数据结构Java实现04----循环链表、仿真链表
- 单向循环链表
- 双向循环链表
- 仿真链表
一、单向循环链表:
1、概念:
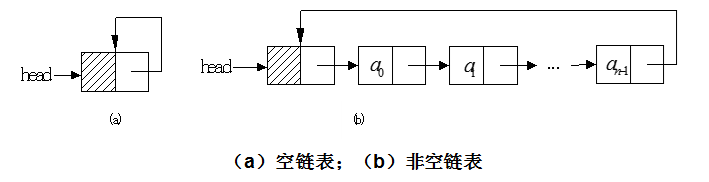
单向循环链表是单链表的另一种形式,其结构特点是链表中最后一个结点的指针不再是结束标记,而是指向整个链表的第一个结点,从而使单链表形成一个环。
和单链表相比,循环单链表的长处是从链尾到链头比较方便。当要处理的数据元素序列具有环型结构特点时,适合于采用循环单链表。
和单链表相同,循环单链表也有带头结点结构和不带头结点结构两种,带头结点的循环单链表实现插入和删除操作时,算法实现较为方便。
带头结点的循环单链表的操作实现方法和带头结点的单链表的操作实现方法类同,差别仅在于:
(1)在构造函数中,要加一条head.next = head 语句,把初始时的带头结点的循环单链表设计成上图中(a)所示的状态。
(2)在index(i)成员函数中,把循环结束判断条件current != null改为current != head。
2、单链表的代码实现:
先回顾上一篇文章,定位到第三段“三、单项链表的代码实现”,我们是需要修改这段里面的(3)LinkList.java代码,(1)和(2)的代码不变。
(3)LinkList.java:单项循环链表类:(核心代码)
1 //单向循环链表类
2 public class CycleLinkList implements List {
3
4 Node head; //头指针
5 Node current;//当前结点对象
6 int size;//结点个数
7
8 //初始化一个空链表
9 public CycleLinkList()
10 {
11 //初始化头结点,让头指针指向头结点。并且让当前结点对象等于头结点。
12 this.head = current = new Node(null);
13 this.size =0;//单向链表,初始长度为零。
14 this.head.next = this.head;
15 }
16
17 //定位函数,实现当前操作对象的前一个结点,也就是让当前结点对象定位到要操作结点的前一个结点。
18 //比如我们要在a2这个节点之前进行插入操作,那就先要把当前节点对象定位到a1这个节点,然后修改a1节点的指针域
19 public void index(int index) throws Exception
20 {
21 if(index <-1 || index > size -1)
22 {
23 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
24 }
25 //说明在头结点之后操作。
26 if(index==-1) //因为第一个数据元素结点的下标是0,那么头结点的下标自然就是-1了。
27 return;
28 current = head.next;
29 int j=0;//循环变量
30 while(current != head&&j<index)
31 {
32 current = current.next;
33 j++;
34 }
35
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 public void delete(int index) throws Exception {
40 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
41 //判断链表是否为空
42 if(isEmpty())
43 {
44 throw new Exception("链表为空,无法删除!");
45 }
46 if(index <0 ||index >size)
47 {
48 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
49 }
50 index(index-1);//定位到要操作结点的前一个结点对象。
51 current.setNext(current.next.next);
52 size--;
53 }
54
55 @Override
56 public Object get(int index) throws Exception {
57 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
58 if(index <-1 || index >size-1)
59 {
60 throw new Exception("参数非法!");
61 }
62 index(index);
63
64 return current.getElement();
65 }
66
67 @Override
68 public void insert(int index, Object obj) throws Exception {
69 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
70 if(index <0 ||index >size)
71 {
72 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
73 }
74 index(index-1);//定位到要操作结点的前一个结点对象。
75 current.setNext(new Node(obj,current.next));
76 size++;
77 }
78
79 @Override
80 public boolean isEmpty() {
81 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
82 return size==0;
83 }
84 @Override
85 public int size() {
86 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
87 return this.size;
88 }
89
90
91 }
14行是添加的代码,30行是修改的代码。
3、单项循环链表的应用举例:
编写击鼓传花小游戏。
游戏规则:N个人围成一个圈,从第一个人开始传花,当数到M时,该人退出游戏,直到剩下最后一个人。
代码实现:
(4)Game.java:
1 //游戏类
2 public class Game {
3
4 //单向循环链表
5 CycleLinkList list = new CycleLinkList();
6 //总人数
7 int num;
8 //数到几退出
9 int key;
10
11 //游戏初始化方法
12 public Game(int num,int key)
13 {
14 this.num = num;
15 this.key = key;
16 }
17
18 public void play() throws Exception
19 {
20 for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
21 {
22 list.insert(i, i);
23 }
24
