%% 蚁群算法及Matlab实现——TSP问题
% 《MATLAB数学建模方法与实践》(《MATLAB在数学建模中的应用》升级版),北航出版社,卓金武、王鸿钧编著.
%% 数据准备
% 清空环境变量
clear all
clc
% 程序运行计时开始
t0 = clock;
%导入数据
citys=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx', 'B2:C31');
x=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','B2:B31');
y=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','C2:C31');
%% 计算城市间相互距离
n = size(citys,1);
D = zeros(n,n);
r=6371;
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
if i ~= j
D(i,j) = r*acos(cos(y(i))*cos(y(j))*cos(x(i)-x(j))+sin(y(i))*sin(y(j)));
else
D(i,j) = 1e-4; %设定的对角矩阵修正值
end
end
end
%% 初始化参数
m = 75; % 蚂蚁数量
alpha = 1; % 信息素重要程度因子
beta = 5; % 启发函数重要程度因子
vol = 0.2; % 信息素挥发(volatilization)因子
Q = 10; % 常系数
Heu_F = 1./D; % 启发函数(heuristic function)
Tau = ones(n,n); % 信息素矩阵
Table = zeros(m,n); % 路径记录表
iter = 1; % 迭代次数初值
iter_max = 100; % 最大迭代次数
Route_best = zeros(iter_max,n); % 各代最佳路径
Length_best = zeros(iter_max,1); % 各代最佳路径的长度
Length_ave = zeros(iter_max,1); % 各代路径的平均长度
Limit_iter = 0; % 程序收敛时迭代次数
%% 迭代寻找最佳路径
while iter <= iter_max
% 随机产生各个蚂蚁的起点城市
start = zeros(m,1);
for i = 1:m
temp = 1;
start(i) = temp(1);
end
Table(:,1) = start;
% 构建解空间
citys_index = 1:n;
% 逐个蚂蚁路径选择
for i = 1:m
% 逐个城市路径选择
for j = 2:n
tabu = Table(i,1:(j - 1)); % 已访问的城市集合(禁忌表)
allow_index = ~ismember(citys_index,tabu); % 参加说明1(程序底部)
allow = citys_index(allow_index); % 待访问的城市集合
P = allow;
% 计算城市间转移概率
for k = 1:length(allow)
P(k) = Tau(tabu(end),allow(k))^alpha * Heu_F(tabu(end),allow(k))^beta;
end
P = P/sum(P);
% 轮盘赌法选择下一个访问城市
Pc = cumsum(P); %参加说明2(程序底部)
target_index = find(Pc >= rand);
target = allow(target_index(1));
Table(i,j) = target;
end
end
% 计算各个蚂蚁的路径距离
Length = zeros(m,1);
for i = 1:m
Route = Table(i,:);
for j = 1:(n - 1)
