一、13个超实用的Linux性能监测命令行工具
http://os.51cto.com/art/201304/388673_all.htm
1. Top:监测Linux进程
Linux Top命令是一个性能监测程序,它经常被许多系统管理员用来监测Linux性能,在许多类似Linux/Unix的操作系统环境下都能找到。Top命令可用于显示所有运行中和活动的实时进程(按顺序排列),并且定期更新。它可显示处理器使用情况、内存使用情况、交换内存、缓存大小、缓冲器大小、进程标识符(PID)、用户、命令及更多的信息。它还显示了某个运行中进程大量使用内存和处理器的情况。Top命令对系统管理员大有用处,可用来监测,需要时还可采取正确的行动。不妨看看Top命令的实际使用情况。
# top
Top命令示例
2. VmStat:显示虚拟内存方面的统计信息
Linux VmStat命令用来显示虚拟内存、内核线程、磁盘、系统进程、输入/输出块、中断、处理器活动及更多方面的统计信息。默认情况下,vmstat命令并不出现在Linux系统环境下,你需要安装一个名为sysstat的程序包,该程序包里面含有一个vmstat程序。命令格式通常这样使用:
# vmstat
| procs -----------memory----------swap-- -----io---- --system-- -----cpu----
r b swpd free inact active si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st 1 0 0 810420 97380 70628 0 0 115 4 89 79 1 6 90 3 0 |
3. Lsof:列出打开的文件
Lsof命令用于许多类似Linux/Unix的系统中,用来显示所有打开的文件和进程。打开的文件包括:磁盘文件、网络套接字、管道、设备和进程。使用这个命令的主要场合之一是,当磁盘无法卸载,显示文件被使用或被打开这个错误信息时。有了这个命令,你很容易查明哪些文件在使用中。这个命令最常见的格式如下:
# lsof
| COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE NODE NAME
init 1 root cwd DIR 104,2 4096 2 / init 1 root rtd DIR 104,2 4096 2 / init 1 root txt REG 104,2 38652 17710339 /sbin/init init 1 root mem REG 104,2 129900 196453 /lib/ld-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 1693812 196454 /lib/libc-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 20668 196479 /lib/libdl-2.5.so init 1 root mem REG 104,2 245376 196419 /lib/libsepol.so.1 init 1 root mem REG 104,2 93508 196431 /lib/libselinux.so.1 init 1 root 10u FIFO 0,17 953 /dev/initctl |
4. Tcpdump:网络数据包分析器
Tcpdump是使用最广泛的命令行网络数据包分析器或数据包嗅探程序之一,用于捕捉或过滤在网络上通过某个接口接收或传输的TCP/IP数据包。它还提供了这个选项:把捕捉到的数据包保存到一个文件中,供以后分析。Tcpdump几乎出现在所有主要的Linux发行版环境下。
# tcpdump -i eth0
| tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes 22:08:59.617628 IP tecmint.com.ssh > 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472: P 2532133365:2532133481(116) ack 3561562349 win 9648 22:09:07.653466 IP tecmint.com.ssh > 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472: P 116:232(116) ack 1 win 9648 22:08:59.617916 IP 115.113.134.3.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in.28472 > tecmint.com.ssh: . ack 116 win 64347 |
5. Netstat:显示网络方面的统计信息
除了用于监测接口方面的统计信息外,Netstat这个命令行工具还用于监测进出的网络数据包方面的统计信息。它对每个系统管理员来说是个很有用的工具,可用于监测网络性能,并排查网络相关问题。
# netstat -a | more
| Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:sunrpc *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:realm-rusd *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:ftp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:ipp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp localhost.localdomain:42709 TIME_WAIT tcp 0 0 localhost.localdomain:smtp localhost.localdomain:42710 TIME_WAIT tcp 0 0 *:http *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:https *:* LISTEN |
6. Htop:监测Linux进程
Htop是一款非常先进的交互式实时Linux进程监测工具。它非常类似Linux top命令,但是有一些丰富的功能特性,比如易于使用的界面,可用于管理进程、快捷键、进程的垂直和水平视图以及其他对象。Htop是一个第三方工具,并不包含在Linux系统中,你需要使用YUM程序包管理器工具来安装它。想了解安装方面的更多信息,请参阅本文。
# htop
Htop命令示例的屏幕截图
7. Iotop:监测Linux磁盘的输入/输出
Iotop也非常类似top命令和Htop程序,但是它有记账功能,可用于监测和显示实时磁盘输入/输出及进程。这个工具非常有用,可用于查找具体的进程以及进程的频繁使用的磁盘读取/写入操作。
# iotop
Iotop命令示例的屏幕截图
8. Iostat:显示输入/输出方面的统计信息
IoStat是款简单的工具,可以收集和显示系统输入/输出存储设备方面的统计信息。这个工具经常用于追查存储设备性能方面的问题,包括设备、本地磁盘和NFS等远程磁盘。
# iostat
| Linux 2.6.18-238.9.1.el5 (tecmint.com) 09/13/2012
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle 2.60 3.65 1.04 4.29 0.00 88.42 Device: tps Blk_read/s Blk_wrtn/s Blk_read Blk_wrtn cciss/c0d0 17.79 545.80 256.52 855159769 401914750 cciss/c0d0p1 0.00 0.00 0.00 5459 3518 cciss/c0d0p2 16.45 533.97 245.18 836631746 384153384 cciss/c0d0p3 0.63 5.58 3.97 8737650 6215544 cciss/c0d0p4 0.00 0.00 0.00 8 0 cciss/c0d0p5 0.63 3.79 5.03 5936778 7882528 cciss/c0d0p6 0.08 2.46 2.34 3847771 3659776 |
