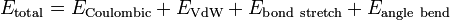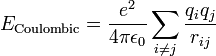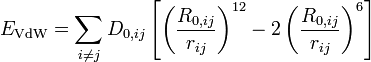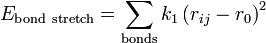Angle bending describes the change in energy due to change in the angle
between two sequential covalent bonds from the equilibrium value
Torsion describes the change in energy of three bonds connected as IJ, JK
and KL due to change in the dihedral (or torsional) angle between the planes
IJK and JKL from the equilibrium value
Inversion describes the energy of three atoms bonded to one central atom
in the same plane due to an out of plane configuration
Clayff力场收集1:http://www.sklogwiki.org/SklogWiki/index.php/CLAYFF_force_field
ClayFFis a general force field suitable for the simulation of hydrated and multicomponent mineral systems and their interfaces with aqueous solutions. With the issue of rising atmospheric concentration of the greenhouse (global warming) gas, carbon dioxide (CO2) also comes a burgeoning interest in novel repositories in which to inexpensively "bury" CO2 to reduce its atmospheric load. This issue, among others, has prompted scientists to examine various ubiquitous and inexpensive clays (for example, montmorrillonite or kaolinite) as potential CO2 repositories. But clays are heterogeneous, somewhat unstructured and molecularly complex entities (by comparison to, for example, pure salt --- sodium chloride --- crystals), and there are uncertainties in experimental methods for studying the binding and retention of other atoms, ions, and molecules (such as CO2) to hydrated (water-wettened) clays. Hence, it is important to apply theoretical molecular modelsto achieve a fundamental atomic-level understanding, interpretation, and prediction of these chemical phenomena. ClayFF is available in molecular simulation codes (for example, MCCCS Towhee andOpenMD) and was developed by Sandia National Laboratories chemist, Randall Cygan, and collaborators at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. It is suitable for the simulation of hydrated and multicomponent mineral systems and their interfaces with aqueous solutions. The ClayFF approach treats most inter-atomic interactions as being non-bonded. This allows the use of the force field for a wide variety of phases and properly accounts for energy and momentum transfer between the fluid phase and the solid, while keeping the number of parameters small enough to permit modelling of relatively large and highly disordered systems such as clays.
Functional form
The functional form of ClayFF is given by:
where (Eq. 2 [1]):
(Eq. 3):
(Eq. 6 [1]):
(Eq. 7 [1]):
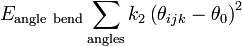
- Clayff力场收集2:http://lammps.sandia.gov/threads/msg54106.html
Dear all,
I want to use Materials Studio to build the structure, and use Lammps to run the simulation.
After assigning the atom type with clayff, I run a few steps of geometry optimization in Materials Studio. Then I export the .car and .mdf files. However, I meet the following errors when I produce Lammps data with msi2lmp:
Unable to find bond data for st ob
I checked Jian-Jie Liang's clayff.frc which he posted on the Accerlys' Community. I can't find the bond data for st ob since clayff doesn't calculate them. From my understanding, clayff only calculate bond for water and hydroxyl.
Sincerely,
Jingjing
追答:Jingjing,