import os import sys import random import math import re import time import numpy as np import cv2 import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from config import Config import utils import model as modellib import visualize from model import log %matplotlib inline # Root directory of the project ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd() # Directory to save logs and trained model MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs") # Local path to trained weights file COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5") # Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH): utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
class ShapesConfig(Config): """Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset. Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific to the toy shapes dataset. """ # Give the configuration a recognizable name NAME = "shapes" # Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each # GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU). GPU_COUNT = 1 IMAGES_PER_GPU = 8 # Number of classes (including background) NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes # Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side # the large side, and that determines the image shape. IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 128 IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 128 # Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8, 16, 32, 64, 128) # anchor side in pixels # Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have # few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs. TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 32 # Use a small epoch since the data is simple STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100 # use small validation steps since the epoch is small VALIDATION_STEPS = 5 config = ShapesConfig() config.display()

def get_ax(rows=1, cols=1, size=8): """Return a Matplotlib Axes array to be used in all visualizations in the notebook. Provide a central point to control graph sizes. Change the default size attribute to control the size of rendered images """ _, ax = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(size*cols, size*rows)) return ax
class ShapesDataset(utils.Dataset): """Generates the shapes synthetic dataset. The dataset consists of simple shapes (triangles, squares, circles) placed randomly on a blank surface. The images are generated on the fly. No file access required. """ def load_shapes(self, count, height, width): """Generate the requested number of synthetic images. count: number of images to generate. height, the size of the generated images. """ # Add classes self.add_class("shapes", 1, "square") self.add_class("shapes", 2, "circle") self.add_class("shapes", 3, "triangle") # Add images # Generate random specifications of images (i.e. color and # list of shapes sizes and locations). This is more compact than # actual images. Images are generated on the fly in load_image(). for i in range(count): bg_color, shapes = self.random_image(height, width) self.add_image("shapes", image_id=i, path=None, width=width, height=height, bg_color=bg_color, shapes=shapes) def load_image(self, image_id): """Generate an image from the specs of the given image ID. Typically this function loads the image from a file, but in this case it generates the image on the fly from the specs in image_info. """ info = self.image_info[image_id] bg_color = np.array(info['bg_color']).reshape([1, 1, 3]) image = np.ones([info['height'], info['width'], 3], dtype=np.uint8) image = image * bg_color.astype(np.uint8) for shape, color, dims in info['shapes']: image = self.draw_shape(image, shape, dims, color) return image def image_reference(self, image_id): """Return the shapes data of the image.""" info = self.image_info[image_id] if info["source"] == "shapes": return info["shapes"] else: super(self.__class__).image_reference(self, image_id) def load_mask(self, image_id): """Generate instance masks for shapes of the given image ID. """ info = self.image_info[image_id] shapes = info['shapes'] count = len(shapes) mask = np.zeros([info['height'], info['width'], count], dtype=np.uint8) for i, (shape, _, dims) in enumerate(info['shapes']): mask[:, :, i:i+1] = self.draw_shape(mask[:, :, i:i+1].copy(), shape, dims, 1) # Handle occlusions occlusion = np.logical_not(mask[:, :, -1]).astype(np.uint8) for i in range(count-2, -1, -1): mask[:, :, i] = mask[:, :, i] * occlusion occlusion = np.logical_and(occlusion, np.logical_not(mask[:, :, i])) # Map class names to class IDs. class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s[0]) for s in shapes]) return mask, class_ids.astype(np.int32) def draw_shape(self, image, shape, dims, color): """Draws a shape from the given specs.""" # Get the center x, y and the size s x, y, s = dims if shape == 'square': cv2.rectangle(image, (x-s, y-s), (x+s, y+s), color, -1) elif shape == "circle": cv2.circle(image, (x, y), s, color, -1) elif shape == "triangle": points = np.array([[(x, y-s), (x-s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s), (x+s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s), ]], dtype=np.int32) cv2.fillPoly(image, points, color) return image def random_shape(self, height, width): """Generates specifications of a random shape that lies within the given height and width boundaries. Returns a tuple of three valus: * The shape name (square, circle, ...) * Shape color: a tuple of 3 values, RGB. * Shape dimensions: A tuple of values that define the shape size and location. Differs per shape type. """ # Shape shape = random.choice(["square", "circle", "triangle"]) # Color color = tuple([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]) # Center x, y buffer = 20 y = random.randint(buffer, height - buffer - 1) x = random.randint(buffer, width - buffer - 1) # Size s = random.randint(buffer, height//4) return shape, color, (x, y, s) def random_image(self, height, width): """Creates random specifications of an image with multiple shapes. Returns the background color of the image and a list of shape specifications that can be used to draw the image. """ # Pick random background color bg_color = np.array([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]) # Generate a few random shapes and record their # bounding boxes shapes = [] boxes = [] N = random.randint(1, 4) for _ in range(N): shape, color, dims = self.random_shape(height, width) shapes.append((shape, color, dims)) x, y, s = dims boxes.append([y-s, x-s, y+s, x+s]) # Apply non-max suppression wit 0.3 threshold to avoid # shapes covering each other keep_ixs = utils.non_max_suppression(np.array(boxes), np.arange(N), 0.3) shapes = [s for i, s in enumerate(shapes) if i in keep_ixs] return bg_color, shapes
# Training dataset dataset_train = ShapesDataset() dataset_train.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1]) dataset_train.prepare() # Validation dataset dataset_val = ShapesDataset() dataset_val.load_shapes(50, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1]) dataset_val.prepare()
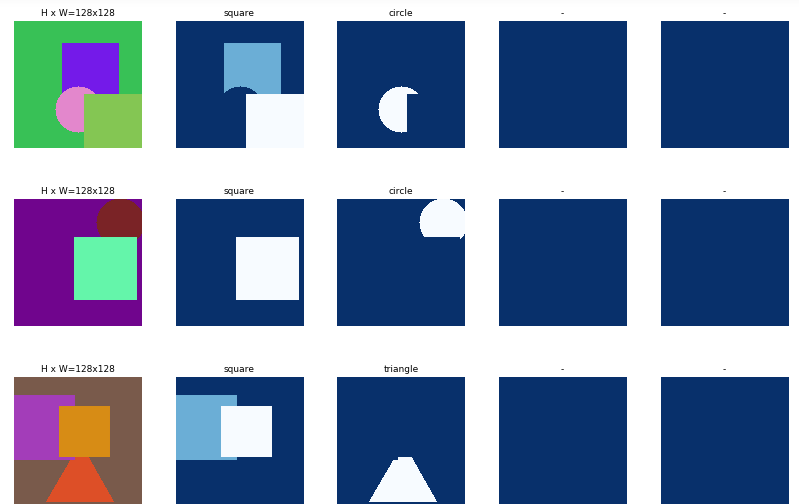
# Load and display random samples image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_train.image_ids, 4) for image_id in image_ids: image = dataset_train.load_image(image_id) mask, class_ids = dataset_train.load_mask(image_id) visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset_train.class_names)
# Create model in training mode model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config, model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Which weights to start with? init_with = "coco" # imagenet, coco, or last if init_with == "imagenet": model.load_weights(model.get_imagenet_weights(), by_name=True) elif init_with == "coco": # Load weights trained on MS COCO, but skip layers that # are different due to the different number of classes # See README for instructions to download the COCO weights model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True, exclude=["mrcnn_class_logits", "mrcnn_bbox_fc", "mrcnn_bbox", "mrcnn_mask"]) elif init_with == "last": # Load the last model you trained and continue training model.load_weights(model.find_last()[1], by_name=True)
# Train the head branches # Passing layers="heads" freezes all layers except the head # layers. You can also pass a regular expression to select # which layers to train by name pattern. model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val, learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE, epochs=1, layers='heads')

