一个很清晰的架构实践,同时刨刨MySQL的坑。
一、洋葱架构简介
洋葱架构出来的其实有一点年头了。大约在2017年下半年,就有相关的说法了。不过,大量的文章在于理论性的讨论,而我们今天会用一个项目来完成这个架构。
洋葱架构,有时候也被叫做整洁架构,它本身是为高质量的软件而存在的。
相对其它架构而言,洋葱架构具有更好的可测试性、实用性和稳定性,并且足够灵活,完全适应项目未来可能的成长和进化。可以这么说,洋葱架构完美解决了三层或N层架构所面临的困难和问题。
牛吹完了,下面来看张图:
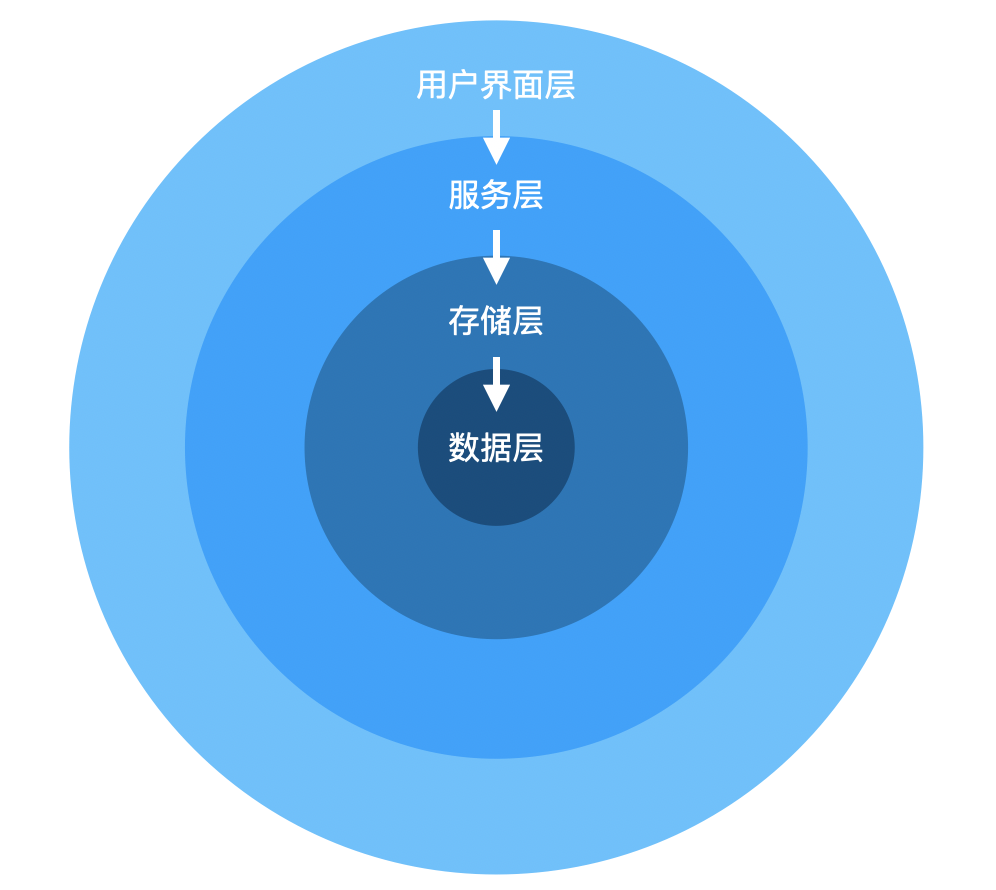
这张图,充分解释了它为什么叫洋葱架构。
不过,这不是重点。这个架构最重要的是里面的代码依赖原则:从外向内,并且只有这一个方向。处于内环的代码,不应该知道外环的任何东西。
从上面图也可以看到,洋葱架构,也使用层的概念。不过,它不同于我们习惯的三层或N层。我们来看看每个层的情况:
- 数据层(Domain Layer)
存在于架构的中心部分,由所有业务数据的实体组成。大多数情况下,就是我们的数据模型。后面的实践代码中,我是用EF(Entity Framework)来操作的数据库。
- 存储层(Repository Layer)
存储层在架构中充当服务层和数据模型之间的纽带,并且在这一层将保持所有数据库操作和应用数据的上下文。通常的做法是接口,用接口来描述数据访问所涉及的读写操作。
- 服务层(Services Layer)
服务层用于实现存储层和项目之间的通信,同时,还可以保存实体的业务逻辑。在这一层,服务接口与实现分离,以实现解耦和焦点分离。
- 用户界面层(UI Layer)
这个不解释了。项目最终对外的一层。注意,这儿可能是网站,也可能是API。不需要纠结有没有实际的界面。咱们的实践代码中,我用的是API。
为了防止不提供原网址的转载,特在这里加上原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tiger-wang/p/14547702.html
二、实践
好,现在直接进入代码。
1. 创建工程
这个不解释了,都是套路:
% dotnet new webapi -o demo -f netcoreapp3.1
我这个工程用的是Dotnet Core 3.1。框架不重要,基本上哪个版本都可以用。
下面设置Swagger
这个是我的习惯,而且这个项目是个WebApi,装个Swagger方便。
% dotnet add package swashbuckle.aspnetcore
Swagger的设置不是本文的重点,略过。需要的同学可以去看源代码。
下面,我们在工程中建三个目录:
- DomainLayer
- RepositoryLayer
- ServicesLayer
这三个目录对应上面的三个层。UI在这个项目里其实就是控制器Controller,已经存在了。
建这三个目录的目的,是为了放置三个层的代码。后面编码的时候,你会看到这三个层之间的关系。另外,这三个层在实际应用时,可以独立为三个类库,这样会更清晰。
前边说了,我会用EF操作数据库。所以,这儿还需要引入三个库:
% dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
% dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational
% dotnet add package Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql
注意,微软的EF框架没有提供MySQL的接入,所以引用了一个三方的库。
至此,项目的准备工作完成。
2. 实现数据层
在DomainLayer目录里,建一个Models目录。在Models目录下,建两个类:
BaseEntity.cs
public class BaseEntity
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public DateTime CreatedDate { get; set; }
public DateTime ModifiedDate { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
}
Customer.cs
public class Customer : BaseEntity
{
public string CustomerName { get; set; }
public string PurchasesProduct { get; set; }
public string PaymentType { get; set; }
}
两个类,Customer派生自BaseEntity。没什么特殊的含义,也是一个习惯。而且,后面到存储层写着方便。
后面,我们会用到Customer和BaseEntity实体类创建的数据表。为了让大家看的明白,我在这儿建一个目录EntityMapper,在目录里写个表结构映射。
CustomerMap.cs
public class CustomerMap : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Customer>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Customer> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(x => x.Id)
.HasName("pk_customerid");
builder.Property(x => x.Id).ValueGeneratedOnAdd()
.HasColumnName("id")
.HasColumnType("INT");
builder.Property(x => x.CustomerName)
.HasColumnName("customer_name")
.HasColumnType("NVARCHAR(100)");
builder.Property(x => x.PurchasesProduct)
.HasColumnName("purchased_product")
.HasColumnType("NVARCHAR(100)")
.IsRequired();