9. IPTraf:实时监测IP局域网
IPTraf是一个基于控制台的开源实时网络(IP LAN)监测实用工具,面向Linux。它可以收集通过网络传输的众多信息(比如IP流量监测器),包括TCP标记信息、ICMP详细信息、TCP/UDP流量故障、TCP连接数据包以及字节计数。它还可以收集接口方面普通和详细的统计信息,比如TCP、UDP、IP、ICMP、非IP、IP校验和错误以及接口活动等。
IP流量监测器
10. psacct或acct:监测用户活动
psacct或acct这两个工具大有用处,可用于监测系统上每个用户的活动。这两个守护程序都在后台运行,监测系统上每个用户的总体活动,还监测它们在使用什么资源。
这些工具对系统管理员们来说大有用处,可用于跟踪每个用户的活动,比如用户在从事什么操作,他们发出了什么命令,他们使用了多少资源,以及他们在系统上处于活动状态已有多久,等等。
11. Monit:监测Linux进程和服务
Monit是一款免费的开源、基于Web的进程监测实用工具,可以自动监测和管理系统进程、程序、文件、目录、许可权限、校验和以及文件系统。
它可以监测Apache、MySQL、Mail、FTP、ProFTP、Nginx和SSH等服务。可以从命令行或使用其自己的Web界面来查看系统状态。
Monit Linux进程监测
12. NetHogs:监测每个进程的网络带宽
NetHogs是一款优秀、小巧的开源程序(类似Linux top命令),可密切监测系统上每个进程的网络活动。它还密切跟踪每个程序或应用软件所使用的实时网络流量带宽。
NetHogs Linux带宽监测
13. iftop:监测网络带宽
iftop是另一款基于终端的免费开源系统监测实用工具,可显示一份经常更新的列表,该列表显示了通过系统上网络接口的网络带宽使用情况。iftop通常用于监测网络使用情况,就像top通常用于监测处理器使用情况。iftop是属于top家族的工具,可监测某个所选择的接口,并显示两个主机之间目前的带宽使用情况。
Iftop:网络带宽监测
我们想知道各位使用哪种监测程序来监测Linux服务器的性能?要是我们遗漏了任何你希望我们补充进来的重要工具,请留言告知我们,欢迎分享。
二、20个对Linux专家非常有用命令
http://os.51cto.com/art/201308/406979_all.htm
1. 命令: ifconfig
ifconfig用来配置常驻内核的网络接口信息。在系统启动必要时用来设置网络适配器的信息。之后,它通常是只需要在调试时或当系统需要调整时使用。
检查活动网络适配器
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig
- eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 40:2C:F4:EA:CF:0E
- inet addr:192.168.1.3 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
- inet6 addr: fe80::422c:f4ff:feea:cf0e/64 Scope:Link
- UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
- RX packets:163843 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:124990 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
- RX bytes:154389832 (147.2 MiB) TX bytes:65085817 (62.0 MiB)
- Interrupt:20 Memory:f7100000-f7120000
- lo Link encap:Local Loopback
- inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
- inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
- UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
- RX packets:78 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:78 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:4186 (4.0 KiB) TX bytes:4186 (4.0 KiB)
检查所有的网络适配器
“-a”参数用来显示所有网络适配器(网卡)的详细信息,包括那些停用的适配器。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig -a
- eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 40:2C:F4:EA:CF:0E
- inet addr:192.168.1.3 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
- inet6 addr: fe80::422c:f4ff:feea:cf0e/64 Scope:Link
- UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
- RX packets:163843 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:124990 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
- RX bytes:154389832 (147.2 MiB) TX bytes:65085817 (62.0 MiB)
- Interrupt:20 Memory:f7100000-f7120000
- lo Link encap:Local Loopback
- inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
- inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
- UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
- RX packets:78 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:78 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:4186 (4.0 KiB) TX bytes:4186 (4.0 KiB)
- virbr0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 0e:30:a3:3a:bf:03
- inet addr:192.168.122.1 Bcast:192.168.122.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
- UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
- RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
- TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
- collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
- RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
停用网络适配器
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 down
启用网络适配器
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 up
指定IP地址到网络适配器
为网络适配器eth0设定IP地址“192.168.1.12”.
