往是稀疏的,在这种情况下,图的表示方法依旧显示很好的性能
(2)除此以外还有2种表示方式,其一是维持边的数组,将所有的边记录下来,但是这种方式对于遍历顶点的邻接顶点极其麻烦。其二是使用二维矩阵表示图的邻接矩阵,由于(1)的特性,会造成该矩阵巨大,但是稀疏,对空间造成极大的浪费。
二.深度优先算法Depth-first Search
1.目标(作用):
(1)连通性的判断:判断给定的顶点是否连通
(2)单点路径:找出与起点s连通的所有顶点和对应的路径
2.思想:mimic maze exploration。在访问一个顶点的时候:
(1)将它标记为已访问
(2)递归地访问它的所有未被标记的领域顶点
3.算法:
(1)使用递归
(2)标记每一个已访问的顶点,并记录到达它的顶点
(3)当没有未访问的点时返回
4.举例
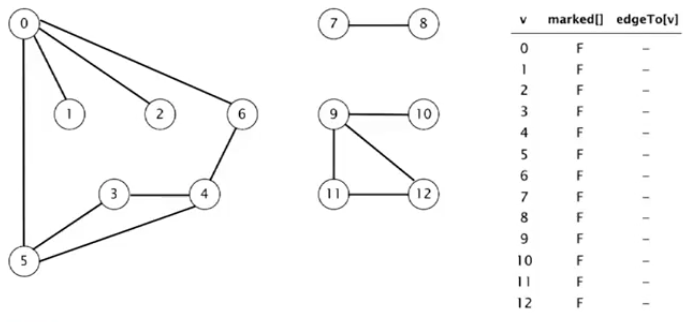
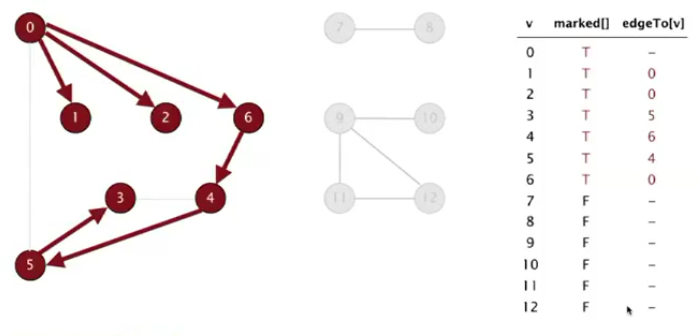
如图所示:起点是0,marked[]用于标记是否已访问过该顶点,edgeTo[v]用于记录从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点,便于记录这条路径。
首先处理起点0,记录marked为T,然后遍历所有邻域5,1,2,6(DFS),例如先处理6,marked[6]=T,edge[6]=0。处理6的邻域,只能是4,因为0已被标记。记录marked[4]=T,edge[4]=6。处理4的领域,6已被标记,遍历所有邻域3,5。例如处理5,marked[5]=T,edge[5]=4。处理5的未标记邻域,只能是3,marked[3]=T,edge[3]=5。3没有未标记的邻域,返回。同理5,4,6也没有未处理的邻域。最后分别处理1,2。深度优先算法结束。
5.代码实现

package com.cx.graph; import java.util.Stack; public class DepthFirstPaths { //用于标记是否已访问过该顶点 private boolean[] marked; //用于标记从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点 //边v-w是第一次访问w经过的路径,则edgeTo(w)=v,从而可以记住该路径 private int[] edgeTo; //起点为s private int s; //递归的标记与起点s连通的所有顶点 public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G,int s) { marked=new boolean[G.V()]; edgeTo=new int[G.V()]; s=this.s; //找到和s连通的顶点 dfs(G,s); } //标记每一个已访问的顶点,并记录到达它的顶点 private void dfs(Graph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; for(int w:G.adj(v)) { //访问所有未被标记的邻域顶点 if(!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w]=v; dfs(G, w); } } } //判断任意两个顶点是否连通 public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return marked[v]; } //找到一条s-v的路径 public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<Integer> path=new Stack<Integer>(); //从终点逆向得到路径 for(int x=v;v!=s;x=edgeTo[x]) { path.push(x); } path.push(s); return path; } }
6.说明:
(1)标记与起点连通的所有顶点所需的时间和顶点的度数之和成正比
(2)在DFS以后,可以在常数时间内找到与s连通的所有顶点,并且找到从起点到任意标记顶点的路径所需的时间与路径的长度成正比
(3)递归的时候,每个顶点仅标记一次,并且对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止。
三.广度优先算法 Breadth-first Search
1.用处:
(1)连通性的判断:判断给定的顶点是否连通
(2)单点最短路径:找出与起点s连通的所有顶点和对应的最短路径
2.算法:将起点加入队列,然后重复以下步骤直到队列为空:
(1)取队列中的下一个顶点v并标记它
(2)将与v相邻的所有未被标记过的顶点加入队列
3.举例说明
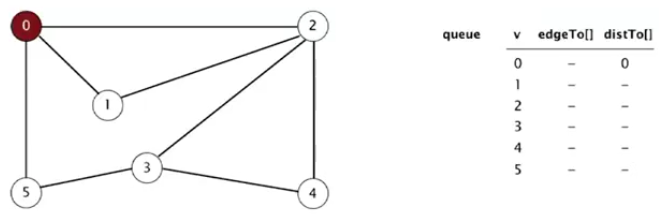
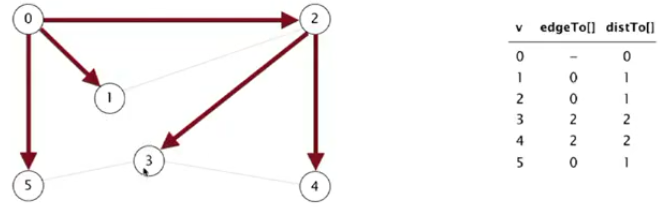
将起点0,加入队列,取0并标记,然后将2,1,5加入队列。比如先加入的2,则取2并标记,将3.4加入队列。取1出队列,并标记,没有未标记的相邻顶点,不加新元素到队列。同理。取5出队列,并标记。取3出队列并标记,取4出队列并标记。
edgeTo[]用于记录到达该点路径的上一个点,distTo[]记录到顶点的距离。
4.代码实现

