去年七月份因为学校项目需要开始接触图像处理,但那时候只是到网上找车牌识别代码,然后加入到自己的项目中,不太清楚细节原理。
现在自己重新一步步实现车牌识别。
车牌识别流程:

高斯模糊:
车牌识别中利用高斯模糊将图片平滑化,去除干扰的噪声对后续图像处理的影响。
高斯模糊(GaussianBlur()),也叫高斯平滑。
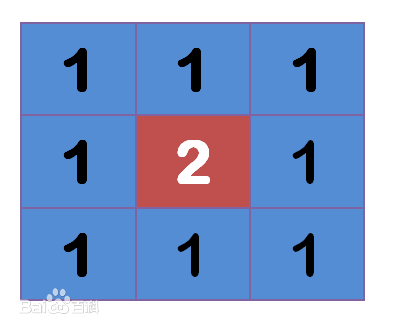

src:输入图片,可以使是任意通道数,该函数对通道是独立处理的,但是深度只能是CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_16S, CV_32F or CV_64F.
sigmaX:高斯内核在X方向的标准方差。
sigmaY:高斯内核在Y方向的标准方差。如果sigmaY为0,他将和sigmaX的值相同,如果他们都为0,那么他们由ksize.width和ksize.height计算得出。
borderType:用于判断图像边界的模式。

1 Mat Gaussian(Mat &img) { 2 Mat out; 3 GaussianBlur(img, out, Size(3, 3), 4 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT); 5 return out; 6 7 }
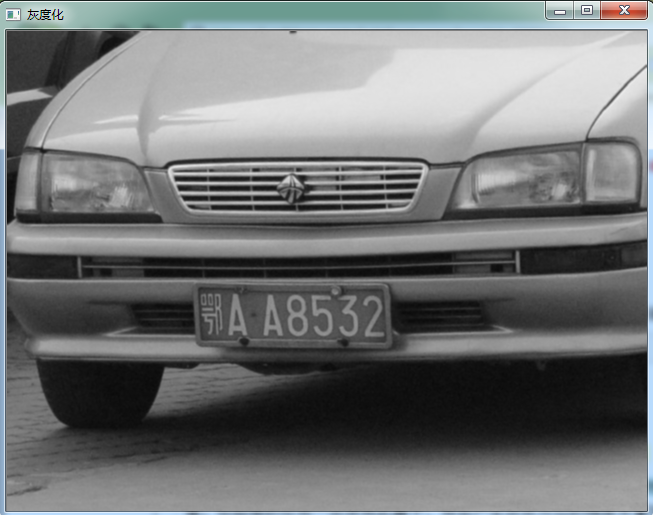
原图:(来自百度)


灰度化:
在车牌识别中我们需要将图像转化为灰度图像,这样有利于后续步骤的开展,如Soble算子只能作用于灰度图像。
灰度化,在RGB模型中,如果R=G=B时,则彩色表示一种灰度颜色,其中R=G=B的值叫灰度值,因此,灰度图像每个像素只需一个字节存放灰度值(又称强度值、亮度值),灰度范围为0-255。
Opencv中函数
void cvtColor(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int code, int dstCn=0 )
参数详解:
src:输入图像:8位无符号的16位无符号(cv_16uc…)或单精度浮点。
dst:的大小和深度src.
code:输出图像颜色空间转换的代码。
dstCn:目标图像中的信道数;如果参数为0,则从SRC和代码自动导出信道的数目。

1 Mat Grayscale(Mat &img) { 2 Mat out; 3 cvtColor(img, out, CV_RGB2GRAY); 4 5 return out; 6 }
Sobel算子(X方向):
车牌定位的核心算法,水平方向上的边缘检测,检测出车牌区域。
主要用于获得数字图像的一阶梯度,常见的应用和物理意义是边缘检测。在技术上,它是一个离散的一阶差分算子,用来计算图像亮度函数的一阶梯度之近似值。在图像的任何一点使用此算子,将会产生该点对应的梯度矢量或是其法矢量。
参数:
src: 源图像。
dst:相同大小和相同数量的通道的目标图像。
ddepth:目标图像的深度。
xorder:阶导数的X.
yorder:阶导数的Y.
ksize:扩展Sobel算子–大小。它必须是1, 3, 5,或者7。
scale:计算衍生值的可选刻度因子。默认情况下,不应用缩放。看到getderivkernels()详情。
delta :可选的delta值,在将它们存储在DST之前添加到结果中。
bordertype:像素外推方法。
convertScaleAbs()——先缩放元素再取绝对值,最后转换格式为8bit型。

