按序号查看
- 1.改变数组形状
- 2.数组展开
- 3.轴移动
- 4.轴交换
- 5.数组转置
- 6.维度改变
- 7.类型转换
- 8.数组连接
- 9.数组堆叠
- 10.数组拆分
- 11.元素删除
- 12.插入
- 13.附加
- 14.重设尺寸
- 15.翻转数组
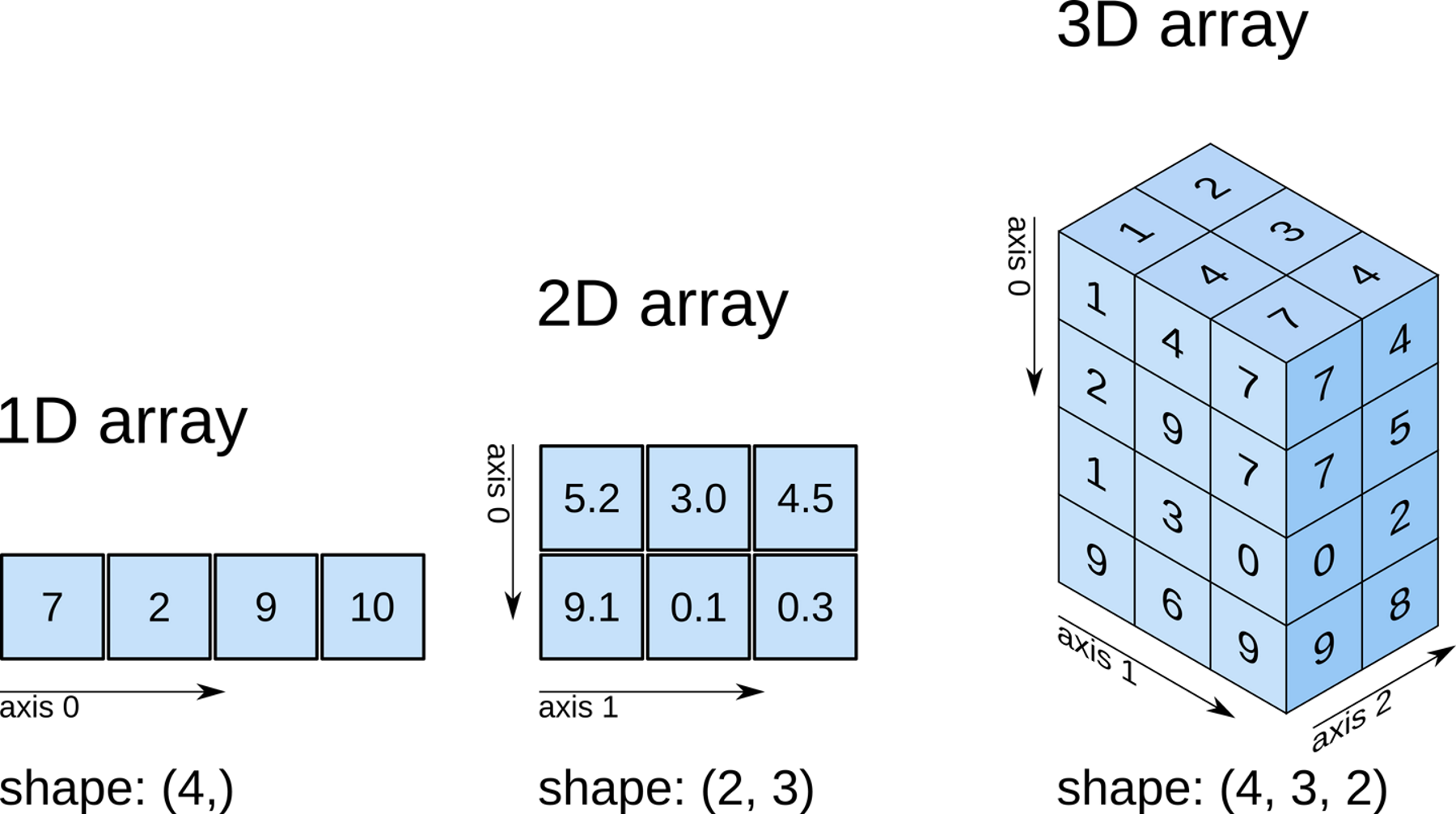
0. NumPy 数组图示
注意axis定义,shape返回的大小与axis轴对应
1. 改变数组形状
reshape 可以在不改变数组数据的同时,改变数组的形状:
numpy.reshape(a, newshape) //newshape 用于指定新的形状(整数或者元组)。
2. 数组展开
目的是将任意形状的数组扁平化,变为 1 维数组
numpy.ravel(a, order='C')
a.ravel() //同方法
//order 表示变换时的读取顺序,默认是按行依次读取,当 ='F' 时,可以按列依次读取排序。
3. 轴移动
numpy.moveaxis(a, source, destination)
• a:数组。
• source:要移动的轴的原始位置。
• destination:要移动的轴的目标位置。
example:
a = np.ones((1, 2, 3)) // a.shape=(1,2,3)
np.moveaxis(a, 0, -1) // a.shape=(2,3,1) 将0轴移到末端
4. 轴交换
numpy.swapaxes(a, axis1, axis2)
• a:数组。
• axis1:需要交换的轴 1 位置。
• axis2:需要与轴 1 交换位置的轴 1 位置。
5. 数组(矩阵)转置、求逆
np.linalg.inv(A) //求逆
a.T //转置
numpy.transpose(a, axes=None) //转置
• axis:该值默认为'none',表示转置。如果有值,那么则按照值替换轴。
example:(axis无值则与转置同效果)
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3) //a.shape=(0,1,2)
b=np.transpose(a, (1,0,2)) //a.shape=(1,0,2)
6. 维度改变
将输入数据直接视为 x维。这里的 x 可以表示:1,2,3。方法分别为:
numpy.atleast_1d()
numpy.atleast_2d()
numpy.atleast_3d()
example:
np.atleast_3d([7, 8, 9,7,5,1,2,4,8,5,3])
结果:
array[[[7]
[8]
[9]
[7]
[5]
[1]
[2]
[4]
[8]
[5]
[3]]]
7. 类型转换
在 NumPy中,还有一系列以as 开头的方法,它们可以将特定输入转换为数组,亦可将数组转换为矩阵、标量,ndarray 等
a.tolist():转换为python的list类型
np.mat(A):将A转为矩阵mat类型
asarray(a,dtype,order):将特定输入转换为数组。
asanyarray(a,dtype,order):将特定输入转换为 ndarray。
asmatrix(data,dtype):将特定输入转换为矩阵。
asfarray(a,dtype):将特定输入转换为 float 类型的数组。
asarray_chkfinite(a,dtype,order):将特定输入转换为数组,检查NaN或infs。
asscalar(a):将大小为 1 的数组转换为标量。
8. 数组连接
numpy.concatenate((a1, a2, ...), axis=0)
• (a1, a2, ...):需要连接的数组。
• axis:指定连接轴。
example:按axis=0轴连接
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
b = np.array([[7, 8], [9, 10]])
c = np.array([[11, 12]])
