方法1:用一个辅助栈
把链表中所有元素存储到栈中,也就实现了将链表中的元素逆序存放到栈中。然后再将栈中元素一个一个出栈并和链表比对,将链表一个一个往下指
时空间复杂度:O(n)
public static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return true;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer> ();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null){
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
while (head != null){
if(stack.pop() != head.val){
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
方法二:还是用一个辅助栈,但是只放链表中一半的结点到栈中
链表长度为N,将后N/2的结点放到栈中。压入完成后,再检查栈顶到栈底值出现的顺序是否和链表左半部分的值相对应
方法二可以直观地理解为将链表的右半部分“折过去”,然后让它和左半部分比较
这里也相当于快慢指针了,叫快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,当快指针不难再走的时候,慢指针也到右半区了
代码:
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode right = head.next;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr.next != null && curr.next.next != null){
curr = curr.next.next;
right = right.next;
}
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<> ();
while (right != null){
stack.push(right);
right = right.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
if(head.val != stack.pop().val){
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
方法三:不需要额外空间
1.将链表右半区反转,最后指向中间结点
1->2->3->2->1如左图,1->2->3->3->2->1如右图
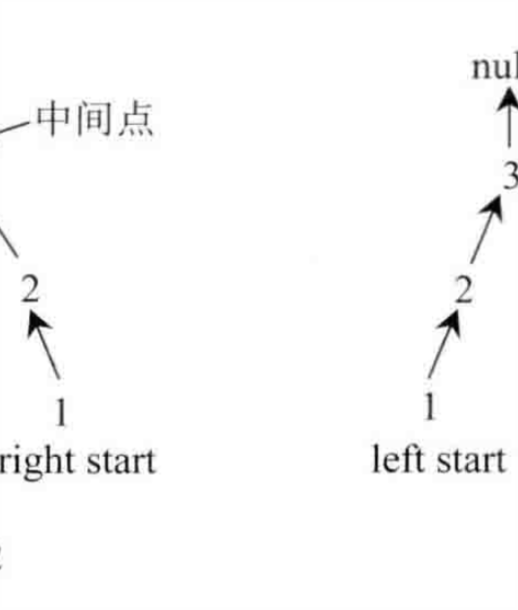
将左半区的第一个节点记为leftStart,右半区反转之后最右边的结点(也就是原链表的最后一个结点)记为rightStart
2.leftStart和rightStart同时向中间结点移动,移动每步都比较两者的值
3.不管最后返回结果是什么,都要把链表恢复成原来的样子
4.链表恢复原来的结构之后,返回检查结果
代码:
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode n1 = head;
ListNode n2 = head;
//找到中间结点
while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null){
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}
n2 = n1.next;//n2是右半区的第一个结点
n1.next = null;
ListNode n3 = null;
//右半区反转
while (n2 != null) {
n3 = n2.next;
n2.next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
n3 = n1;//n3->保存最后一个结点,以便后续恢复用
n2 = head;//n2是左边第一个结点
boolean res = true;
//检查回文
while (n1 != null && n2 != null){
if(n1.val != n2.val){
res = false;//这里不能直接return false,要把链表结构还原再return
break;//跳出
}
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
n1 = n3.next;
n3.next = null;
while (n1 != null){
n2 = n1.next;
n1.next = n3;
n3 = n1;
n1 = n2;
}
return res;
}