一、容器(Collection):数组是一种容器,集合也是一种容器
java编程中,装其他各种各样的对象(引用类型)的一种东西,叫容器
注意:
1、数组的长度是固定的
2、集合:长度不固定, 可以随时添加和删除,只要不超出内存, 随便往里添加
二、集合接口(六大接口)
1、Collection(包括List接口和Set接口)
List---(有顺序, 可以重复-->可以互相equals(引用类型))---下标(重复的标准就是相互equals)
LinkedList(链表)---(改快,查慢)
*ArrayList(数组)---(改慢,查快)
Set---(没有顺序, 不可以重复)
*HashSet(hash码表)(必须重写hashCode()方法)
TreeSet(二叉树---数据结构)
2、Map(键值对,每次往里放的时候都是一对一对的)(键不能重复,既不能相互equals)
*HashMap
TreeMap
3、Comparable(一个方法(comparaTo))
4、Iterator(循环遍历, 3个方法)
boolean hasNext()
Object next()
remove()
用法:
while(hasNext()) {
next()
}
三、Collection接口的方法
1、Collection接口的使用
Collection c = new ArrayList();
2、c.add(参数类型必须是Object)
3、c.remove方法: 通过判断两个对象是否互相的equals来确定是不是该删除该对象, 自定义的类, 需要自己重写父类的equals方法
重写equals方法, 也应该重写hashCode方法
4、hashCode通常用来做索引, 一个对象通过它的hashCode的值可以找到它在内存中的地址, 所以两个对象如果equals了, 而且又要作为索引的情况下, hashCode的值必须相等