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.12
更改网络适配器eth0的子网掩码:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 netmask 255.255.255.
更改网络适配器eth0的广播地址:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
为网络适配器eth0指定IP地址,子网掩码,广播地址:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.12 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
注Note: 如果你设置一块无线网卡的信息,你可以使用的命令是“iwconfig”.欲知更多ifconfig命令的例子和使用方法,读“15个有用的ifconfig 命令”。
2. 命令: netstat
netstat命令显示各种网络相关的信息,如网络连接,路由表,接口统计,伪装连接,组播成员身份等....
列出所有的网络端口
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ netstat -a
- Active UNIX domain sockets (servers and established)
- Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 741379 /run/user/user1/keyring-I5cn1c/gpg
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 8965 /var/run/acpid.socket
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 18584 /tmp/.X11-unix/X0
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 741385 /run/user/user1/keyring-I5cn1c/ssh
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 741387 /run/user/user1/keyring-I5cn1c/pkcs11
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 20242 @/tmp/dbus-ghtTjuPN46
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 13332 /var/run/samba/winbindd_privileged/pipe
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 13331 /tmp/.winbindd/pipe
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 11030 /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 19308 /tmp/ssh-qnZadSgJAbqd/agent.3221
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 436781 /tmp/HotShots
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 46110 /run/user/ravisaive/pulse/native
- unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 19310 /tmp/gpg-zfE9YT/S.gpg-agent
- ....
显示所有tcp相关端口
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ netstat -at
- Active Internet connections (servers and established)
- Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
- tcp 0 0 localhost:mysql *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 *:5901 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 *:5902 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 *:x11-1 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 *:x11-2 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 *:5938 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 localhost:5940 *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPl:domain *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPl:domain *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 localhost:ipp *:* LISTEN
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPle:48270 ec2-23-21-236-70.c:http ESTABLISHED
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPle:48272 ec2-23-21-236-70.c:http TIME_WAIT
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPle:48421 bom03s01-in-f22.1:https ESTABLISHED
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPle:48269 ec2-23-21-236-70.c:http ESTABLISHED
- tcp 0 0 ravisaive-OptiPle:39084 channel-ecmp-06-f:https ESTABLISHED
- ...
显示所有连接的统计信息
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ netstat -s
- Ip:
- 4994239 total packets received
- 0 forwarded
- 0 incoming packets discarded
- 4165741 incoming packets delivered
- 3248924 requests sent out
- 8 outgoing packets dropped
- Icmp:
- 29460 ICMP messages received
- 566 input ICMP message failed.
- ICMP input histogram:
- destination unreachable: 98
- redirects: 29362
- 2918 ICMP messages sent
- 0 ICMP messages failed
- ICMP output histogram:
- destination unreachable: 2918
- IcmpMsg:
- InType3: 98
- InType5: 29362
- OutType3: 2918
- Tcp:
- 94533 active connections openings
- 23 passive connection openings
- 5870 failed connection attempts
- 7194 connection resets received
- ....
好的!由于某些原因如果你不想解析netstat 输出的主机、端口和用户名称的话 。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ netstat -an
好,你可能需要获取的 netstat 持续输出的动态信息,通过传递中断输出指令 (ctrl + c)来停止。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ netstat -c
更多关于“netstat”的例子和使用方法,浏览文章“20个netstat 的使用案例”。
3. 命令: nslookup
网络实用程序,用于获得互联网服务器的信息。顾名思义,该实用程序将发现通过查询 DNS 域的名称服务器信息。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup tecmint.com
- Server: 192.168.1.1
- Address: 192.168.1.1#53
- Non-authoritative answer:
- Name: tecmint.com
- Address: 50.16.67.239
查询邮件 交换器 记录
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup -query=mx tecmint.com
- Server: 192.168.1.1
- Address: 192.168.1.1#53
- Non-authoritative answer:
- tecmint.com mail exchanger = 0 smtp.secureserver.net.