1 Mat Sobel(Mat &img) { 2 Mat out; 3 Mat grad_x, grad_y; 4 Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; 5 6 //X方向 7 //Sobel(img, grad_x, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 8 //convertScaleAbs(grad_x, abs_grad_x); 9 Sobel(img, img, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 10 convertScaleAbs(img, out); 11 12 //Y方向 13 //Sobel(img, grad_y, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 14 //convertScaleAbs(grad_y, abs_grad_y); 15 //convertScaleAbs(img, out); 16 17 //合并 18 //addWeighted(abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, out); 19 20 return out; 21 }

二值化:
进一步对图像进行处理,强化目标区域,弱化背景。
图像的二值化,就是将图像上的像素点的灰度值设置为0或255,也就是将整个图像呈现出明显的只有黑和白的视觉效果。
OpenCV中函数
double threshold(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double thresh, double maxVal, int thresholdType)
参数:
src:源阵列(单通道,32位浮点8位)。
dst:相同大小和类型的目标数组。
thresh:门限阈值。
Maxval:最大值使用的thresh_binary和thresh_binary_inv阈值类型。
thresholdtype:阈值型,如下。
THRESH_BINARY 当前点值大于阈值时,取Maxval,也就是第四个参数,下面再不说明,否则设置为0
THRESH_BINARY_INV 当前点值大于阈值时,设置为0,否则设置为Maxval
THRESH_TRUNC 当前点值大于阈值时,设置为阈值,否则不改变
THRESH_TOZERO 当前点值大于阈值时,不改变,否则设置为0
THRESH_TOZERO_INV 当前点值大于阈值时,设置为0,否则不改变

1 Mat TwoValued(Mat &img) { 2 Mat out; 3 threshold(img, out, 0, 255, CV_THRESH_OTSU + CV_THRESH_BINARY); 4 //threshold(img, out, 100, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); 5 6 return out; 7 }

闭操作:
闭操作可以将目标区域连成一个整体,便于后续轮廓的提取。
闭操作可使轮廓线更光滑,但与开操作相反的是,闭操作通常消弥狭窄的间断和长细的鸿沟,消除小的空洞,并填补轮廓线中的断裂。
参数:
src:源图像。
dst:相同大小和类型的目标图像。
element:内核类型 用getStructuringElement函数得到。
OP:
可以是以下形式之一的形态学操作的类型:
morph_open -开启操作
morph_close -闭合操作
morph_gradient -形态学梯度
morph_tophat“顶帽”
morph_blackhat -“黑帽”
iterations:侵蚀和膨胀的次数被应用。
bordertype–像素外推方法。
bordervalue–边界值在一个恒定的边界情况。默认值有特殊含义。
关注前4个参数即可,后面用默认参数。

1 Mat Close(Mat &img) { 2 Mat out; 3 //Mat element(5, 5, CV_8U, cv::Scalar(1)); 4 Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(17, 5)); 5 morphologyEx(img, out, cv::MORPH_CLOSE, element); 6 7 return out; 8 }