builder.Property(x => x.PaymentType)
.HasColumnName("payment_type")
.HasColumnType("NVARCHAR(50)")
.IsRequired();
builder.Property(x => x.CreatedDate)
.HasColumnName("created_date")
.HasColumnType("datetime");
builder.Property(x => x.ModifiedDate)
.HasColumnName("modified_date")
.HasColumnType("datetime");
builder.Property(x => x.IsActive)
.HasColumnName("is_active")
.HasColumnType("bit");
}
}
或者也可以自己创建一个表ef.Customer:
CREATE TABLE `Customer` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`created_date` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`customer_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`is_active` bit(1) DEFAULT NULL,
`modified_date` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`payment_type` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`purchased_product` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
)
3. 实现存储层
这个层,主要用来操作数据库。
先在Startup.cs中配置数据库引用:
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContextPool<ApplicationDbContext>(
options => options.UseMySql(
"server=192.168.0.241;user=root;password=xxxxxx;database=ef",
new MySqlServerVersion(new Version(8, 0, 21)),
mysqlOptions =>
{
mysqlOptions.CharSetBehavior(CharSetBehavior.NeverAppend);
}
));
}
}
这儿偷个懒,连接串就直接写代码里了。正式做项目时,最好写在配置文件中。
在RepositoryLayer目录中建一个DataContext,里面用来放置相关数据库会话,和操作的实例:
ApplicationDbContext.cs
public partial class ApplicationDbContext : DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new CustomerMap());
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
再建个目录RespositoryPattern,用来存放数据库操作的类。按照注入的原则,会是两个文件,一个接口定义,一个实现类:
IRepository.cs
public interface IRepository<T> where T : BaseEntity
{
IEnumerable<T> GetAll();
T Get(int Id);
void Insert(T entity);
void Update(T entity);
void Delete(T entity);
void Remove(T entity);
void SaveChanges();
}
Repository.cs
public class Repository<T> : IRepository<T> where T : BaseEntity
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _applicationDbContext;
private DbSet<T> entities;
public Repository(ApplicationDbContext applicationDbContext)
{
_applicationDbContext = applicationDbContext;
entities = _applicationDbContext.Set<T>();
}
public void Delete(T entity)
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
entities.Remove(entity);
_applicationDbContext.SaveChanges();
}
public T Get(int Id)
{
return entities.SingleOrDefault(c => c.Id == Id);
}
public IEnumerable<T> GetAll()
{
return entities.AsEnumerable();
}
public void Insert(T entity)
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
entities.Add(entity);
_applicationDbContext.SaveChanges();
}
public void Remove(T entity)
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
entities.Remove(entity);
}
public void SaveChanges()
{
_applicationDbContext.SaveChanges();
}
public void Update(T entity)