- tecmint.com mail exchanger = 10 mailstore1.secureserver.net.
- Authoritative answers can be found from:
查询域名服务器
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup -type=ns tecmint.com
- Server: 192.168.1.1
- Address: 192.168.1.1#53
- Non-authoritative answer:
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns3404.com.
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns3403.com.
- Authoritative answers can be found from:
查询DNS记录
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup -type=any tecmint.com
- Server: 192.168.1.1
- Address: 192.168.1.1#53
- Non-authoritative answer:
- tecmint.com mail exchanger = 10 mailstore1.secureserver.net.
- tecmint.com mail exchanger = 0 smtp.secureserver.net.
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns06.domaincontrol.com.
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns3404.com.
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns3403.com.
- tecmint.com nameserver = ns05.domaincontrol.com.
- Authoritative answers can be found from:
查询 起始 授权机构
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup -type=soa tecmint.com
- Server: 192.168.1.1
- Address: 192.168.1.1#53
- Non-authoritative answer:
- tecmint.com
- origin = ns3403.hostgator.com
- mail addr = dnsadmin.gator1702.hostgator.com
- serial = 2012081102
- refresh = 86400
- retry = 7200
- expire = 3600000
- minimum = 86400
- Authoritative answers can be found from:
查询端口号
更改使用你想要连接的端口号:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nslookup -port 56 tecmint.com
- Server: tecmint.com
- Address: 50.16.76.239#53
- Name: 56
- Address: 14.13.253.12
更多阅读 8个Nslookup 命令。
4. 命令: dig
dig是查询DNS 域名服务器的工具,可以查询的主机地址、 邮件交流、 域名服务器相关的信息。在任何 Linux (Unix) 或 Macintosh OS X 操作系统上,都可以使用该工具。dig的最典型的用法是单个主机的查询。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;; Got answer:
- ;; ->>HEADER<
关闭注释行
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +nocomments
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com +nocomments
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;tecmint.com. IN A
- tecmint.com. 14400 IN A 40.216.66.239
- ;; Query time: 418 msec
- ;; SERVER: 192.168.1.1#53(192.168.1.1)
- ;; WHEN: Sat Jun 29 13:53:22 2013
- ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 45
关闭认证块
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +noauthority
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com +noauthority
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;; Got answer:
- ;; ->>HEADER<
关闭其他块
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +noadditional
- ; <<>> DiG 9.9.2-P1 <<>> tecmint.com +noadditional
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;; Got answer:
- ;; ->>HEADER<
关闭统计块
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +nostats
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com +nostats
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;; Got answer:
- ;; ->>HEADER<
关闭回复块
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +noanswer
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com +noanswer
- ;; global options: +cmd
- ;; Got answer:
- ;; ->>HEADER<
关闭所有块
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ dig tecmint.com +noall
- ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.17.rc1.el6 <<>> tecmint.com +noall
- ;; global options: +cmd
阅读更多10 个Linux Dig 命令实例。
5.命令: uptime
你连接到你的 Linux 服务器时发现一些不寻常或恶意的东西,你会做什么?猜测......不,绝不!你可以运行uptime来验证当服务器无人值守式到底发生了什么事情。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ uptime
- 14:37:10 up 4:21, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.04
6. 命令: wall
对系统管理员来说一个最重要的命令.wall发送一条消息到大家登录端将其 mesg 权限设置为"yes"。这条信息可以被wall作为参数,或者可以将它作为wall的标准输入。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ wall "we will be going down for maintenance for one hour sharply at 03:30 pm"
- Broadcast message from root@localhost.localdomain (pts/0) (Sat Jun 29 14:44:02 2013):
- we will be going down for maintenance for one hour sharply at 03:30 pm
7. 命令: mesg
其他人们可以使用"wtrite"命令,将在在向您发送文本到屏幕上。你可以控制是否显示。
- mesg [<strong>n</strong>|<strong>y</strong>] <strong>n</strong> - prevents the message from others popping up on the screen. <strong>y</strong> – Allows messages to appear on your screen.
