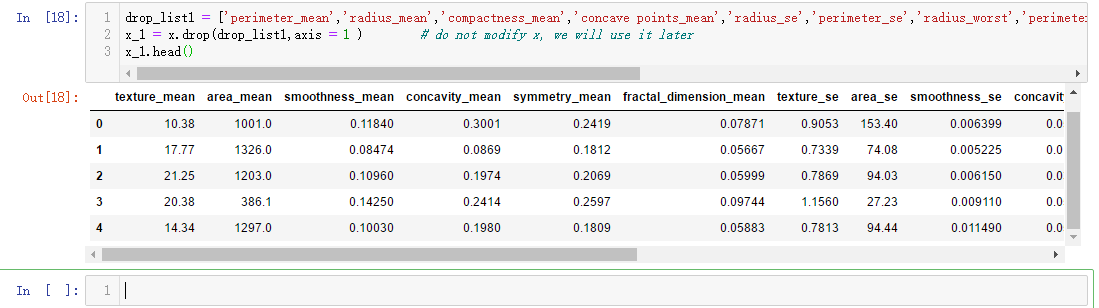
drop_list1 = ['perimeter_mean','radius_mean','compactness_mean','concave points_mean','radius_se','perimeter_se','radius_worst','perimeter_worst','compactness_worst','concave points_worst','compactness_se','concave points_se','texture_worst','area_worst'] x_1 = x.drop(drop_list1,axis = 1 ) # do not modify x, we will use it later x_1.head()
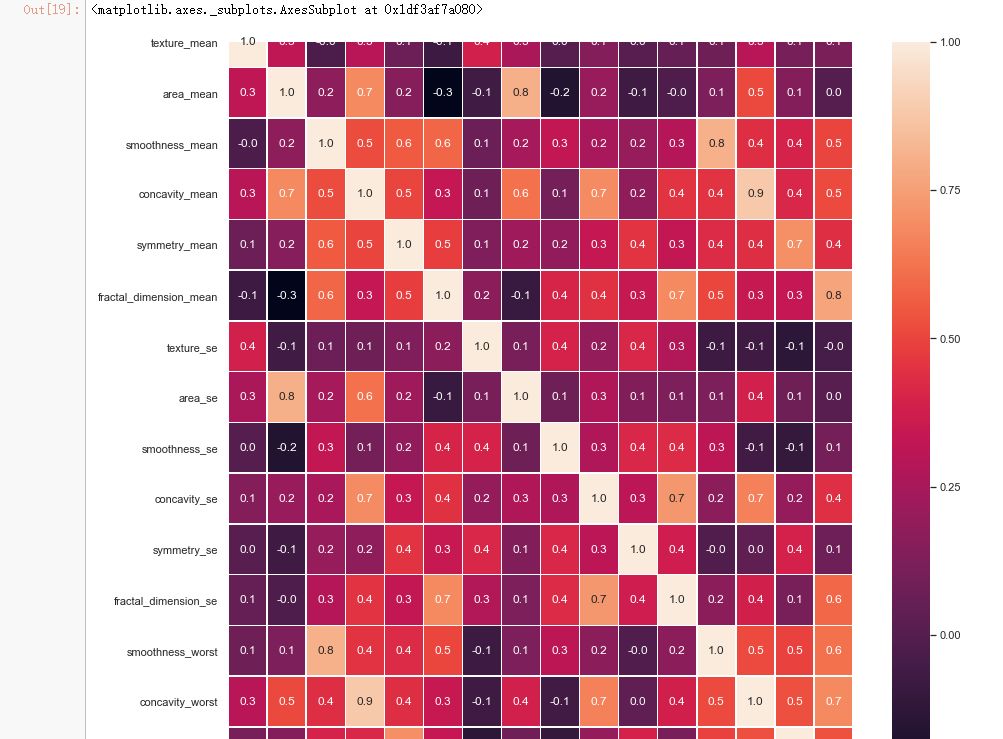
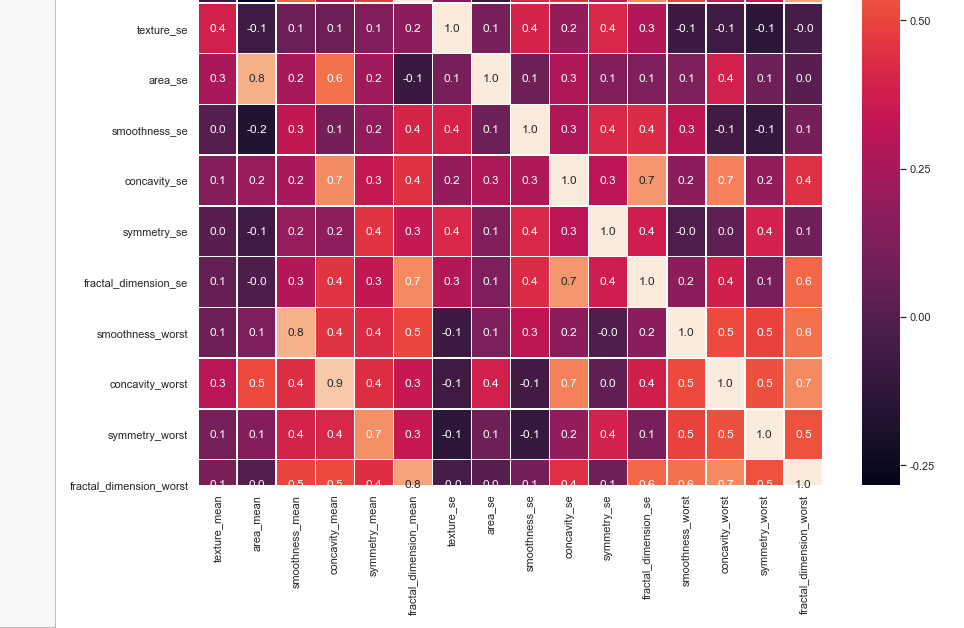
#correlation map f,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 14)) sns.heatmap(x_1.corr(), annot=True, linewidths=.5, fmt= '.1f',ax=ax)
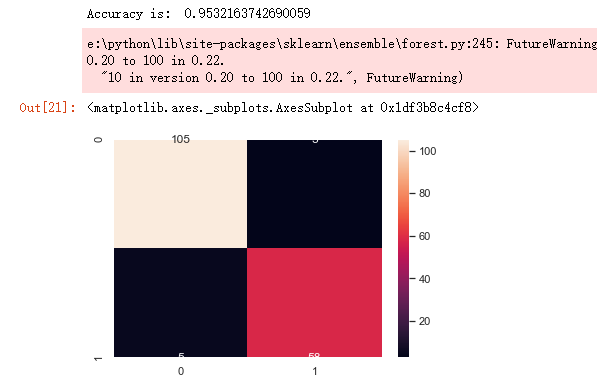
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import f1_score,confusion_matrix from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score # split data train 70 % and test 30 % x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_1, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42) #random forest classifier with n_estimators=10 (default) clf_rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=43) clr_rf = clf_rf.fit(x_train,y_train) ac = accuracy_score(y_test,clf_rf.predict(x_test)) print('Accuracy is: ',ac) cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,clf_rf.predict(x_test)) sns.heatmap(cm,annot=True,fmt="d")
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2 # find best scored 5 features select_feature = SelectKBest(chi2, k=5).fit(x_train, y_train)
print('Score list:', select_feature.scores_) print('Feature list:', x_train.columns)