Length(i) = Length(i) + D(Route(j),Route(j + 1));
end
Length(i) = Length(i) + D(Route(n),Route(1));
end
% 计算最短路径距离及平均距离
if iter == 1
[min_Length,min_index] = min(Length);
Length_best(iter) = min_Length;
Length_ave(iter) = mean(Length);
Route_best(iter,:) = Table(min_index,:);
Limit_iter = 1;
else
[min_Length,min_index] = min(Length);
Length_best(iter) = min(Length_best(iter - 1),min_Length);
Length_ave(iter) = mean(Length);
if Length_best(iter) == min_Length
Route_best(iter,:) = Table(min_index,:);
Limit_iter = iter;
else
Route_best(iter,:) = Route_best((iter-1),:);
end
end
% 更新信息素
Delta_Tau = zeros(n,n);
% 逐个蚂蚁计算
for i = 1:m
% 逐个城市计算
for j = 1:(n - 1)
Delta_Tau(Table(i,j),Table(i,j+1)) = Delta_Tau(Table(i,j),Table(i,j+1)) + Q/Length(i);
end
Delta_Tau(Table(i,n),Table(i,1)) = Delta_Tau(Table(i,n),Table(i,1)) + Q/Length(i);
end
Tau = (1-vol) * Tau + Delta_Tau;
% 迭代次数加1,清空路径记录表
iter = iter + 1;
Table = zeros(m,n);
end
%% 结果显示
[Shortest_Length,index] = min(Length_best);
Shortest_Route = Route_best(index,:);
Time_Cost=etime(clock,t0);
disp(['最短距离:' num2str(Shortest_Length)]);
disp(['最短路径:' num2str([Shortest_Route Shortest_Route(1)])]);
disp(['收敛迭代次数:' num2str(Limit_iter)]);
disp(['程序执行时间:' num2str(Time_Cost) '秒']);
%% 绘图
figure(1)
plot([citys(Shortest_Route,1);citys(Shortest_Route(1),1)],... %三点省略符为Matlab续行符
[citys(Shortest_Route,2);citys(Shortest_Route(1),2)],'o-');
grid on
for i = 1:size(citys,1)
text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)]);
end
text(citys(Shortest_Route(1),1),citys(Shortest_Route(1),2),' 起点');
text(citys(Shortest_Route(end),1),citys(Shortest_Route(end),2),' 终点');
xlabel('城市位置横坐标')
ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')
title(['ACA最优化路径(最短距离:' num2str(Shortest_Length) ')'])