8. 命令: write
如果 'mesg' 是 'y',让你的文本直接发送到另一台 Linux 机器的屏幕。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ write ravisaive
9. 命令: talk
增强的write命令,talk命令可让你与其他登录的用户交谈。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ talk ravisaive
注释: 如果 talk 命令没安装的话,可以通过apt 或yum 安装所需的包.
- view sourceprint?
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ yum install talk
- OR
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ apt-get install talk
10. 命令:w
是否觉得命令'w'很滑稽?但是事实上不是的。它是一个命令,尽管只有一个字符长!命令"w"是uptime和who命令,以前后的顺序组合在一起。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ w
- 15:05:42 up 4:49, 3 users, load average: 0.02, 0.01, 0.00
- USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
- server tty7 :0 14:06 4:43m 1:42 0.08s pam: gdm-passwo
- server pts/0 :0.0 14:18 0.00s 0.23s 1.65s gnome-terminal
- server pts/1 :0.0 14:47 4:43 0.01s 0.01s bash
11. 命令: rename
见名知意,这个命令重命名文件。rename将会通过从文件名的首字符开始替换,重命名为指定的文件名。
- Give the file names a1, a2, a3, a4.....1213
仅仅写这些命令:[@Lesus 注: 在Ubuntu上不支持这种格式, rename与mv不同的是,rename可以批量修改,如同带了while的mv操作。]
- view sourceprint?
- rename a1 a0 a?
- rename a1 a0 a??
12. 命令: top
显示CPU进程信息。这个命令自动刷新,默认是持续显示CPU进程信息,除非使用了中断指令。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ top
- top - 14:06:45 up 10 days, 20:57, 2 users, load average: 0.10, 0.16, 0.21
- Tasks: 240 total, 1 running, 235 sleeping, 0 stopped, 4 zombie
- %Cpu(s): 2.0 us, 0.5 sy, 0.0 ni, 97.5 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
- KiB Mem: 2028240 total, 1777848 used, 250392 free, 81804 buffers
- KiB Swap: 3905532 total, 156748 used, 3748784 free, 381456 cached
- PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
- 23768 ravisaiv 20 0 1428m 571m 41m S 2.3 28.9 14:27.52 firefox
- 24182 ravisaiv 20 0 511m 132m 25m S 1.7 6.7 2:45.94 plugin-containe
- 26929 ravisaiv 20 0 5344 1432 972 R 0.7 0.1 0:00.07 top
- 24875 ravisaiv 20 0 263m 14m 10m S 0.3 0.7 0:02.76 lxterminal
- 1 root 20 0 3896 1928 1228 S 0.0 0.1 0:01.62 init
- 2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.06 kthreadd
- 3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:17.28 ksoftirqd/0
- 5 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0H
- 7 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/u:0H
- 8 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.12 migration/0
- 9 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 rcu_bh
- 10 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:26.94 rcu_sched
- 11 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.95 watchdog/0
- 12 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:02.00 watchdog/1
- 13 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:17.80 ksoftirqd/1
- 14 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.12 migration/1
- 16 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/1:0H
- 17 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 cpuset
- 18 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 khelper
- 19 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kdevtmpfs
- 20 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 netns
- 21 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.04 bdi-default
- 22 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kintegrityd
- 23 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kblockd
- 24 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 ata_sff
另查看 12 TOP命令例子 ·[@Lesus 注:htop比top命令更好用,不过需要自己安装]
13. 命令: mkfs.ext4
这个命令在指定的设备上创建一个新的ext4文件系统,如果这个命令后面跟的是个错误的设备,那么整个设备就会被擦除和格式化,所以建议不要运行这个命令,除非你清楚自己正在干什么。
- Mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1 (sda1 block will be formatted)
- mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 (sdb1 block will be formatted)
更多查看: Ext4是什么及怎么创建和转换
14. vi/emac/nano 命令
vi (visual), emac, nano 是 linux 中最常用的一些编辑器。它们经常用于编辑文本,配置,… 等文件. A quick guide to work around vi and nano is, emac is a.
vi 编辑器:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ touch a.txt (创建一个名为a.txt的文本文件)
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ vi a.txt (用vi打开a.txt)
[按下‘i’键进入插入模式, 否则你不能输入任何内容]
- echo "Hello" (这里的文本会存到文件中)
- alt+x (退出插入模式, 记得在最后的字符间留有一些空格.
- ctrl+x 命令或你上一个单词将被删除).
- :wq! (以当前的文本保存文件, 记住‘!’ 是覆盖的意思).
nano 编辑器:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ nano a.txt (用nano打开 a.txt)
- edit, with the content, required
ctrl +x (关闭编辑器).它会显示如下的提示输出信息:
- Save modified buffer (ANSWERING "No" WILL DESTROY CHANGES) ?