25 System.out.println("
-------游戏开始之前---------
");
26 for(int i=0;i<list.size;i++)
27 {
28 System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
29 }
30 System.out.println("
-------游戏开始---------
");
31 int iCount=num; //开始等于总人数num
32 int j=0; //累加器,计算是否能被key整除。
33
34 Node node = list.head;
35 while(iCount!=1)
36 {
37 if(node.getElement()!=null&& Integer.parseInt(node.getElement().toString())!=-1)
38 {
39 j++;
40 if(j%key==0)
41 {
42 node.setElement(-1);
43 iCount--;
44 System.out.println();
45 for(int i=0;i<list.size;i++)
46 {
47 System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
48 }
49 }
50 }
51 node = node.next;
52 }
53 System.out.println("
-------游戏结束---------
");
54 for(int i=0;i<list.size;i++)
55 {
56 System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
57 }
58 }
59
60 }
(5)Test.java:
1 public class Test {
2
3 /**
4 * @param args
5 */
6 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
8 /*
9 CycleLinkList list = new CycleLinkList();
10 for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
11 {
12 int temp = ((int)(Math.random()*100))%100;
13 list.insert(i, temp);
14 System.out.print(temp+" ");
15 }
16 list.delete(4);
17 System.out.println("
------删除第五个元素之后-------");
18 for(int i=0;i<list.size;i++)
19 {
20 System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
21 }*/
22
23 Game game = new Game(10,3);
24 game.play();
25
26 }
27 }
二、双向循环链表:
双向链表:
双向链表是每个结点除后继指针外还有一个前驱指针。和单链表类同,双向链表也有带头结点结构和不带头结点结构两种,带头结点的双向链表更为常用;另外,双向链表也可以有循环和非循环两种结构,循环结构的双向链表更为常用。
双向循环链表:
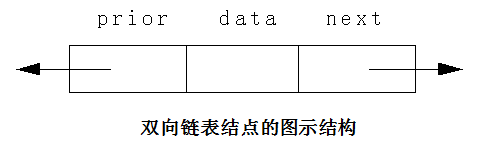
在双向链表中,每个结点包括三个域,分别是element域、next域和prior域,其中element域为数据元素域,next域为指向后继结点的对象引用,prior域为指向前驱结点的对象引用。下图为双向链表结点的图示结构:
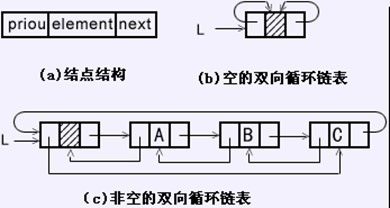
如下图是带头结点的双向循环链表的图示结构。双向循环链表的next和prior各自构成自己的单向循环链表:
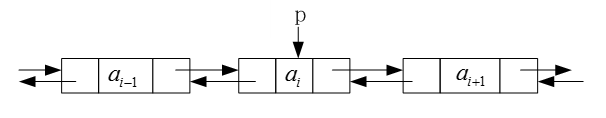
在双向链表中,有如下关系:设对象引用p表示双向链表中的第i个结点,则p.next表示第i+1个结点,p.next.prior仍表示第i个结 点,即p.next.prior == p;同样地,p.prior表示第i-1个结点,p.prior.next仍表示第i个结点,即p.prior.next == p。下图是双向链表上述关系的图示:
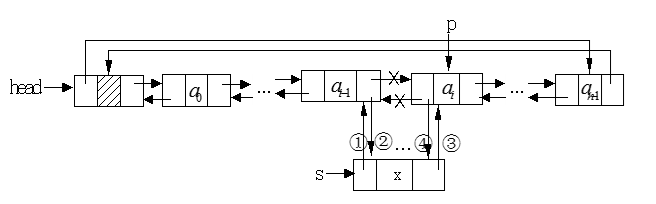
双向循环链表的插入过程:
下图中的指针p表示要插入结点的位置,s表示要插入的结点,①、②、③、④表示实现插入过程的步骤:
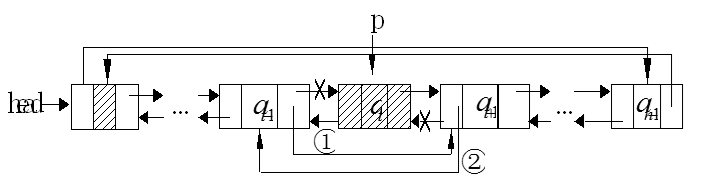
循环双向链表的删除过程:
下图中的指针p表示要插入结点的位置,①、②表示实现删除过程的步骤:
2、双向循环链表的代码实现:
(1)List.java:
1 //线性表接口
2 public interface List {
3 //获得线性表长度
4 public int size();
5
6 //判断线性表是否为空
7 public boolean isEmpty();
8
9 //插入元素
10 public void insert(int index, Object obj) throws Exception;
11
12 //删除元素
13 public void delete(int index) throws Exception;
14
15 //获取指定位置的元素
16 public Object get(int index) throws Exception;
17 }
(2)Node.java:
1 //结点类
2 public class Node {
3
4 Object element; //数据域
5 Node next; //后继指针域
6 Node prior; //前驱指针域
7
8 //头结点的构造方法
9 public Node(Node nextval) {
10 this.next = nextval;
11 }
12
13 //非头结点的构造方法
14 public Node(Object obj, Node nextval) {
15 this.element = obj;
16 this.next = nextval;
17 }
18
19 //获得当前结点的后继结点
20 public Node getNext() {
21 return this.next;
22 }
23
24 //获得当前结点的前驱结点
25 public Node getPrior() {
26 return this.prior;
27 }
28
29 //获得当前的数据域的值
30 public Object getElement() {
31 return this.element;
32 }
33
34 //设置当前结点的后继指针域
35 public void setNext(Node nextval) {
36 this.next = nextval;
37 }
38
39 //设置当前结点的前驱指针域
