一 . 概述
springmvc作为一个当前最为流行的mvc框架,从本质的设计上讲还是延续了前端控制器模式来完成整合设计.
但是springmvc凭借和spring的无缝连接,获得了IOC和AOP的能力,于是功能强大了很多.
本次,我们需要从原理上说一下springmvc,然后找到一些扩展点,完成对springmvc的学习.
二 .springmvc的架构
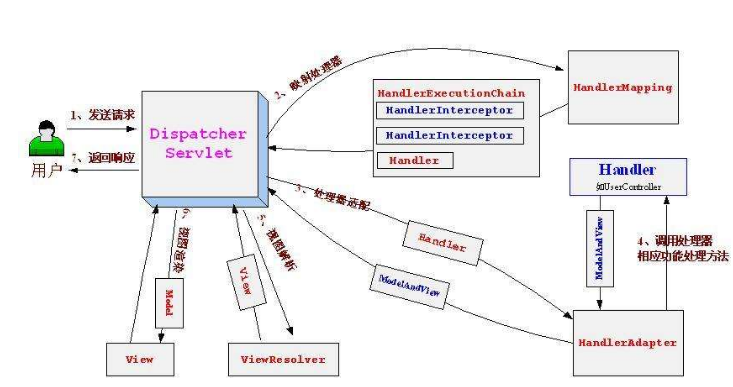
在上面的图中,我们看到了整个springmvc的运行流程.
我们发现整个流程还是比较复杂的,其实当我们在后面分析的时候,整个流程还会更加的复杂.但是现在我们不需要进行这方面的讲述.
我们首先来看看整个流程的运行.
[1]用户向web浏览器发起请求.
[2]请求转发到前端控制器,进入了springmvc的控制流程之中.
[3]首先请求转发给{处理器映射器},返回的是一个处理器执行链,其中包括处理器和拦截器.
[4]前端控制器将这个处理器执行链转发给处理器适配器,进行真正的发放的执行,在这里就有很多的扩展点.
[5]视图渲染
我们现在只需要简单的了解这个过程就好了.
三 . 前端控制器
springmvc的前端控制器是一个Servlet,我们首先看一下这个Servlet的基本结构.
下面是整个Springmvc的DispatcherServlet的核心方法doDispatch().我们首先分析一下流程.
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; //将请求换成一个处理请求的引用 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; // 定义处理器质性链 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; // 是否跟文件上传有关 //这个是异步的行为,我们这里不去关心 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; // 返回值 Exception dispatchException = null; //异常 try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); //检查是否含有文件上传 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); //如果是文件上传,进行请求的转换 // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); //通过请求,寻找对象的处理器映射器 if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); //没有处理器映射器,就说明这个请求的地址没有注册 return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//1.首先从处理器映射器之中获取处理器执行链
// 2/ 然后将处理器执行链转换为处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 处理器执行链的前置拦截行为 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } //调用真正的处理器方法 // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } //转换视图等行为,为域对象存放值等行为 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//应该处理器拦截链的后置处理行为 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; //如果出现异常,这个异常就有了整体处理的地方 } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
从上面的代码之中,我们整体的分析了springmvc的运转流程,单从流程上讲比较简单,但是后面我们的重点就是
寻找扩展点和原理,最终比较完成的学习完springmvc.