- Y Yes
- N No ^C Cancel
点击‘y’ 选择 yes 并输入文件名,就完成编辑了。
15. 命令: rsync
Rsync复制文件,参数-P开启进度条。如果你已经安装了rsync,你可以使用一个简单的别名。
- alias cp='rsync -aP'
现在尝试在终端复制一个大文件,这样将会看到显示剩余部分的输出,与进度条类似。
而且,保持和维护备份是系统管理员不得不做的最重要、最无聊的工作之一。Rsync是一个用于新建和维护备份的非常好用的终端工具(也存在许多其它工具)。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ rsync -zvr IMG_5267 copy=33 copy=ok.jpg ~/Desktop/
- sending incremental file list
- IMG_5267 copy=33 copy=ok.jpg
- sent 2883830 bytes received 31 bytes 5767722.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 2882771 speedup is 1.00
注意: -z表示压缩, -v表示详细信息,-r表示递归。
16. 命令: free
跟踪内存的使用和资源一样重要,就像管理员执行的任何其它任务,可以使用 'free' 命令来在这里救援。
当前内存使用状态Current Usage Status of Memory
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 2028240 1788272 239968 0 69468 363716
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1355088 673152
- Swap: 3905532 157076 3748456
设置输出单位为KB,MB或GB
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -b
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 2076917760 1838272512 238645248 0 71348224 372670464
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1394253824 682663936
- Swap: 3999264768 160845824 3838418944
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -k
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 2028240 1801484 226756 0 69948 363704
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1367832 660408
- Swap: 3905532 157076 3748456
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -m
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 1980 1762 218 0 68 355
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1338 641
- Swap: 3813 153 3660
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -g
- 3
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 1 1 0 0 0 0
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1 0
- Swap: 3 0 3
以可读的格式显示,检查当前内存使用:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -h
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 1.9G 1.7G 208M 0B 68M 355M
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1.3G 632M
- Swap: 3.7G 153M 3.6G
设定 时间间隔 后 ,持续检查使用状态:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ free -s 3
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 2028240 1824096 204144 0 70708 364180
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1389208 639032
- Swap: 3905532 157076 3748456
- total used free shared buffers cached
- Mem: 2028240 1824192 204048 0 70716 364212
- -/+ buffers/cache: 1389264 638976
- Swap: 3905532 157076 3748456
阅读更多10个Free命令使用实例。
17. mysqldump 命令
好了,现在你从名字上就能明白这个命令所代表的作用。mysqldump 命令会转储(备份)数据库的全部或特定一部分数据到一个给定的文件中。例如:
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > /home/server/Desktop/backupfile.sql
注意: mysqldump 需要 mysql 在运行中并且有正确的授权密码。我们在 用mysqldump命令备份数据库中讨论了一些有用的 “mysqldump” 命令用法。
18. mkpasswd 命令
根据指定的长度,产生一个难猜的随机密码。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ mkpasswd -l 10
- zI4+Ybqfx9
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ mkpasswd -l 20
- w0Pr7aqKk&hmbmqdrlmk
注意: -l 10 产生一个10个字符的随机密码,而-l 20 产生 20个字符的密码,它可以设置为任意长度来取得所希望的结果。这个命令很有用,经常在脚本语言里使用来产生随机的密码。你可能需要 yum 或 apt ‘expect’ 包来使用这个命令。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ yum install expect