40 public void setPrior(Node priorval) {
41 this.prior = priorval;
42 }
43
44 //设置当前结点的数据域
45 public void setElement(Object obj) {
46 this.element = obj;
47 }
48
49 public String toString() {
50 return this.element.toString();
51 }
52 }
(3)DoubleCycleLinkList.java:
1 //单向链表类
2 public class DoubleCycleLinkList implements List {
3
4 Node head; //头指针
5 Node current;//当前结点对象
6 int size;//结点个数
7
8 //初始化一个空链表
9 public DoubleCycleLinkList() {
10 //初始化头结点,让头指针指向头结点。并且让当前结点对象等于头结点。
11 this.head = current = new Node(null);
12 this.size = 0;//单向链表,初始长度为零。
13 this.head.next = head;
14 this.head.prior = head;
15 }
16
17 //定位函数,实现当前操作对象的前一个结点,也就是让当前结点对象定位到要操作结点的前一个结点。
18 public void index(int index) throws Exception {
19 if (index < -1 || index > size - 1) {
20 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
21 }
22 //说明在头结点之后操作。
23 if (index == -1)
24 return;
25 current = head.next;
26 int j = 0;//循环变量
27 while (current != head && j < index) {
28 current = current.next;
29 j++;
30 }
31
32 }
33
34 @Override
35 public void delete(int index) throws Exception {
36 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
37 //判断链表是否为空
38 if (isEmpty()) {
39 throw new Exception("链表为空,无法删除!");
40 }
41 if (index < 0 || index > size) {
42 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
43 }
44 index(index - 1);//定位到要操作结点的前一个结点对象。
45 current.setNext(current.next.next);
46 current.next.setPrior(current);
47 size--;
48 }
49
50 @Override
51 public Object get(int index) throws Exception {
52 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
53 if (index < -1 || index > size - 1) {
54 throw new Exception("参数非法!");
55 }
56 index(index);
57
58 return current.getElement();
59 }
60
61 @Override
62 public void insert(int index, Object obj) throws Exception {
63 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
64 if (index < 0 || index > size) {
65 throw new Exception("参数错误!");
66 }
67 index(index - 1);//定位到要操作结点的前一个结点对象。
68 current.setNext(new Node(obj, current.next));
69 current.next.setPrior(current);
70 current.next.next.setPrior(current.next);
71
72 size++;
73 }
74
75 @Override
76 public boolean isEmpty() {
77 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
78 return size == 0;
79 }
80
81 @Override
82 public int size() {
83 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
84 return this.size;
85 }
86
87
88 }
(4)Test.java:
1 public class Test {
2
3 /**
4 * @param args
5 */
6 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
8 DoubleCycleLinkList list = new DoubleCycleLinkList();
9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
10 int temp = ((int) (Math.random() * 100)) % 100;
11 list.insert(i, temp);
12 System.out.print(temp + " ");
13 }
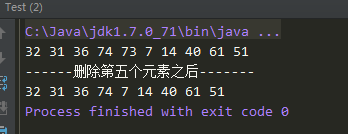
14 list.delete(4);
15 System.out.println("
------删除第五个元素之后-------");
16 for (int i = 0; i < list.size; i++) {
17 System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
18 }
19 }
20
21 }
运行效果:
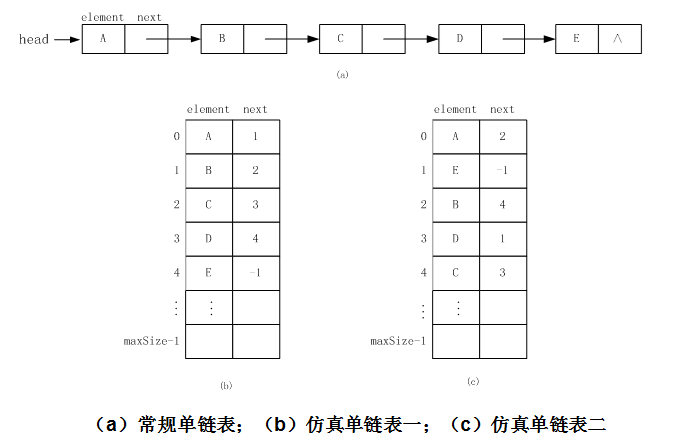
三、仿真链表:
在链式存储结构中,我们实现数据元素之间的次序关系依靠指针。我们也可以用数组来构造仿真链表。方法是在数组中增加一个(或两个)int类型的变量域,这些变量用来表示后一个(或前一个)数据元素在数组中的下标。我们把这些int类型变量构造的指针称为仿真指针。这样,就可以用仿真指针构造仿真的单链表(或仿真的双向链表)。