np.concatenate((a, b, c), axis=0)
结果:array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10],
[11, 12]])
example:按axis=1轴连接
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
b = np.array([[7, 8, 9]])
np.concatenate((a, b.T), axis=1)
结果:array([[1, 2, 7],
[3, 4, 8],
[5, 6, 9]])
9. 数组堆叠
stack(arrays,axis):沿着新轴连接数组的序列。
column_stack():将 1 维数组作为列堆叠到 2 维数组中。
hstack():按水平方向堆叠数组。
vstack():按垂直方向堆叠数组。
dstack():按深度方向堆叠数组。
example :
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
np.stack((a, b)) //默认axis=0
结果:array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
example :
np.stack((a, b), axis=-1) //因为维度为二维,axis=-1等效axis=1
结果:array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]])
10. 数组拆分
split(ary,indices_or_sections,axis):将数组拆分为多个子数组,indices_or_sections拆成几份
dsplit(ary,indices_or_sections):按深度方向将数组拆分成多个子数组。
hsplit(ary,indices_or_sections):按水平方向将数组拆分成多个子数组。
vsplit(ary,indices_or_sections):按垂直方向将数组拆分成多个子数组。
example:
a = np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5)
np.split(a, 2)
结果:[array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), array([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])]
11. 删除元素
delete(arr,obj,axis):沿特定轴删除数组中的子数组
example:
delete(a, 2, 1):删除a中第3列
12. 插入
insert(arr,obj,values,axis):依据索引在特定轴之前插入值。
example:
a = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
b = np.arange(4)
np.insert(a, 2, b, 0)
结果:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
13. 附加:相当于在末端插入
append(arr,values,axis):将值附加到数组的末尾,并返回 1 维数组(即展开)。
example:
a = np.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)
b = np.arange(3)
np.append(a, b)
结果:
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2])
14. 重设尺寸
shape是相当于拷贝后变换,resize是直接对原数组动刀
resize(a,new_shape):对数组尺寸进行重新设定。
15. 翻转数组
fliplr(m):左右翻转数组。
flipud(m):上下翻转数组。