- 或
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ apt-get install expect
19. Command: paste
合并两个或多个文本文件,按行来进行合并。示例。如果 file1 的内容是:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- file2 是这样的:
- a
- b
- c
- d
- <pre class="shell">[avishek@tecmint ~]$ paste file1 file2 > file3</pre>
- <br>
- 结果file3将是:
- 1 a
- 2 b
- 3 c
- d
20.Command: lsof
lsof 是"list open files("列表中打开的文件") 的缩写,显示您的系统当前已打开的所有文件。这是非常有用的对于想找出哪些进程使用某一特定文件,或显示为单个进程打开所有文件。一些有用的 10 个lsof 命令示例,你可能会感兴趣阅读。
- [avishek@tecmint ~]$ lsof
- COMMAND PID TID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
- init 1 root cwd DIR 8,1 4096 2 /
- init 1 root rtd DIR 8,1 4096 2 /
- init 1 root txt REG 8,1 227432 395571 /sbin/init
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 47080 263023 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnss_files-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 42672 270178 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnss_nis-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 87940 270187 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnsl-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 30560 263021 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnss_compat-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 124637 270176 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libpthread-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 1770984 266166 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 30696 262824 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/librt-2.17.so
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 34392 262867 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libjson.so.0.1.0
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 296792 262889 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libdbus-1.so.3.7.2
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 34168 262840 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnih-dbus.so.1.0.0
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 95616 262848 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libnih.so.1.0.0
- init 1 root mem REG 8,1 134376 270186 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.17.so
- init 1 root 0u CHR 1,3 0t0 1035 /dev/null
- init 1 root 1u CHR 1,3 0t0 1035 /dev/null
- init 1 root 2u CHR 1,3 0t0 1035 /dev/null
- init 1 root 3r FIFO 0,8 0t0 1714 pipe
- init 1 root 4w FIFO 0,8 0t0 1714 pipe
- init 1 root 5r 0000 0,9 0 6245 anon_inode
- init 1 root 6r 0000 0,9 0 6245 anon_inode
- init 1 root 7u unix 0xf5e91f80 0t0 8192 @/com/ubuntu/upstart
- init 1 root 8w REG 8,1 3916 394 /var/log/upstart/teamviewerd.log.1 (deleted)
这里并没有结束,系统管理员会很多东西,为你提供漂亮的界面,服务于你的工作。系统管理实际上是学习和实现的一门优雅的艺术。我们会尽力给你介绍 linux 专业人员必须了解的知识以及一些其他必要东西,linux本身是基础的,简单的。深入理解是不断学习的过程。你的美言好词总是在不断鼓励我们写出更多的优秀,丰富的文章。“喜之以分享,助我来传播”。
三、11 个很有用但鲜有人知的 Linux 命令
http://os.51cto.com/art/201310/414075.htm
这篇文章的目的是介绍一些少有人知的Linux命令,它们一定会高效地帮你管理你的桌面/服务器。
1. sudo !!命令
没有特定输入sudo命令而运行,将给出没有权限的错误。那么,你不需要重写整个命令,仅仅输入'!!'就可以抓取最后的命令。
- $ apt-get update
- E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/apt/lists/lock - open(13: Permission denied)