package com.cx.graph; import java.util.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; public class BreadthFirstPaths { private boolean[] marked; private int[] edgeTo; private int s; public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G,int s) { marked=new boolean[G.V()]; edgeTo=new int[G.V()]; s=this.s; //找到和s连通的顶点 bfs(G,s); } private void bfs(Graph G,int s) { Queue<Integer> queue=new Queue<Integer>(); queue.enqueue(s); marked[s]=true; while(!queue.isEmpty()) { int v=queue.dequeue(); for(int w:G.adj(v)) { if(!marked[w]) { //1.标记 marked[w]=true; //2.入队列 queue.enqueue(w); //3.写前一个顶点 edgeTo[w]=v; } } } } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return marked[v]; } public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<Integer> path=new Stack<Integer>(); //从终点逆向得到路径 for(int x=v;v!=s;x=edgeTo[x]) { path.push(x); } path.push(s); return path; } }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Queue.java * Execution: java Queue < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt * * A generic queue, implemented using a linked list. * * % java Queue < tobe.txt * to be or not to be (2 left on queue) * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code Queue} class represents a first-in-first-out (FIFO) * queue of generic items. * It supports the usual <em>enqueue</em> and <em>dequeue</em> * operations, along with methods for peeking at the first item, * testing if the queue is empty, and iterating through * the items in FIFO order. * <p> * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class for * linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedQueue} for the version from the * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. * The <em>enqueue</em>, <em>dequeue</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em> * operations all take constant time in the worst case. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this queue */ public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; // beginning of queue private Node<Item> last; // end of queue private int n; // number of elements on queue // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty queue. */ public Queue() { first = null; last = null; n = 0; } /** * Returns true if this queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this queue is empty; {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this queue. * * @return the number of items in this queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Returns the item least recently added to this queue. * * @return the item least recently added to this queue * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Adds the item to this queue. * * @param item the item to add */ public void enqueue(Item item) { Node<Item> oldlast = last; last = new Node<Item>(); last.item = item; last.next = null; if (isEmpty()) first = last; else oldlast.next = last; n++; } /** * Removes and returns the item on this queue that was least recently added. * * @return the item on this queue that was least recently added * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); Item item = first.item; first = first.next; n--; if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering return item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this queue. * * @return the sequence of items in FIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the {@code Queue} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) queue.enqueue(item); else if (!queue.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + queue.size() + " left on queue)"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/
5.说明:
(1)广度优先算法计算从给定顶点s到所有别的顶点的最短路径需要的时间和E+V成正比。
(2)是一种非递归的算法
(3)深度优先通过栈来实现,广度优先通过队列来实现
四.连通分量
1.目标:常数时间内判断v和w是否相连接。
2.连通分量:相互连接的顶点的最大集合。
如果可以给定连通分量,则可以实现上述目标,即在常数时间内判断v和w是否相连接。
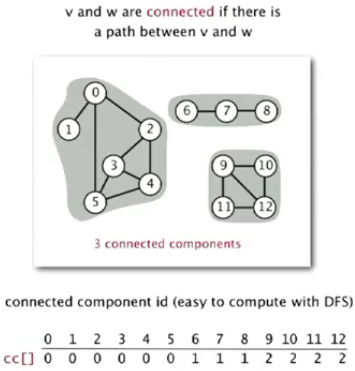
3.连通分量的确定可以使用类似深度优先算法的思想。遍历所有未标记的顶点,例如v,做如下操作:
(1)将v标记为已访问
(2)递归的访问所有和v邻接且未标记的顶点
4.代码实现:

package com.cx.graph; public class CC { private boolean[] marked; //v所在的连通分量的标识符 private int[] id; //连通分量个数 private int count; public CC(Graph G) { marked=new boolean[G.V()]; id=new int[G.V()]; //对所有顶点执行dfs操作进行标记 for(int s=0;s<G.V();s++) { //对未标记的执行dfs if(!marked[s]) { dfs(G,s); count++; } } } private void dfs(Graph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; id[v]=count; for(int w:G.adj(v)) { if(!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } //判断是否连通 public boolean connected(int v,int w) { return id[v]==id[w]; } public int id(int v) { return id[v]; } public int count() { return count; } }
5.说明:
(1)预处理使用的时间和空间与V+E成正比且可以在常数时间内处理关于图的连通性的查询