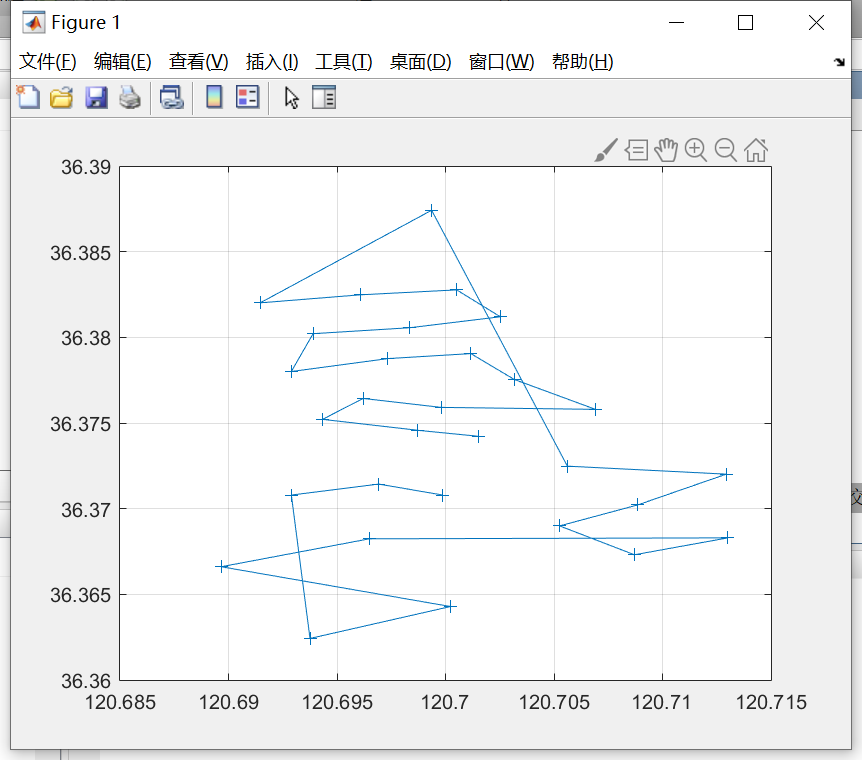
figure(2)
plot(1:iter_max,Length_best,'b')
legend('最短距离')
xlabel('迭代次数')
ylabel('距离')
title('算法收敛轨迹')
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 程序解释或说明
% 1. ismember函数判断一个变量中的元素是否在另一个变量中出现,返回0-1矩阵;
% 2. cumsum函数用于求变量中累加元素的和,如A=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 那么cumsum(A)=[1, 3, 6, 10, 15]。
运行结果
最短距离:433.5578
最短路径:1 2 8 3 10 7 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 28 6 4 5 29 23 22 25 24 30 27 26 20 19 18 21 1
收敛迭代次数:5
程序执行时间:9.502秒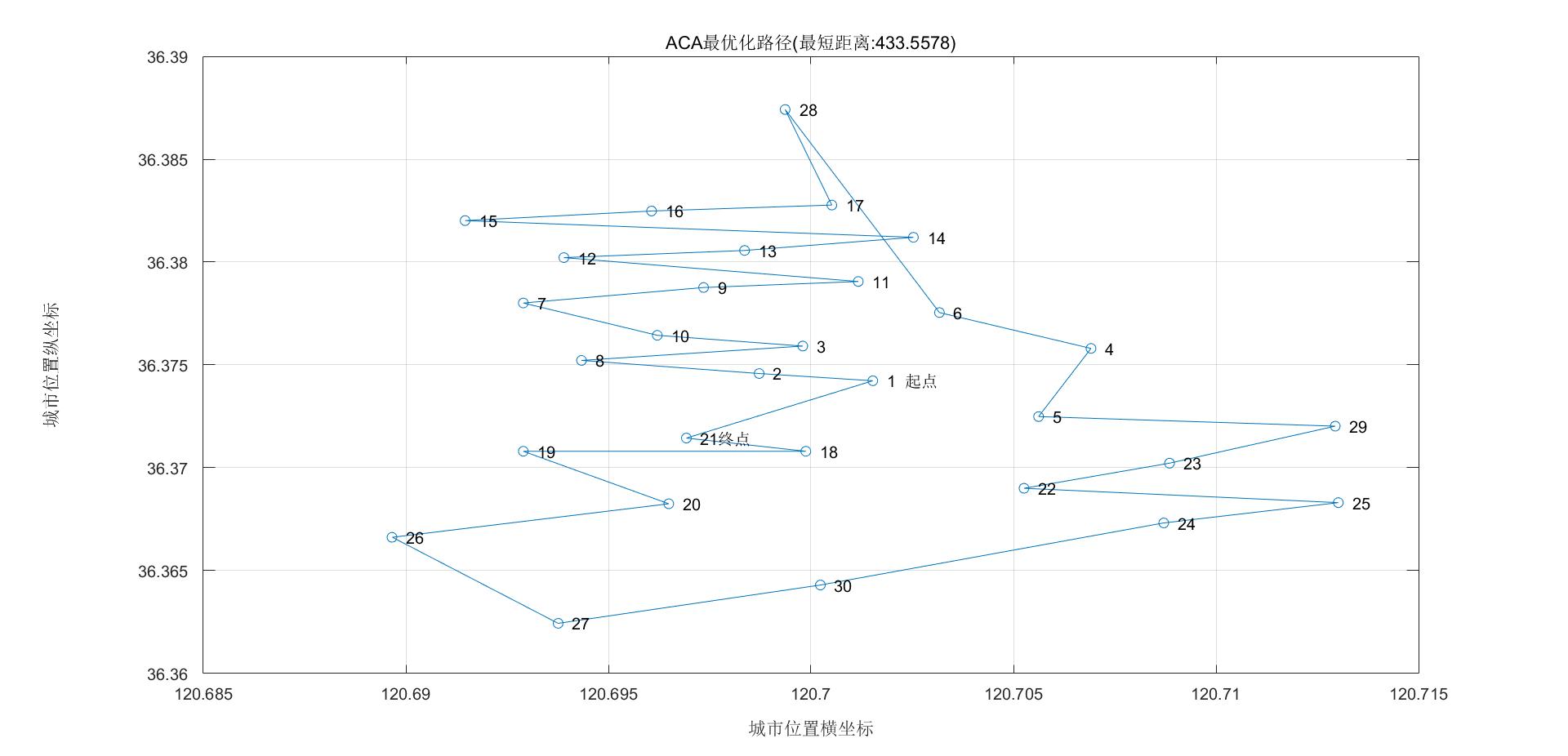
退火算法
clear
clc
num=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx', 'B2:C31');
x=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','B2:B31');
y=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','C2:C31');
a = 0.99; % 温度衰减函数的参数
t0 = 97; tf = 3; t = t0;
Markov_length = 10000; % Markov链长度
coordinates = [num,x,y];
coordinates(:,1) = [];
amount = size(coordinates,1); % 城市的数目
%% 计算城市间相互距离
n = size(num,1);
D = zeros(n,n);
r=6371;
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
if i ~= j
D(i,j) = r*acos(cos(y(i))*cos(y(j))*cos(x(i)-x(j))+sin(y(i))*sin(y(j)));
else
D(i,j) = 1e-4; %设定的对角矩阵修正值
end
end
end
sol_new = 1:amount; % 产生初始解
% sol_new是每次产生的新解;sol_current是当前解;sol_best是冷却中的最好解;
E_current = inf;E_best = inf; % E_current是当前解对应的回路距离;
% E_new是新解的回路距离;
% E_best是最优解的
sol_current = sol_new; sol_best = sol_new;
p = 1;
while t>=tf
for r=1:Markov_length % Markov链长度
% 产生随机扰动
if (rand < 0.5) % 随机决定是进行两交换还是三交换
% 两交换
ind1 = 0; ind2 = 0;
while (ind1 == ind2)
ind1 = ceil(rand.*amount);
ind2 = ceil(rand.*amount);
end
tmp1 = sol_new(ind1);
sol_new(ind1) = sol_new(ind2);
sol_new(ind2) = tmp1;
else
% 三交换
ind1 = 0; ind2 = 0; ind3 = 0;
while (ind1 == ind2) || (ind1 == ind3) ...
