1. UUID: (Universally Unique Identifier) 通用唯一标识符,
是一个标识符标准用于软件架构,由开放软件基金会(OSF)作为分布式计算环境(DCE)的一部分而制作的标准。
UUID的目的是让分布式系统中的所有元素都能有唯一的辨识资讯,不需要透过中央控制端来做辨认资讯的制定。如此一来每个人都建立一个与其他人不同的标识符,这样在存储到数据库中时,就不用担心名称相同的事情(功能类似数据库中的主键,但是数据库的主键只是在一张表中有效).
这个标准现在被广泛应用在微软的全球唯一标识上面(GUID)。
2. GUID:(Globally Unique Identifier) 全球唯一标识符,是一个假随机数用于软件中。
GUID的特点:
(1). 全球唯一性:
世界上两台计算机生成的GUID都不相同,GUID主要用于拥有多个节点、多台计算机组成的计算机网络和系统中,分配具有唯一性的标志符。在时间和空间上都能保证唯一性,保证在同一时间不同的地点生成的GUID值不同。
(2). 组成结构:通过特定算法生成的一个二进制长度为为128的字符串,在用GUID时是由算法自动生成,不需要任何机构来帮助。
GUID 的格式为“xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx”,其中每个 x 是 0-9 或 a-f 范围内的一个十六进制的数字。
例如:6F9619FF-8B86-D011-B42D-00C04FC964FF 即为有效的 GUID 值。------>一个16进制是4个二进制,所以共32位。
(3). 应用:世界上所有用户的每一个Office文档计算机都会自动生成一个GUID值,并作为这个Office的唯一标识符;而且这个GUID值与计算机的网卡是相关的,
但是这个GUID值对作者是不可见的。作者的信息可以通过GUID的值找到。
当某台ESX主机上的虚拟机(例如:Windows 2003)都是由一个模版(Template Window 2003)发布而来,当其中一台A,需要增加系统盘空间的时候,这时候我会做一个操作,将A关机;之后,将A机的系统盘挂载到B机上,准备进行增加容量操作;但在启动B机后,就会弹出错误框,说UUID相同,即UUID冲突,B机启动失败。
修改之前,首先必须关闭将被修改的虚拟机,否则会收到如下错误:
Failed to open 'XXXX.vmdk' : Device or resource busy (1048585).
使用ESX自带命令: vmkfstools(推荐)
1、使用SSH client 连接到ESX主机
2、转到UUID相同的磁盘存放路径(我的例子为B机磁盘存放路径)
3、输入命令:vmkfstools -J setuuid XXXX.vmdk
命令成功执行后,会显示新分配的UUID。
例如: UUID is 56 4d c6 6c c7 67 cf 73-ee a9 62 54 d6 63 1c c5
补充:vmkfstools -J getuuid XXXX.vmdk 可以查看当前系统的UUID
wmic path win32_computersystemproduct get uuid
wmic bios get name, serialnumber, version
wmic csproduct get name, identifyingnumber, uuid
wmic cpu get name, CurrentClockSpeed, MaxClockSpeed
WMIC csproduct list /format
get-wmiobject Win32_ComputerSystemProduct -computername RANTPC | Select-Object -ExpandProperty UUID
5、查看电脑SID和域SID方法:
注册表:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE-----SAM---SAM--Domain---Builtin-Aliases--Members--
查看SID客户端加入域时,RID角色的域控制器会分配给客户端一个对象的SID(域SID+RID),SID一般不会变,除非重新加入域。
6、sysprep重新生成SID
Sysprep.exe可用于重新生成SID,运行sysprep.exe后,重新封装计算机)
在虚拟机上安装好操作系统中,进入c:windowssystem32sysprep进入系统全新体验OOBE勾选通用然后关机
再复制此系统就不会重复系统SID
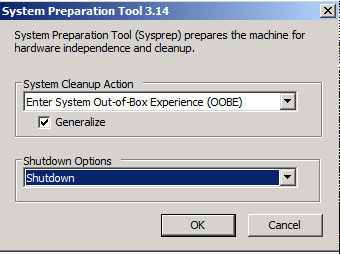
参考http://www.cnblogs.com/thescentedpath/p/registerkey.html
A computer that is running Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, or Windows XP does not appear in the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) console.
This issue occurs if the computer was set up by using a Windows 2000 image, a Windows Server 2003 image, or a Windows XP image in which the registry value for SusClientID is populated before it is deployed to client computers.
When you use Sysprep to generalize an image for a virtual machine, or when you use a unique SID-generating technology to create the images, the SusClientId registry value is not cleared if it is populated within the image before the image is deployed.
Note In WSUS 3.0, the client changes its SusClientID if the hardware configuration changes. For Windows Vista, for Windows Server 2008, and for later versions, Sysprep is changed to reset the SusClientID. Therefore, this problem affects only virtual machines that run pre-Windows Vista operating systems, or that were not created by using Sysprep.