举例说明:
package util; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; public class TextCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { //接口Collection不能直接new,必须由它的实现类来new,因为接口是抽象类,没有方法体,没法直接用 Collection c = new ArrayList(); //父类的引用指向子类的对象 c.add(1); c.add("nihao"); c.add(new Person()); System.out.println(c); //输出结果为:[1, nihao, Person [哈哈]] c.remove(1); c.remove("nihao"); c.remove(new Person());//new在内存中的指向不一样,必须equals System.out.println(c.size()); //输出结果为:1 System.out.println(c); //输出结果为:[Person [哈哈]] } } class Person{ @Override public String toString() { return "Person [哈哈]"; } }
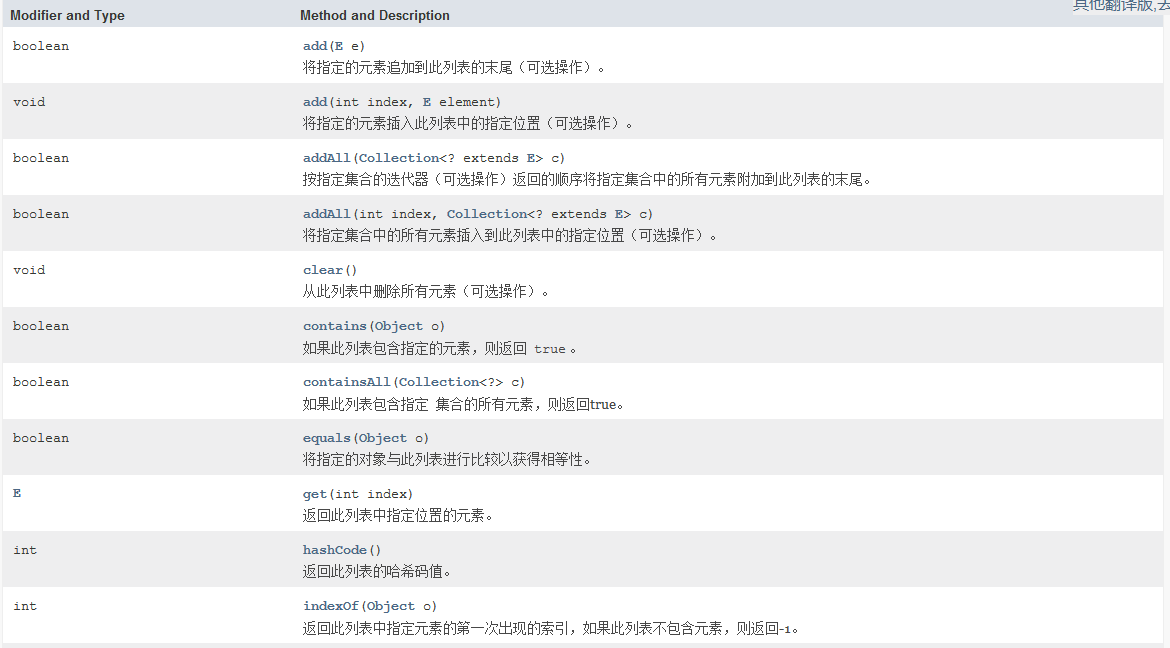
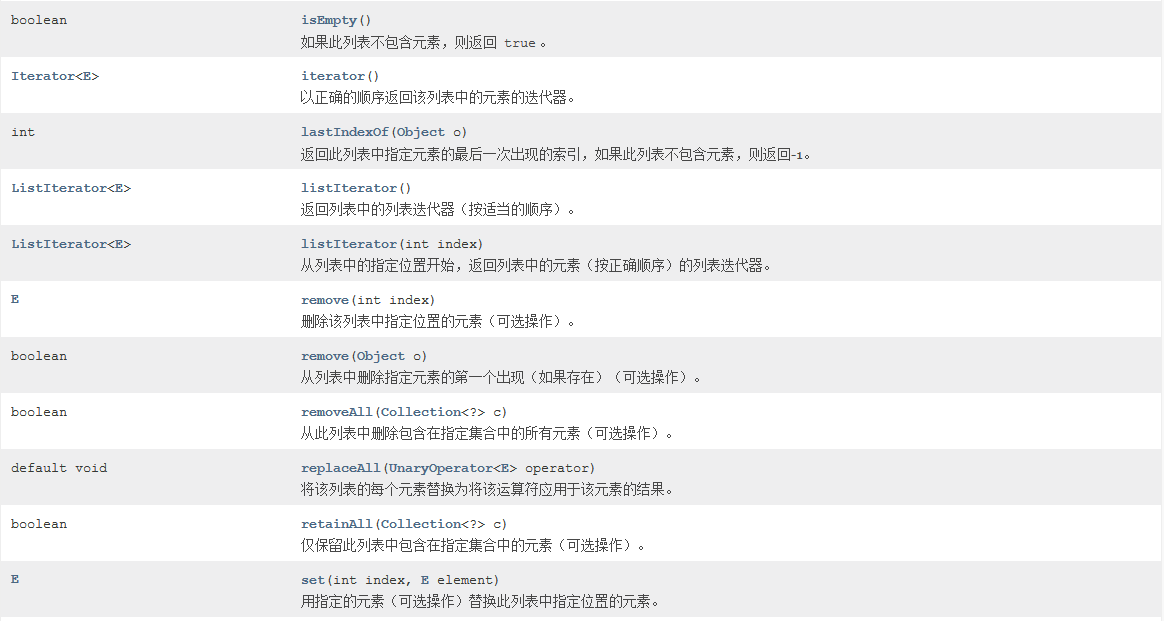
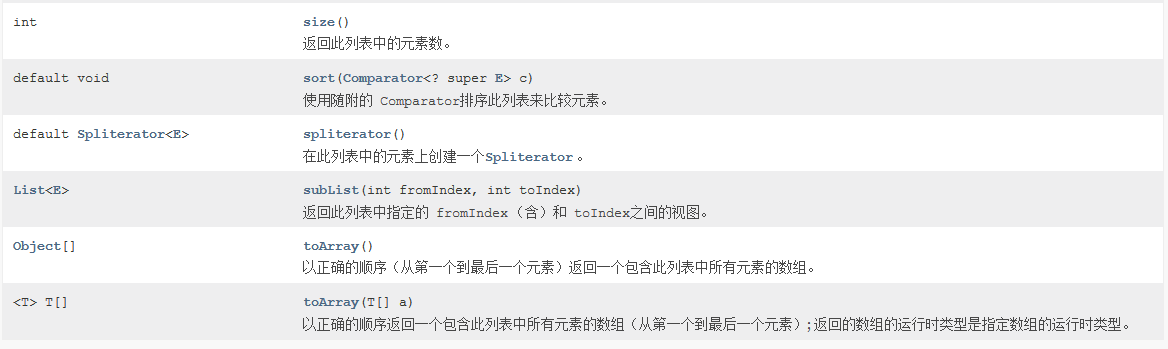
四、List接口
ArrayList(API中说初始容量为10的, 注意这个问题), LinkedList
有顺序, 可以重复添加
set(有一个返回值要注意 !)
