public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 25; int d = 25; System.out.println("a + b = " + (a + b) ); System.out.println("a - b = " + (a - b) ); System.out.println("a * b = " + (a * b) ); System.out.println("b / a = " + (b / a) ); System.out.println("b % a = " + (b % a) ); System.out.println("c % a = " + (c % a) ); System.out.println("a++ = " + (a++) ); System.out.println("a-- = " + (a--) ); // 查看 d++ 与 ++d 的不同 System.out.println("d++ = " + (d++) ); System.out.println("++d = " + (++d) ); } }

public class selfAddMinus{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 3;//定义一个变量; int b = ++a;//自增运算 int c = 3; int d = --c;//自减运算 System.out.println("进行自增运算后的值等于"+b); System.out.println("进行自减运算后的值等于"+d); } }
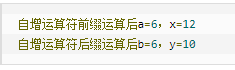
public class selfAddMinus{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 5;//定义一个变量; int b = 5; int x = 2*++a; int y = 2*b++; System.out.println("自增运算符前缀运算后a="+a+",x="+x); System.out.println("自增运算符后缀运算后b="+b+",y="+y); } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; System.out.println("a == b = " + (a == b) ); System.out.println("a != b = " + (a != b) ); System.out.println("a > b = " + (a > b) ); System.out.println("a < b = " + (a < b) ); System.out.println("b >= a = " + (b >= a) ); System.out.println("b <= a = " + (b <= a) ); } }

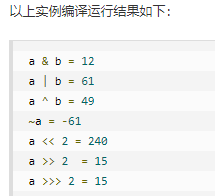
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */ int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */ int c = 0; c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */ System.out.println("a & b = " + c ); c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */ System.out.println("a | b = " + c ); c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */ System.out.println("a ^ b = " + c ); c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */ System.out.println("~a = " + c ); c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */ System.out.println("a << 2 = " + c ); c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 1111 */ System.out.println("a >> 2 = " + c ); c = a >>> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */ System.out.println("a >>> 2 = " + c ); } }
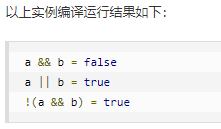
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean a = true; boolean b = false; System.out.println("a && b = " + (a&&b)); System.out.println("a || b = " + (a||b) ); System.out.println("!(a && b) = " + !(a && b)); } }
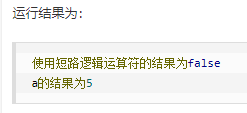
public class LuoJi{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 5;//定义一个变量; boolean b = (a<4)&&(a++<10); System.out.println("使用短路逻辑运算符的结果为"+b); System.out.println("a的结果为"+a); } }
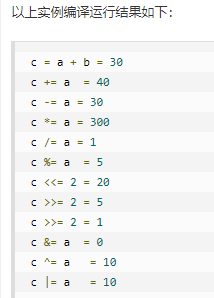
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 0; c = a + b; System.out.println("c = a + b = " + c ); c += a ; System.out.println("c += a = " + c ); c -= a ; System.out.println("c -= a = " + c ); c *= a ; System.out.println("c *= a = " + c ); a = 10; c = 15; c /= a ; System.out.println("c /= a = " + c ); a = 10; c = 15; c %= a ; System.out.println("c %= a = " + c ); c <<= 2 ; System.out.println("c <<= 2 = " + c ); c >>= 2 ; System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c ); c >>= 2 ; System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c ); c &= a ; System.out.println("c &= a = " + c ); c ^= a ; System.out.println("c ^= a = " + c ); c |= a ; System.out.println("c |= a = " + c ); } }
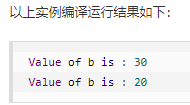
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ int a , b; a = 10; // 如果 a 等于 1 成立,则设置 b 为 20,否则为 30 b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30; System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b ); // 如果 a 等于 10 成立,则设置 b 为 20,否则为 30 b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30; System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b ); } }