django是一个快速开发web应用的框架, 笔者也在django框架上开发不少web应用,闲来无事,就想探究一下django底层到底是如何实现的,本文记录了笔者对django源码的分析过程
I believe to become a better developer you MUST get a better understanding of the underlying software systems you use on a daily basis and that includes programming languages, compilers and interpreters, databases and operating systems, web servers and web frameworks. And, to get a better and deeper understanding of those systems you MUST re-build them from scratch, brick by brick, wall by wall.
笔者摘抄了一段话,送给阅读本文的读者
正文
如何分析django源码,笔者选择从django项目的启动方式开始 python manage.py runserver,本文主要分析了django项目的启动流程
#!/usr/bin/env python import os import sys if __name__ == "__main__": os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "order.settings") try: from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line except ImportError: # The above import may fail for some other reason. Ensure that the # issue is really that Django is missing to avoid masking other # exceptions on Python 2. try: import django except ImportError: raise ImportError( "Couldn't import Django. Are you sure it's installed and " "available on your PYTHONPATH environment variable? Did you " "forget to activate a virtual environment?" ) raise execute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
在manage.py文件中,我们看到启动文件的入口是 excute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
def execute_from_command_line(argv=None): """ A simple method that runs a ManagementUtility. """ utility = ManagementUtility(argv) utility.execute()
这个函数是将命令行参数传递给了ManagementUtility类,这个类的execute方法负责执行,这个方法主要是一些django的初始化参数的检查,以及通过sys.argv获取命令,得到相应的命令后,执行命令。
execute方法中的部分代码
... if settings.configured: # Start the auto-reloading dev server even if the code is broken. # The hardcoded condition is a code smell but we can't rely on a # flag on the command class because we haven't located it yet. if subcommand == 'runserver' and '--noreload' not in self.argv: try: autoreload.check_errors(django.setup)() except Exception: # The exception will be raised later in the child process # started by the autoreloader. Pretend it didn't happen by # loading an empty list of applications. apps.all_models = defaultdict(OrderedDict) apps.app_configs = OrderedDict() apps.apps_ready = apps.models_ready = apps.ready = True ...
execute方法中有一段代码autoreload.check_errors(django.setup)(),会对django项目进行一些必要的初始化,并检查初始化的错误 django.setup()方法会注册项目app和配置日志文件,注册app即对settings.INSTALLED_APPS中的app进行导入,并执行一些初始化方法
进行完所有初始化动作,继续执行代码
execute方法中的部分代码
... elif self.argv[1:] in (['--help'], ['-h']): sys.stdout.write(self.main_help_text() + ' ') else: self.fetch_command(subcommand).run_from_argv(self.argv) ...
self.fetch_command(subcommand)会返回一个BaseCommand类,主要是分析subcommand参数(subcommand是sys.argv里面获取到的),导入相应的命令类,最后返回类
我们通过分析,runserver参数最终获取到的命令类是django/contrib/staticfiles/management/command/runserver.py 里的Command类
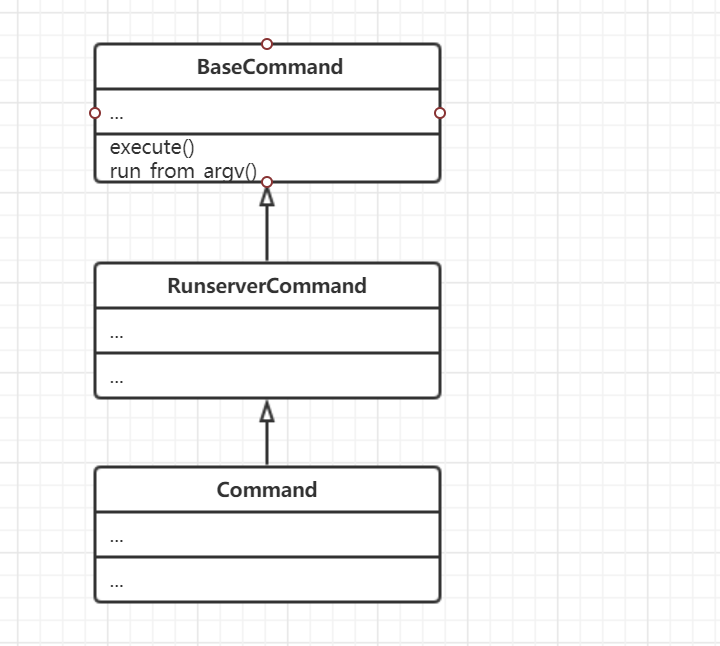
这是Command类的继承关系图。Command类通过run_from_argv(self.argv)执行命令
BaseCommand类中run_from_argv方法的部分代码
... try: self.execute(*args, **cmd_options) except Exception as e: if options.traceback or not isinstance(e, CommandError): raise ...
run_from_argv(self.argv)方法中主要通过execute()来继续执行,excute中会对django项目进行检查,然后通过self.handle()继续执行
RunserverCommand类里面的handle方法部分代码
def handle(self, *args, **options):
...
if not self.addr: self.addr = '::1' if self.use_ipv6 else '127.0.0.1' self._raw_ipv6 = self.use_ipv6 self.run(**options)
handle()方法里面也进行了一些检查,然后继续执行self.run()来启动服务器
RunserverCommand中的部分代码 def run(self, **options): """ Runs the server, using the autoreloader if needed """ use_reloader = options['use_reloader'] if use_reloader: autoreload.main(self.inner_run, None, options) else: self.inner_run(None, **options) def inner_run(self, *args, **options): ... try: handler = self.get_handler(*args, **options) run(self.addr, int(self.port), handler, ipv6=self.use_ipv6, threading=threading, server_cls=self.server_cls) except socket.error as e: ...
run方法中选择了启动的解释器,最后都是通过inner_run中的run方法来执行,会启动一个WSGIServer, WSGIServer需要一个回调函数handler(或者application),来执行django视图里面代码。
至此,django项目服务器启动流程完毕,启动了一个简单的WSGIServer,开始接受请求,解析请求参数,将请求参数传递给回调函数handler(或者application,django框架的核心内容),handler根据参数执行相应的代码,返回数据给WSGIServer,WSGIServer最终将数据返回给浏览器。
关于wsgi可以参考这篇文章,理解Python WSGI
总结:
我认为django启动流程中对于我们开发者最重要的一步在于django.setup(),里面做了很多初始化的工作,包括导入各个app的models,运行各个app的run函数,配置日志文件。我们如果想要在项目的启动的时候做一些我们自己的初始化动作,可以选择在这个地方下手。