string是序列的一种和tuple一样是不可以改变的
1、len:计算string长度 ,返回整数
>>> len('abc')
3
2、index(),返回某个元素在string里的下标,从0开始,若元素不存在则返回ValueError
>>> a = 'abv'
>>> a.index('a')
0
>>> a.index('c')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#17>", line 1, in <module>
a.index('c')
ValueError: substring not found
3、slice分片,和list的用法一致,但是string不能改变,所以list的分片赋值不适用string
>>> b = 'this is a good time'
>>> b[0:3]
'thi'
4、string简单格式化,使用字符串格式化操作符(%),左边放需要格式化的字符串,右侧放需要格式化的值(可以使用一个值,也可以使用元组或者字典)
>>> 'this is a %s time'%'beautiful'
'this is a beautiful time'
>>> 'the price is %f'%7.89
'the price is 7.890000'
# 元组,元组中的元素每一个都要对应一个%s
>>> "%s is a smart %s"%('Judy','younglady')
'Judy is a smart younglady'
5、sring 模板格式化,从string模块导入substitute模板,这个模板是用关键字替换需要格式化string里的内容,格式$x,如果替换内容是单词的一部分需要用${x}
>>> from string import Template
>>> s = Template('$x, glorious $x')
>>> s.substitute(x='slurm')
'slurm, glorious slurm'
#如果替换内容是单词的一部分需要用${x}
>>> from string import Template
>>> s = Template("It's ${x}tastic ")
>>> s.substitute(x='slurm')
"It's slurmtastic "
#字典模式
>>> from string import Template
>>> s = Template("A $thing must never $action")
>>> d={'thing':'gentleman','action':'show his socks'}
>>> s.substitute(d)
'A gentleman must never show his socks'
#只映射一个值 使用safe_substitute
s = Template("A $thing must never $action")
>>> a = {'thing':"gentleman"}
>>> s.substitute(a)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#97>", line 1, in <module>
s.substitute(a)
File "C:Python37libstring.py", line 132, in substitute
return self.pattern.sub(convert, self.template)
File "C:Python37libstring.py", line 125, in convert
return str(mapping[named])
KeyError: 'action'
>>> s.safe_substitute(a)
'A gentleman must never $action'
6、string格式化完整版
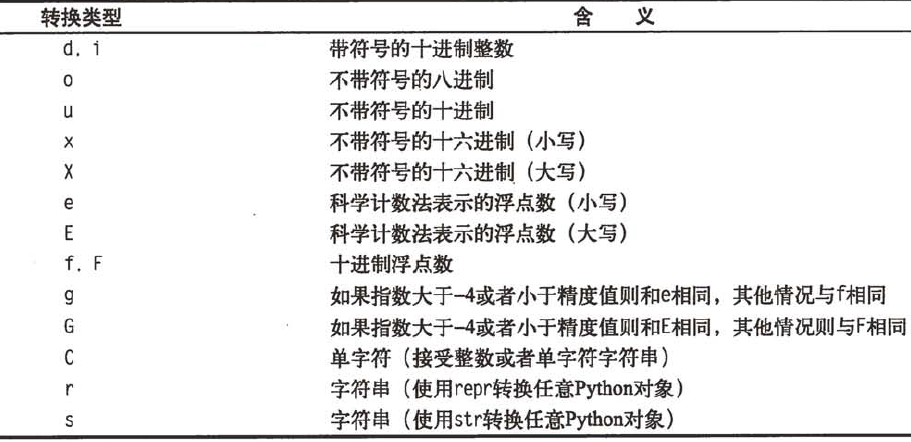
基本的转换说明符
- %字符,标记转换说明符的开始
- 转换标识(可选):-表示左对齐;+表示在转换值之前都要加上正负号;“”空字符串表示正数之前要保留空格;0表示转换值若位数不够用0填充;
- 最小字段宽度(可选):转换后的字符串至少要具有该值指定的宽度。如果是*,则这个值要从值元组中获取(有点类似给*赋一个int类型正整数)
- 点(.)后面跟精度值(可选):如果转换的是实数,精度值表示小数点后保留的位数;如果转换的是字符串,表示字符串的取值位数,也就是字符串的最大宽度;如果是*则表示这个值要从值元素中获取
- 支持的转换类型
实例:
简单转换:
>>> 'price of eggs: $%d'%42
'price of eggs: $42'
>>> 'the float number is %.2f'%3.1415
'the float number is 3.14'
>>> 'Using str:%s'%42 ###%s会把格式化的值用str转换成字符串
'Using str:42'
>>> 'Using str:%s'%'中国'
'Using str:中国'
>>> 'Using str:%r'%'中国' ###%r表示系统中存储的格式原样输出
"Using str:'中国'"
宽度和精度
宽度:就是制定转换后的字符串占用的宽度(字符数);若用*,则从值元组里取值
精度:数字来说就是保留小数点后面数字的位数,字符串来讲就是截取的字符串的最大长度;若用*,则从值元组里取值
>>> from math import pi
>>> '%10f'%pi
' 3.141593'
>>> '%10.2f'%pi
' 3.14'
>>> '%.5s'%'Guido van Rossum'
'Guido'
>>> "%.*s"%(5,'Guido van Rossum')#### *=5
'Guido'
>>> "%*.*s"%(10,5,'Guido van Rossum')#### 第一个*=10,第二个*=5 相当于“%10.5s”%('Guido van Rossum')
' Guido'
7、-左对齐,位置在%后面第一位,宽度之前
>>> "%-10.2f"%4.235
'4.24 '
8、0填充
>>> "%010.2f"%4.235
'0000004.24'
9、“”空字符串儿,在正数前用空格填充,必须用“”,python3.7不支持‘’,会提示ValueError
>>> "%""10.2f"%4.235
' 4.24'
10、+不论正数还是负数都会显示正号或者负号,在数据对其时有用
>>> "%-+10.2f%+d"%(4.235,-3)
'+4.24 -3'
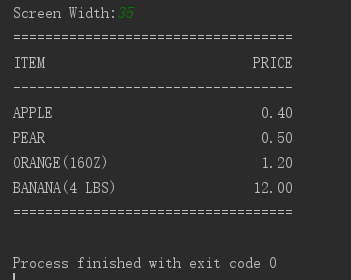
实例:根据顾客给定的宽度打印一份水果价格表
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
screen_width = input('Screen Width:')
price_width =10
item_width = int(screen_width)-10
header_format = '%-*s%*s'
format = '%-*s%*.2f'
print("="*int(screen_width))
print(header_format%(item_width,'ITEM',price_width,'PRICE'))
print("-"*int(screen_width))
print(format%(item_width,'APPLE',price_width,0.4))
print(format%(item_width,'PEAR',price_width,0.5))
print(format%(item_width,'ORANGE(16OZ)',price_width,1.2))
print(format%(item_width,'BANANA(4 LBS)',price_width,12))
print("="*int(screen_width))
这是结果:
8、find(),在一个长的的字符串儿里查找一个子字符串,找到则返回子字符串最左边的字符在长字符串的下标index;找不到则返回-1;还可以指定查找的起止位置含前不含后
>>> a = "tHis is a test!"