取轮廓:
将前面处理的车牌目标区域提取出来。
相关函数:
查找轮廓:
void findContours(InputOutputArray image, OutputArrayOfArrays contours, OutputArray hierarchy, int mode, int method, Point offset=Point())
image: 输入的 8-比特、单通道图像. 非零元素被当成 1, 0 象素值保留为 0 - 从而图像被看成二值的。为了从灰度图像中得到这样的二值图像,可以使用 cvThreshold, cvAdaptiveThreshold 或 cvCanny. 本函数改变输入图像内容。
storage :得到的轮廓的存储容器
first_contour :输出参数:包含第一个输出轮廓的指针
header_size :如果 method=CV_CHAIN_CODE,则序列头的大小 >=sizeof(CvChain),否则 >=sizeof(CvContour) .
mode :
提取模式.
CV_RETR_EXTERNAL - 只提取最外层的轮廓
CV_RETR_LIST - 提取所有轮廓,并且放置在 list 中
CV_RETR_CCOMP - 提取所有轮廓,并且将其组织为两层的 hierarchy: 顶层为连通域的外围边界,次层为洞的内层边界。
CV_RETR_TREE - 提取所有轮廓,并且重构嵌套轮廓的全部 hierarchy
method :
逼近方法 (对所有节点, 不包括使用内部逼近的 CV_RETR_RUNS).
CV_CHAIN_CODE - Freeman 链码的输出轮廓. 其它方法输出多边形(定点序列).
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE - 将所有点由链码形式翻译(转化)为点序列形式
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE - 压缩水平、垂直和对角分割,即函数只保留末端的象素点;
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,
CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS - 应用 Teh-Chin 链逼近算法. CV_LINK_RUNS - 通过连接为 1 的水平碎片使用完全不同的轮廓提取算法。仅有 CV_RETR_LIST 提取模式可以在本方法中应用.
offset :
每一个轮廓点的偏移量. 当轮廓是从图像 ROI 中提取出来的时候,使用偏移量有用,因为可以从整个图像上下文来对轮廓做分析.
函数 cvFindContours 从二值图像中提取轮廓,并且返回提取轮廓的数目。指针 first_contour 的内容由函数填写。它包含第一个最外层轮廓的指针,如果指针为 NULL,则没有检测到轮廓(比如图像是全黑的)。其它轮廓可以从 first_contour 利用 h_next 和 v_next 链接访问到。 在 cvDrawContours 的样例显示如何使用轮廓来进行连通域的检测。轮廓也可以用来做形状分析和对象识别 - 见CVPR2001 教程中的 squares 样例。该教程可以在 SourceForge 网站上找到。
绘制轮廓:
void drawContours(InputOutputArray image, InputArrayOfArrays contours, int contourIdx, const Scalar& color, intthickness=1, int lineType=8, InputArray hierarchy=noArray(), int maxLevel=INT_MAX, Point offset=Point() )

相关参数参考——http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/modules/imgproc/doc/structural_analysis_and_shape_descriptors.html?highlight=drawcontours#cv.DrawContours
漫水填充算法:
int floodFill(InputOutputArray image, Point seed, Scalar newVal, Rect* rect=0, Scalar loDiff=Scalar(), ScalarupDiff=Scalar(), int flags=4 )



相关参数参考——http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/modules/imgproc/doc/miscellaneous_transformations.html?highlight=floodfill#cv.FloodFill
尺寸判断函数

1 bool verifySizes(RotatedRect mr) 2 { 3 float error = 0.3; 4 //Spain car plate size: 52x11 aspect 4,7272 5 //China car plate size: 440mm*140mm,aspect 3.142857 6 float aspect = 3.142857; 7 //Set a min and max area. All other patchs are discarded 8 int min= 1*aspect*1; // minimum area 9 int max= 2000*aspect*2000; // maximum area 10 //int min = 44 * 14 * m_verifyMin; // minimum area 11 //int max = 44 * 14 * m_verifyMax; // maximum area 12 //Get only patchs that match to a respect ratio. 13 float rmin = aspect - aspect*error; 14 float rmax = aspect + aspect*error; 15 16 int area = mr.size.height * mr.size.width; 17 float r = (float)mr.size.width / (float)mr.size.height; 18 if (r < 1) 19 { 20 r = (float)mr.size.height / (float)mr.size.width; 21 } 22 23 if ((area < min || area > max) || (r < rmin || r > rmax)) 24 { 25 return false; 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 return true; 30 } 31 }
均衡直方图:

1 Mat histeq(Mat in) 2 { 3 Mat out(in.size(), in.type()); 4 if (in.channels() == 3) { 5 Mat hsv; 6 vector<Mat> hsvSplit; 7 cvtColor(in, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV); 8 split(hsv, hsvSplit); 9 equalizeHist(hsvSplit[2], hsvSplit[2]); 10 merge(hsvSplit, hsv); 11 cvtColor(hsv, out, CV_HSV2BGR); 12 } 13 else if (in.channels() == 1) { 14 equalizeHist(in, out); 15 } 16 17 return out; 18 19 }
整体代码:

1 void Contour(Mat &img, Mat &out) { 2 RNG rng(12345); 3 4 vector< Mat > contours(1000); 5 vector<Vec4i> hierarchy(1000); 6 findContours(img, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0)); 7 8 9 vector< Mat >::iterator itc = contours.begin(); 10 vector<RotatedRect> rects; 11 int t = 0; 12 while (itc != contours.end()) { 13 //Create bounding rect of object 14 RotatedRect mr = minAreaRect(Mat(*itc)); 15 //large the rect for more 16 if (!verifySizes(mr)) { 17 itc = contours.erase(itc); 18 } 19 else { 20 ++itc; 21 rects.push_back(mr); 22 } 23 } 24 25 cv::Mat result; 26 img.copyTo(result); 27 for (int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++) 28 { 29 drawContours(result, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point()); 30 //drawContours(result, contours, i, Scalar(255), 2); 31 } 32 33 //imshow("MASK11", result); 34 35 for (int i = 0; i < rects.size(); i++) { 36 circle(result, rects[i].center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1); 37 38 float minSize = (rects[i].size.width < rects[i].size.height) ? rects[i].size.width : rects[i].size.height; 39 //minSize = minSize - minSize*0.5; 40 41 srand(time(NULL)); 42 Mat mask; 43 mask.create(out.rows + 2, out.cols + 2, CV_8UC1); 44 mask = Scalar::all(0); 45 int loDiff = 30; 46 int upDiff = 30; 47 int connectivity = 4; 48 int newMaskVal = 255; 49 int NumSeeds = 10; 50 Rect ccomp; 51 int flags = connectivity + (newMaskVal << 8) + CV_FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE + CV_FLOODFILL_MASK_ONLY; 52 53 for (int j = 0; j < NumSeeds; j++) { 54 Point seed; 55 seed.x = rects[i].center.x + rand() % (int)minSize - (minSize / 2); 56 seed.y = rects[i].center.y + rand() % (int)minSize - (minSize / 2); 57 circle(result, seed, 1, Scalar(0, 255, 255), -1); 58 int area = floodFill(out, mask, seed, Scalar(255, 0, 0), &ccomp, Scalar(loDiff, loDiff, loDiff), Scalar(upDiff, upDiff, upDiff), flags); 59 } 60 61 //imshow("MASK", mask); 62 63 vector<Point> pointsInterest; 64 Mat_<uchar>::iterator itMask = mask.begin<uchar>(); 65 Mat_<uchar>::iterator end = mask.end<uchar>(); 66 for (; itMask != end; ++itMask) 67 if (*itMask == 255) 68 pointsInterest.push_back(itMask.pos()); 69 70 RotatedRect minRect = minAreaRect(pointsInterest); 71 72 if (verifySizes(minRect)) { 73 // rotated rectangle drawing 74 Point2f rect_points[4]; minRect.points(rect_points); 75 for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) 76 line(result, rect_points[j], rect_points[(j + 1) % 4], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8); 77 78 //Get rotation matrix 79 float r = (float)minRect.size.width / (float)minRect.size.height; 80 float angle = minRect.angle; 81 if (r < 1) 82 angle = 90 + angle; 83 Mat rotmat = getRotationMatrix2D(minRect.center, angle, 1); 84 85 //Create and rotate image 86 Mat img_rotated; 87 warpAffine(out, img_rotated, rotmat, out.size(), CV_INTER_CUBIC);//实现旋转 88 89 //Crop image 90 Size rect_size = minRect.size; 91 if (r < 1) 92 swap(rect_size.width, rect_size.height); 93 Mat img_crop; 94 getRectSubPix(img_rotated, rect_size, minRect.center, img_crop); 95 96 Mat resultResized; 97 resultResized.create(33, 144, CV_8UC3); 98 resize(img_crop, resultResized, resultResized.size(), 0, 0, INTER_CUBIC);; 99 100 ////Equalize croped image 101 Mat grayResult; 102 cvtColor(resultResized, grayResult, CV_BGR2GRAY);// CV_RGB2GRAY 103 blur(grayResult, grayResult, Size(3, 3)); 104 grayResult = histeq(grayResult); 105 106 if (1) { 107 stringstream ss(stringstream::in | stringstream::out); 108 ss << "haha" << "_" << i << ".jpg"; 109 imwrite(ss.str(), grayResult); 110 } 111 112 } 113 } 114 }
主函数:

1 int main() { 2 Mat img; 3 Mat out; 4 //Mat result; 5 6 //载入图片 7 img = imread("test1.jpg");//, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE); 8 img.copyTo(out); 9 //imshow ("原始图", img); 10 11 img = Gaussian(img); 12 //imshow ("高斯模糊", img); 13 14 img = Grayscale(img); 15 //imshow("灰度化", img); 16 17 img = Sobel(img); 18 //imshow("Sobel_X", img); 19 20 img = TwoValued(img); 21 //imshow("二值化", img); 22 23 img = Close(img); 24 //imshow("闭操作", img); 25 26 // 27 Contour(img, out); 28 29 waitKey(0); 30 cvDestroyAllWindows(); 31 }



车牌定位部分完整代码:

1 /*------------------------------ - 程序介绍------------------------------*/ 2 //版本:VS2017 + Opencv2.4.9 3 //描述:OpenCV学习之路——车牌识别之车牌定位 4 /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 5 6 7 #include "opencv.hpp" 8 #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" 9 #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" 10 #include "opencv2corecore.hpp" 11 #include "vector" 12 #include "iostream" 13 #include "time.h" 14 15 using namespace cv; 16 using namespace std; 17 18 Mat histeq(Mat in) 19 { 20 Mat out(in.size(), in.type()); 21 if (in.channels() == 3) { 22 Mat hsv; 23 vector<Mat> hsvSplit; 24 cvtColor(in, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV); 25 split(hsv, hsvSplit); 26 equalizeHist(hsvSplit[2], hsvSplit[2]); 27 merge(hsvSplit, hsv); 28 cvtColor(hsv, out, CV_HSV2BGR); 29 } 30 else if (in.channels() == 1) { 31 equalizeHist(in, out); 32 } 33 34 return out; 35 36 } 37 38 //! 对minAreaRect获得的最小外接矩形,用纵横比进行判断 39 bool verifySizes(RotatedRect mr) 40 { 41 float error = 0.3; 42 //Spain car plate size: 52x11 aspect 4,7272 43 //China car plate size: 440mm*140mm,aspect 3.142857 44 float aspect = 3.142857; 45 //Set a min and max area. All other patchs are discarded 46 int min= 1*aspect*1; // minimum area 47 int max= 2000*aspect*2000; // maximum area 48 //int min = 44 * 14 * m_verifyMin; // minimum area 49 //int max = 44 * 14 * m_verifyMax; // maximum area 50 //Get only patchs that match to a respect ratio. 51 float rmin = aspect - aspect*error; 52 float rmax = aspect + aspect*error; 53 54 int area = mr.size.height * mr.size.width; 55 float r = (float)mr.size.width / (float)mr.size.height; 56 if (r < 1) 57 { 58 r = (float)mr.size.height / (float)mr.size.width; 59 } 60 61 if ((area < min || area > max) || (r < rmin || r > rmax)) 62 { 63 return false; 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 return true; 68 } 69 } 70 71 Mat Gaussian(Mat &img) { 72 Mat out; 73 GaussianBlur(img, out, Size(3, 3), 74 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT); 75 return out; 76 77 } 78 79 Mat Grayscale(Mat &img) { 80 Mat out; 81 cvtColor(img, out, CV_RGB2GRAY); 82 83 return out; 84 } 85 86 Mat Sobel(Mat &img) { 87 Mat out; 88 Mat grad_x, grad_y; 89 Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; 90 91 //X方向 92 //Sobel(img, grad_x, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 93 //convertScaleAbs(grad_x, abs_grad_x); 94 Sobel(img, img, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 95 convertScaleAbs(img, out); 96 97 //Y方向 98 //Sobel(img, grad_y, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); 99 //convertScaleAbs(grad_y, abs_grad_y); 100 //convertScaleAbs(img, out); 101 102 //合并 103 //addWeighted(abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, out); 104 105 return out; 106 } 107 108 Mat TwoValued(Mat &img) { 109 Mat out; 110 threshold(img, out, 0, 255, CV_THRESH_OTSU + CV_THRESH_BINARY); 111 //threshold(img, out, 100, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); 112 113 return out; 114 } 115 116 Mat Close(Mat &img) { 117 Mat out; 118 //Mat element(5, 5, CV_8U, cv::Scalar(1)); 119 Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(17, 5)); 120 morphologyEx(img, out, cv::MORPH_CLOSE, element); 121 122 return out; 123 } 124 125 126 void Contour(Mat &img, Mat &out) { 127 RNG rng(12345); 128 129 vector< Mat > contours(1000); 130 vector<Vec4i> hierarchy(1000); 131 findContours(img, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0)); 132 133 134 vector< Mat >::iterator itc = contours.begin(); 135 vector<RotatedRect> rects; 136 int t = 0; 137 while (itc != contours.end()) { 138 //Create bounding rect of object 139 RotatedRect mr = minAreaRect(Mat(*itc)); 140 //large the rect for more 141 if (!verifySizes(mr)) { 142 itc = contours.erase(itc); 143 } 144 else { 145 ++itc; 146 rects.push_back(mr); 147 } 148 } 149 150 cv::Mat result; 151 