- E: Unable to lock directory /var/lib/apt/lists/
- E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open(13: Permission denied)
- E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), are you root?
- $ sudo !!
- sudoapt-get update
- [sudo] password forserver:
- …
- ..
- Fetched 474 kB in16s (28.0 kB/s)
- Reading package lists... Done
- server@localhost:~$
2. python命令
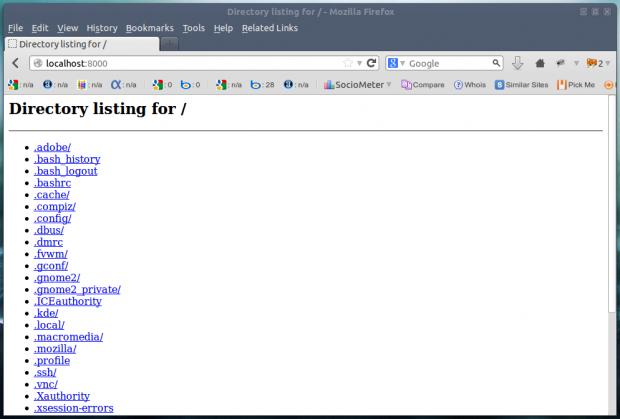
下面的命令生产一个通过HTTP显示文件夹结构树的简单网页,可以通过浏览器在端口8000访问,直到发出中断信号。
- # python -m SimpleHTTPServer
3. mtr命令
我们大多数都熟悉ping和traceroute。那对于把两个命令的功能合二为一的mtr命令呢。如果mtr没在你的机子上安装,apt或者yum需要的包。
- $ sudo apt-get install mtr (On Debian based Systems)
- # yum install mtr (On Red Hat based Systems)
现在运行mtr命令,开始查看mtr运行的主机和google.com直接的网络连接。
- # mtr google.com
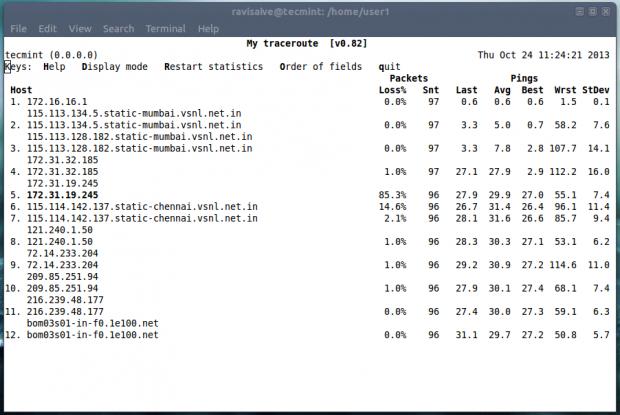
mtr命令
4. Ctrl+x+e命令
这个命令对于管理员和开发者非常有用。为了使每天的任务自动化,管理员需要通过输入vi、vim、nano等打开编辑器。
仅仅从命令行快速的敲击“Ctrl-x-e”,就可以在编辑器中开始工作了。
5. nl命令
“nl命令”添加文件的行数。一个叫做'one.txt'的文件,其每行的内容是(Fedora、Debian、Arch、Slack和Suse),给每行添加行号。首先使用cat命令显示“one.txt”的文件内容。
- # cat one.txt
- fedora
- debian
- arch
- slack
- suse
现在运行“nl命令”,以添加行号的方式来显示。
- # nl one.txt
- 1 fedora
- 2 debian
- 3 arch
- 4 slack
- 5 suse
6. shuf命令
“Shut”命令随机从一个文件或文件夹中选择行/文件/文件夹。首先使用ls命令来显示文件夹的内容。
- # ls
- Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
- # ls | shuf (shuffle Input)
- Music
- Documents
- Templates
- Pictures
- Public
- Desktop
- Downloads
- Videos
- # ls | shuf -n1 (pick on random selection)
- Public
- # ls | shuf -n1
- Videos
- # ls | shuf -n1
- Templates
- # ls | shuf -n1
- Downloads
注意:你可以把‘ n1’替换成‘ n2’来输出两个随机选择或者使用 n3、 n4等数字输出其他任意的随机选择。
7. ss命令
“ss”表示socket统计。这个命令调查socket,显示类似netstat命令的信息。它可以比其他工具显示更多的TCP和状态信息。
- # ss
- State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
- ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:41250 *.*.*.*:http
- CLOSE-WAIT 1 0 127.0.0.1:8000 127.0.0.1:41393
- ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:36239 *.*.*.*:http
- ESTAB 310 0 127.0.0.1:8000 127.0.0.1:41384
- ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.198:41002 *.*.*.*:http
- ESTAB 0 0 127.0.0.1:41384 127.0.0.1:8000
8. last命令
“last”命令显示的是上次登录用户的历史信息。这个命令通过搜索文件“/var/log/wtmp”,显示logged-in和logged-out及其tty‘s的用户列表。
- # last
- server pts/0 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:03 still logged in
- server tty8 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:02 still logged in
- …
- ...
- (unknown tty8 :0 Tue Oct 22 12:02 - 12:02 (00:00)
- server pts/0 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:33 - 12:02 (01:29)
- server tty7 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:05 - 12:02 (01:56)
- (unknown tty7 :0 Tue Oct 22 10:04 - 10:05 (00:00)
- reboot system boot 3.2.0-4-686-pae Tue Oct 22 10:04 - 12:44 (02:39)
- wtmp begins Fri Oct 4 14:43:17 2007
9. curl ifconfig.me
那么如何得到你的外部IP地址呢?使用google?那么这个命令就在你的终端输出你的外部IP地址。
- # curl ifconfig.me
注意:你可能没有按照curl包,你需要 apt/yum来按照包。
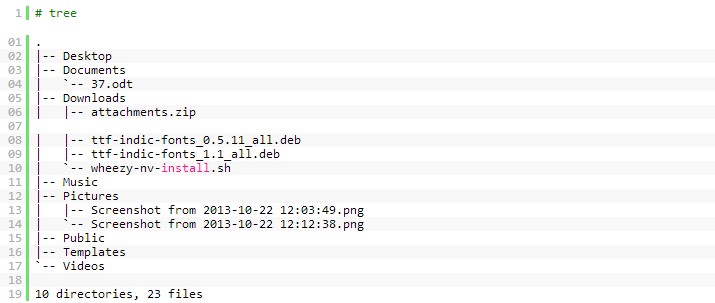
10. tree命令
以树式的格式得到当前文件夹的结构。
11. pstree
这个命令显示当前运行的所有进程及其相关的子进程,输出的是类似‘tree’命令的树状格式
目前为止就这么多。在下篇文章中,我将涉及一些其他很少有人知道的有趣的Linux命令。到那时连接 Tecmint保持收看。喜欢和分享将有助于我们传播。