retainAll(Collection)----返回一个boolean值, 当list的内容被改变的时候返回true, 否则返回false;仅保留此列表中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。
package util; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class TextCollection1 { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static void main(String[] args) { List list1 = new ArrayList(); List list2 = new ArrayList(); List list3 = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { list1.add("String" + i); if(i%2==0){ list2.add("String" + i); list3.add("String" + i*10+1); } } System.out.println(list1); //输出结果为:[String0, String1, String2, String3, String4] System.out.println(list1.get(3)); //输出结果为:String3 System.out.println(list1.set(2, "哈哈")); //输出结果为:String2,有返回值 System.out.println(list1); //输出结果为:[String0, String1, 哈哈, String3, String4] System.out.println(list1.remove(4)); //输出结果为:String4,有返回值 System.out.println(list1); //输出结果为:[String0, String1, 哈哈, String3] System.out.println(list1.indexOf("String3")); //输出结果为:3 System.out.println(list1.lastIndexOf("String3")); //输出结果为:3 //list1.retainAll(list2);//取两个集合中的交集,然后把交集的内容赋值给list1,如果list1中内容改变了,返回true,如果没改变(即两个集合没有交集),返回false System.out.println(list1.retainAll(list2)); //输出结果为:true System.out.println(list1); //输出结果为:[String0] //list1.retainAll(list3); System.out.println(list1.retainAll(list3)); //输出结果为:false System.out.println(list1); //输出结果为:[] } }
五、Map接口
Map接口
put:有个返回值
remove:有个返回值



例子:
package util1; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class TextCollection2 { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { map.put(i, new Person("name" + i)); } System.out.println(map); //输出值为:{0=Person [name0], 1=Person [name1], 2=Person [name2], // 3=Person [name3], 4=Person [name4]} map.put(5, new Person("新人")); System.out.println(map); //输出值为:{0=Person [name0], 1=Person [name1], 2=Person [name2], // 3=Person [name3], 4=Person [name4], 5=Person [新人]} map.put(1, new Person("又来个新人")); System.out.println(map); //输出值为:{0=Person [name0], 1=Person [又来个新人], 2=Person [name2], // 3=Person [name3], 4=Person [name4], 5=Person [新人]} System.out.println(map.get(1)); //输出值为:Person [又来个新人] System.out.println(map.remove(1)); //输出值为:Person [又来个新人] System.out.println(map); //输出值为:{0=Person [name0], 2=Person [name2], 3=Person [name3], //4=Person [name4], 5=Person [新人]} System.out.println(map.remove(0, new Person("name" + 0))); //输出值为:true System.out.println(map); //输出值为:2=Person [name2], 3=Person [name3], 4=Person [name4], //5=Person [新人]} System.out.println(map.containsKey(4));//输出值为:true System.out.println(map.containsValue(new Person("name" + 0)));//输出值为:false,在上一步已经删除 System.out.println(map.size());//输出值为:4 System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//输出值为:false map.clear(); System.out.println(map);//输出值为:{} Map map2 = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { map2.put("a"+i, new Person("====a" + i)); } map.putAll(map2); System.out.println(map);//输出值为:{a1=Person [====a1], a2=Person [====a2], a3=Person [====a3], //a4=Person [====a4], a0=Person [====a0]} } } class Person{ String name; public Person(String name){ this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [" + name + "]"; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Person other = (Person) obj; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true; } }
六、问题: 为什么不直接写ArrayList a = new ArrayList();而是Collection c = new ArrayList();?
Collection是一个接口,而ArrayList 是一个类。 ArrayList 继承并实现了Collection。
Collection c = new ArrayList();这句创建了一个ArrayList的对象后把上溯到了Collection。此时它是一个Collection对象了,有些ArrayList有但是Collection没有的属性和方法,它就不能再用了。而ArrayList a =new ArrayList();创建一对象则保留了ArrayList的所有属性。
为什么一般都使用 Collecton c = new ArrayList() ,而不用 ArrayList a = new ArrayList()呢?
问题就在于Collection有多个实现类,如 LinkedList或者ArrayList等等,现在你用的是ArrayList,也许哪一天你需要换成其它的实现类呢?,这时你只要改变这一行就行了:Collection c = new LinkedList(); 其它使用了Collection地方的代码根本不需要改动。假设你开始用 ArrayList a = new ArrayList(), 这下你有的改了,特别是如果你使用了 ArrayList特有的方法和属性。如果没有特别需求的话,最好使用
Collection c = new ArrayList(); ,便于程序代码的重构. 这就是面向接口编程的好处。