img.copyTo(result); 152 for (int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++) 153 { 154 drawContours(result, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point()); 155 //drawContours(result, contours, i, Scalar(255), 2); 156 } 157 //imshow("画轮廓", out); 158 159 for (int i = 0; i < rects.size(); i++) { 160 circle(result, rects[i].center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1); 161 162 float minSize = (rects[i].size.width < rects[i].size.height) ? rects[i].size.width : rects[i].size.height; 163 //minSize = minSize - minSize*0.5; 164 165 srand(time(NULL)); 166 Mat mask; 167 mask.create(out.rows + 2, out.cols + 2, CV_8UC1); 168 mask = Scalar::all(0); 169 int loDiff = 30; 170 int upDiff = 30; 171 int connectivity = 4; 172 int newMaskVal = 255; 173 int NumSeeds = 10; 174 Rect ccomp; 175 int flags = connectivity + (newMaskVal << 8) + CV_FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE + CV_FLOODFILL_MASK_ONLY; 176 177 for (int j = 0; j < NumSeeds; j++) { 178 Point seed; 179 seed.x = rects[i].center.x + rand() % (int)minSize - (minSize / 2); 180 seed.y = rects[i].center.y + rand() % (int)minSize - (minSize / 2); 181 circle(result, seed, 1, Scalar(0, 255, 255), -1); 182 int area = floodFill(out, mask, seed, Scalar(255, 0, 0), &ccomp, Scalar(loDiff, loDiff, loDiff), Scalar(upDiff, upDiff, upDiff), flags); 183 } 184 imshow("漫水填充", mask); 185 186 vector<Point> pointsInterest; 187 Mat_<uchar>::iterator itMask = mask.begin<uchar>(); 188 Mat_<uchar>::iterator end = mask.end<uchar>(); 189 for (; itMask != end; ++itMask) 190 if (*itMask == 255) 191 pointsInterest.push_back(itMask.pos()); 192 193 RotatedRect minRect = minAreaRect(pointsInterest); 194 195 if (verifySizes(minRect)) { 196 // rotated rectangle drawing 197 Point2f rect_points[4]; minRect.points(rect_points); 198 for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) 199 line(result, rect_points[j], rect_points[(j + 1) % 4], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8); 200 201 //Get rotation matrix 202 float r = (float)minRect.size.width / (float)minRect.size.height; 203 float angle = minRect.angle; 204 if (r < 1) 205 angle = 90 + angle; 206 Mat rotmat = getRotationMatrix2D(minRect.center, angle, 1); 207 208 //Create and rotate image 209 Mat img_rotated; 210 warpAffine(out, img_rotated, rotmat, out.size(), CV_INTER_CUBIC);//实现旋转 211 212 //Crop image 213 Size rect_size = minRect.size; 214 if (r < 1) 215 swap(rect_size.width, rect_size.height); 216 Mat img_crop; 217 getRectSubPix(img_rotated, rect_size, minRect.center, img_crop); 218 219 Mat resultResized; 220 resultResized.create(33, 144, CV_8UC3); 221 resize(img_crop, resultResized, resultResized.size(), 0, 0, INTER_CUBIC);; 222 223 ////Equalize croped image 224 Mat grayResult; 225 cvtColor(resultResized, grayResult, CV_BGR2GRAY);// CV_RGB2GRAY 226 blur(grayResult, grayResult, Size(3, 3)); 227 grayResult = histeq(grayResult); 228 229 if (1) { 230 stringstream ss(stringstream::in | stringstream::out); 231 ss << "haha" << "_" << i << ".jpg"; 232 imwrite(ss.str(), grayResult); 233 } 234 235 } 236 } 237 } 238 239 240 int main() { 241 Mat img; 242 Mat out; 243 //Mat result; 244 245 //载入图片 246 img = imread("test1.jpg");//, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE); 247 img.copyTo(out); 248 //imshow ("原始图", img); 249 img = Gaussian(img); 250 imshow ("高斯模糊", img); 251 252 img = Grayscale(img); 253 imshow("灰度化", img); 254 255 img = Sobel(img); 256 imshow("Sobel_X", img); 257 258 img = TwoValued(img); 259 imshow("二值化", img); 260 261 img = Close(img); 262 imshow("闭操作", img); 263 264 Contour(img, out); 265 266 waitKey(0); 267 cvDestroyAllWindows(); 268 }
总结:
车牌定位部分到此告一段落,但这方面的研究还要继续。
本算法仅适用于特定的图片,对于另一些场合的图片需要重新进行参数测试以判断准确率。需要对算法进一步完善,实现复杂背景下车牌的识别。
同时想要得到更准确的车牌区域,需要进行SVM训练。
注:
注解部分来自百度百科和http://www.opencv.org.cn
学习自——http://www.cnblogs.com/subconscious/p/3979988.html