|| (ind2 == ind3) || (abs(ind1-ind2) == 1)
ind1 = ceil(rand.*amount);
ind2 = ceil(rand.*amount);
ind3 = ceil(rand.*amount);
end
tmp1 = ind1;tmp2 = ind2;tmp3 = ind3;
% 确保ind1 < ind2 < ind3
if (ind1 < ind2) && (ind2 < ind3)
;
elseif (ind1 < ind3) && (ind3 < ind2)
ind2 = tmp3;ind3 = tmp2;
elseif (ind2 < ind1) && (ind1 < ind3)
ind1 = tmp2;ind2 = tmp1;
elseif (ind2 < ind3) && (ind3 < ind1)
ind1 = tmp2;ind2 = tmp3; ind3 = tmp1;
elseif (ind3 < ind1) && (ind1 < ind2)
ind1 = tmp3;ind2 = tmp1; ind3 = tmp2;
elseif (ind3 < ind2) && (ind2 < ind1)
ind1 = tmp3;ind2 = tmp2; ind3 = tmp1;
end
tmplist1 = sol_new((ind1+1):(ind2-1));
sol_new((ind1+1):(ind1+ind3-ind2+1)) = ...
sol_new((ind2):(ind3));
sol_new((ind1+ind3-ind2+2):ind3) = ...
tmplist1;
end
%检查是否满足约束
% 计算目标函数值(即内能)
E_new = 0;
for i = 1 : (amount-1)
E_new = E_new + ...
D(sol_new(i),sol_new(i+1));
end
% 再算上从最后一个城市到第一个城市的距离
E_new = E_new + ...
D(sol_new(amount),sol_new(1));
if E_new < E_current
E_current = E_new;
sol_current = sol_new;
if E_new < E_best
% 把冷却过程中最好的解保存下来
E_best = E_new;
sol_best = sol_new;
end
else
% 若新解的目标函数值小于当前解的,
% 则仅以一定概率接受新解
if rand < exp(-(E_new-E_current)./t)
E_current = E_new;
sol_current = sol_new;
else
sol_new = sol_current;
end
end
end
t=t.*a; % 控制参数t(温度)减少为原来的a倍
end
disp('最优解为:')
disp(sol_best)
disp('最短距离:')
disp(E_best)
运行结果:
最优解为:
1 至 22 列
1 至 22 列
1 5 18 21 19 20 26 27 30 24 25 22 23 29 4 6 11 13 14 17 28 16 15 12
23 至 30 列
9 7 10 3 8 2
最短距离:
405.2805
405.2805
贪心算法
n = 30 ; %用于记录点数
best = 1:1:n; %生成一个用来存储点顺序的矩阵
handle = 1:1:n;
x=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','B2:B31');
y=xlsread('C题附件1.xlsx','C2:C31');
r=6371;
D = zeros(n) ;
for i = 1 : n
for j = 1 : n
D(i,j) = r*acos(cos(y(i))*cos(y(j))*cos(x(i)-x(j))+sin(y(i))*sin(y(j))); %距离矩阵
end
end
best(1) = 1; %默认起点
num = 1;
for a = 1:(n-2) %需要n-2次判断
handle(:,1)=[]; %上一次最优点的数据裁掉
dis = zeros(1,(n-a)); %用来存剩下各个点的距离
for b = 1:(n-a) %用来获取剩下各个点的距离
dis(b) = D (num , handle(b));
end
num1 = find( dis == min(dis) ); %得到最优点所在检索
t = handle(1); %将最优点与最前面的点位置进行交换
handle(1) = handle(num1);
handle(num1) = t;
num = handle(1); %获取下次进行操作的数
best(a+1) = handle(1); %将最优点存入best数组
end
best(n) = handle(num1); %补上最后一个点
plot(x(best),y(best),'-+') ; %用'+'标出点并用实线连接得到最优路径
grid on
disp(best)
运行结果:
最短路径:
1 至 22 列
1 2 8 10 3 4 6 11 9 7 12 13 14 17 16 15 28 5 29 23 22 24
23 至 30 列
25 20 26 30 27 19 21 18
最短距离:484.4739

遗传算法
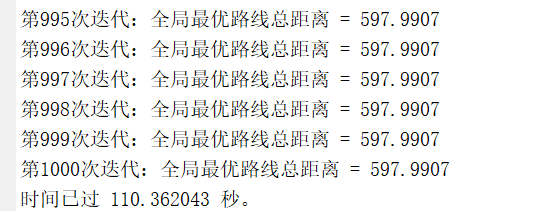
运行结果:
最优路径:1 7 9 12 11 17 28 16 15 13 14 6 8 4 23 22 24 20 30 27 26 25 21 18 29 2 3 10 5 19
最短距离:597.9907


