1.堆:是程序中用来保存长期使用数据的地方,堆上的数据不会自动清除,因此堆是保存数据结构的绝佳场所(例如链表)
2.用堆进行动态存储:
用malloc()申请存储器(相当于储物柜),malloc()返回一个指针
一旦申请了堆上的空间,这块空间就再也不能被分配出去,直到告诉C标准库已经用完了,堆存储器空间有限,如果在代码中不断申请堆空间,很快就会发生存储器泄露。
用free()释放存储器
3.用法:
#include<stdlib.h> //为了使用malloc()和free()函数 malloc(sizeof(island)); //表示“给我足够的空间来保存island结构指针” malloc()返回通用指针 free(p); //释放
4.strdup()复制字符串到堆上
例如:
char *s = "MONA LISA"; char *copy = strdup(s);
注意:栈上的局部变量会被清除,但堆上的不会,所以记得要用free()释放空间
指针不会建立自己的副本,要用strdup()函数
数组会建立自己的副本,不用strdup()函数
5.字符指针不限制字符串的大小
字符数组需要提前决定字符串长度
6.valgrind工具:发现存储器泄露
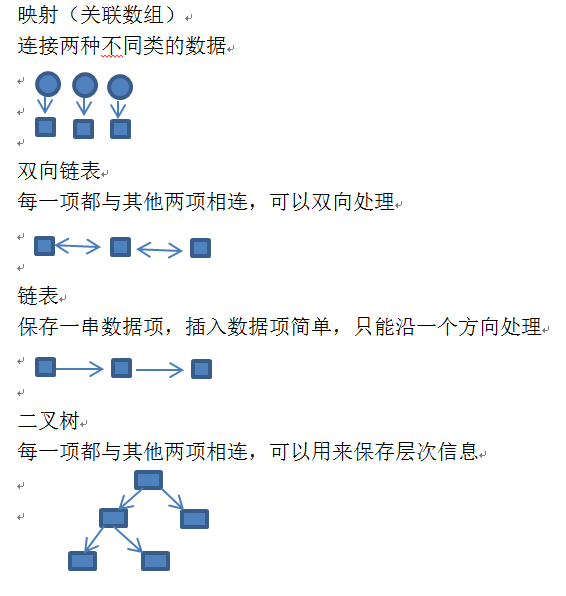
7.数据结构
练习
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> typedef struct node { char *question; struct node *no; struct node *yes; }node;//二叉树 int yes_no(char *question) { char answer[3]; printf("%s?(y/n):",question); fgets(answer,3,stdin); return answer[0] == 'y'; } node *create(char *question)//初始化 { node *n = malloc(sizeof(node)); n->question = strdup(question); n->no = NULL; n->yes = NULL; return n; } void release(node *n)//释放 { if(n) { if(n->no) release(n->no); if(n->yes) release(n->yes); if(n->question) free(n->question); free(n); } } int main() { char question[80]; char suspect[20]; node *start_node = create("Does suspect have a mustache"); start_node->no = create("Loretta Barnsworth"); start_node->yes = create("Vinny the Spoon"); node *current; do { current = start_node; while(1) { if(yes_no(current->question)) { if(current->yes) current = current->yes; else { printf("SUSPECT IDENTIFIED "); break; } } else if(current->no) current = current->no; else { //Make the yes-node the new suspect name printf("Who's the suspect?"); fgets(suspect,20,stdin); node *yes_node = create(suspect); current->yes = yes_node; //Make the no-node a copy of this question node *no_node = create(current->question); current->no = no_node; //Then replace this question with the new question printf("Give me a question that is TRUE for %s but not for %s?",suspect,current->question); fgets(question,80,stdin); current->question = strdup(question); break; } } }while(yes_no("Run again")); release(start_node); return 0; }