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
entities.Update(entity);
_applicationDbContext.SaveChanges();
}
}
4. 实现服务层
服务层用来实现核心的业务逻辑。同样先建一个目录CustomerService,方便注入,也是一个接口一个类:
ICustomerService.cs
public interface ICustomerService
{
IEnumerable<Customer> GetAllCustomers();
Customer GetCustomer(int id);
void InsertCustomer(Customer customer);
void UpdateCustomer(Customer customer);
void DeleteCustomer(int id);
}
CustomerService.cs
public class CustomerService : ICustomerService
{
private IRepository<Customer> _repository;
public CustomerService(IRepository<Customer> repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
public IEnumerable<Customer> GetAllCustomers()
{
return _repository.GetAll();
}
public Customer GetCustomer(int id)
{
return _repository.Get(id);
}
public void InsertCustomer(Customer customer)
{
_repository.Insert(customer);
}
public void UpdateCustomer(Customer customer)
{
_repository.Update(customer);
}
public void DeleteCustomer(int id)
{
Customer customer = GetCustomer(id);
_repository.Remove(customer);
_repository.SaveChanges();
}
}
4. 注入
这儿就是套路了,不解释。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddScoped(typeof(IRepository<>), typeof(Repository<>));
services.AddTransient<ICustomerService, CustomerService>();
}
5. 实现控制器
重要的三层都已经实现。下面做个演示用的控制器:
CustomerController.cs
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class CustomerController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ICustomerService _customerService;
public CustomerController(ICustomerService customerService)
{
_customerService = customerService;
}
[HttpGet(nameof(GetCustomer))]
public IActionResult GetCustomer(int id)
{
var result = _customerService.GetCustomer(id);
if (result != null)
{
return Ok(result);
}
return BadRequest("No records found");
}
[HttpGet(nameof(GetAllCustomer))]
public IActionResult GetAllCustomer()
{
var result = _customerService.GetAllCustomers();
if (result != null)
{
return Ok(result);
}
return BadRequest("No records found");
}
[HttpPost(nameof(InsertCustomer))]
public IActionResult InsertCustomer(Customer customer)
{
_customerService.InsertCustomer(customer);
return Ok("Data inserted");
}
[HttpPut(nameof(UpdateCustomer))]
public IActionResult UpdateCustomer(Customer customer)
{
_customerService.UpdateCustomer(customer);
return Ok("Updation done");
}
[HttpDelete(nameof(DeleteCustomer))]
public IActionResult DeleteCustomer(int Id)
{
_customerService.DeleteCustomer(Id);
return Ok("Data Deleted");
}
}
代码部分全部完成。编译运行~~~
三、总结
通过上面的代码可以看到:
- 洋葱架构各层间通过接口互相关联,数据引入是在运行时进行的
- 应用以区域模型为基础
- 所有的外部依赖,如数据集准入和管理调,都是在外部处理
- 适应性强,设计也方便
总之,从应用来说,洋葱架构算是个很优秀的架构。以我的经验,在多个共同开发的项目中,具有比较大的优势。
本文的相关代码,在https://github.com/humornif/Demo-Code/tree/master/0045/demo
 |
微信公众号:老王Plus 扫描二维码,关注个人公众号,可以第一时间得到最新的个人文章和内容推送 本文版权归作者所有,转载请保留此声明和原文链接 |