>>> a.find('His')
1
>>> a.find("his")
-1
>>> a.find('His',2,8)###开始和结束位置,结束位置是不包含的,实际查找位置是下标2---7
-1
>>> a.find('His',1)###只有开始位置
1
9、join方法,可以看做是splite(分割)方法的逆方法
>>> a = [1,2,3]
>>> "+".join(a)####链接数字列表
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#23>", line 1, in <module>
"+".join(a)
TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found
>>> b = ["1",'2','3']
>>> "+".join(b)####链接字符列表
'1+2+3'
>>> seq = ['','usr','bin','env']
>>> '/'.join(seq)
'/usr/bin/env'
>>> '\'.join(seq)
'\usr\bin\env'
>>> "c:"+'\'.join(seq)
'c:\usr\bin\env'
10、lower()返回字符串的小写字母版,字符串 不可修改所以不会改变原字符串
>>> a = "tHis is a test!"
>>> a.lower()
'this is a test!'
>>> a
'tHis is a test!'
不用区分大小写判断名字是否存在列表中,可以将客户输入的名字和存放名字的列表都转化成小写字符形式,再判断
>>> names = ['Gumby','smith','JONES']
>>> b=[i.lower() for i in names] ###列表推导式
>>> b
['gumby', 'smith', 'jones']
>>> name = input("NAME:").lower()####函数链接从左到右执行
NAME:Smith
>>> if name in b:
print("hello,%s"%name)
hello,smith
11、title方法,将每个单词的首位字母变成大写字母,单词的其他字母变成小写字母
>>> a
'tHis is a test!'
>>> a.title()
'This Is A Test!'
12、replace 方法,返回某字符串的所有匹配项被替换后的新字符串
>>> a= 'tHIS IS a test'
>>> a.replace('t','d')
'dHIS IS a desd'
13、split方法,根据指定的分隔符,分割字符串为一个序列,默认是遇到分割符就分割,也可以指定分割次数
>>> '1+2+3+4'.split("+")
['1', '2', '3', '4']
>>> '1+2+3+4'.split("+",1)###指定分割一次
['1', '2+3+4']
>>> '1 2 3 4 '.split()###不指定分割符,默认把所有空格当成分割符
['1', '2', '3', '4']
14、strip()方法,去除字符串两端的空格,返回新的字符串
>>> a=" this is a good time "###前后留有空格
>>> a.strip()
'this is a good time'
15、python3.7中字符串格式换已经修改了旧的%格式新的格式为:,例如'%03.2f' 现在表示为 '{:03.2f}'.
>>> '{0}, {1}, {2}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')
'a, b, c'
>>> '{}, {}, {}'.format('a', 'b', 'c') # 3.1+ only
'a, b, c'
>>> '{2}, {1}, {0}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')
'c, b, a'
>>> '{2}, {1}, {0}'.format(*'abc') # unpacking argument sequence拆包参数序列 '{2}, {1}, {0}'.format("a",'b','c')
'c, b, a'
>>> '{0}{1}{0}'.format('abra', 'cad') # arguments' indices can be repeated 参数索引可以重复
'abracadabra'
>>> 'Coordinates: {latitude}, {longitude}'.format(latitude='37.24N', longitude='-115.81W')
'Coordinates: 37.24N, -115.81W'
>>> coord = {'latitude': '37.24N', 'longitude': '-115.81W'}
>>> 'Coordinates: {latitude}, {longitude}'.format(**coord)
'Coordinates: 37.24N, -115.81W'
Accessing arguments’ items:
>>> coord = (3, 5)
>>> 'X: {0[0]}; Y: {0[1]}'.format(coord)
'X: 3; Y: 5'
Aligning the text and specifying a
>>> '{:<30}'.format('left aligned')
'left aligned '
>>> '{:>30}'.format('right aligned')
' right aligned'
>>> '{:^30}'.format('centered')
' centered '
>>> '{:*^30}'.format('centered') # use '*' as a fill char
'***********centered***********'
Replacing %s and %r:
>>> "repr() shows quotes: {!r}; str() doesn't: {!s}".format('test1', 'test2')
"repr() shows quotes: 'test1'; str() doesn't: test2"