# Fine tune all layers # Passing layers="all" trains all layers. You can also # pass a regular expression to select which layers to # train by name pattern. model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val, learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10, epochs=2, layers="all")

# Save weights # Typically not needed because callbacks save after every epoch # Uncomment to save manually # model_path = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, "mask_rcnn_shapes.h5") # model.keras_model.save_weights(model_path)
class InferenceConfig(ShapesConfig): GPU_COUNT = 1 IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1 inference_config = InferenceConfig() # Recreate the model in inference mode model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference", config=inference_config, model_dir=MODEL_DIR) # Get path to saved weights # Either set a specific path or find last trained weights # model_path = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, ".h5 file name here") model_path = model.find_last()[1] # Load trained weights (fill in path to trained weights here) assert model_path != "", "Provide path to trained weights" print("Loading weights from ", model_path) model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True)
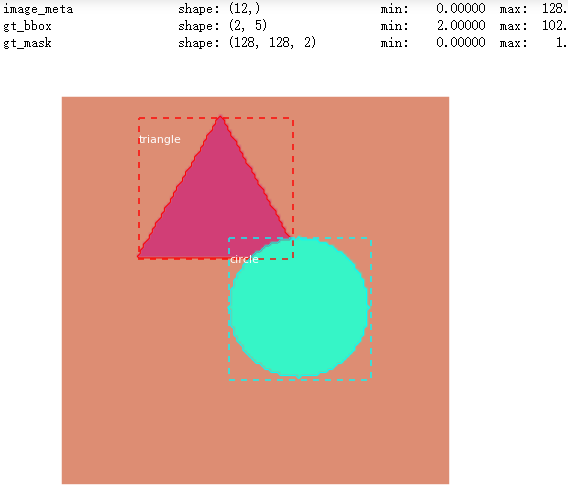
# Test on a random image image_id = random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids) original_image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config, image_id, use_mini_mask=False) log("original_image", original_image) log("image_meta", image_meta) log("gt_class_id", gt_class_id) log("gt_bbox", gt_bbox) log("gt_mask", gt_mask) visualize.display_instances(original_image, gt_bbox, gt_mask, gt_class_id, dataset_train.class_names, figsize=(8, 8))
results = model.detect([original_image], verbose=1) r = results[0] visualize.display_instances(original_image, r['rois'], r['masks'], r['class_ids'], dataset_val.class_names, r['scores'], ax=get_ax())

# Compute VOC-Style mAP @ IoU=0.5 # Running on 10 images. Increase for better accuracy. image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids, 10) APs = [] for image_id in image_ids: # Load image and ground truth data image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config, image_id, use_mini_mask=False) molded_images = np.expand_dims(modellib.mold_image(image, inference_config), 0) # Run object detection results = model.detect([image], verbose=0) r = results[0] # Compute AP AP, precisions, recalls, overlaps = utils.compute_ap(gt_bbox, gt_class_id, gt_mask, r["rois"], r["class_ids"], r["scores"], r['masks']) APs.append(AP) print("mAP: ", np.mean(APs))