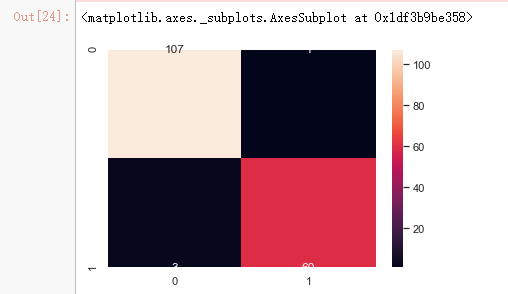
x_train_2 = select_feature.transform(x_train) x_test_2 = select_feature.transform(x_test) #random forest classifier with n_estimators=10 (default) clf_rf_2 = RandomForestClassifier() clr_rf_2 = clf_rf_2.fit(x_train_2,y_train) ac_2 = accuracy_score(y_test,clf_rf_2.predict(x_test_2)) print('Accuracy is: ',ac_2) cm_2 = confusion_matrix(y_test,clf_rf_2.predict(x_test_2)) sns.heatmap(cm_2,annot=True,fmt="d")
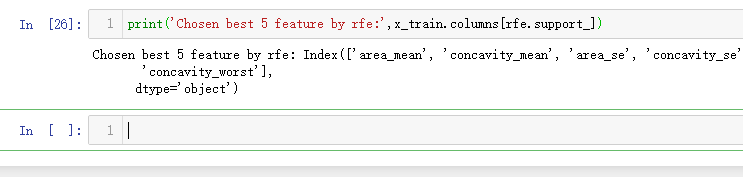
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE # Create the RFE object and rank each pixel clf_rf_3 = RandomForestClassifier() rfe = RFE(estimator=clf_rf_3, n_features_to_select=5, step=1) rfe = rfe.fit(x_train, y_train)
print('Chosen best 5 feature by rfe:',x_train.columns[rfe.support_])
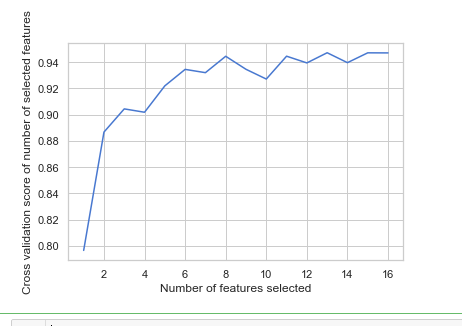
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV # The "accuracy" scoring is proportional to the number of correct classifications clf_rf_4 = RandomForestClassifier() rfecv = RFECV(estimator=clf_rf_4, step=1, cv=5,scoring='accuracy') #5-fold cross-validation rfecv = rfecv.fit(x_train, y_train) print('Optimal number of features :', rfecv.n_features_) print('Best features :', x_train.columns[rfecv.support_])
# Plot number of features VS. cross-validation scores import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.figure() plt.xlabel("Number of features selected") plt.ylabel("Cross validation score of number of selected features") plt.plot(range(1, len(rfecv.grid_scores_) + 1), rfecv.grid_scores_) plt.show()
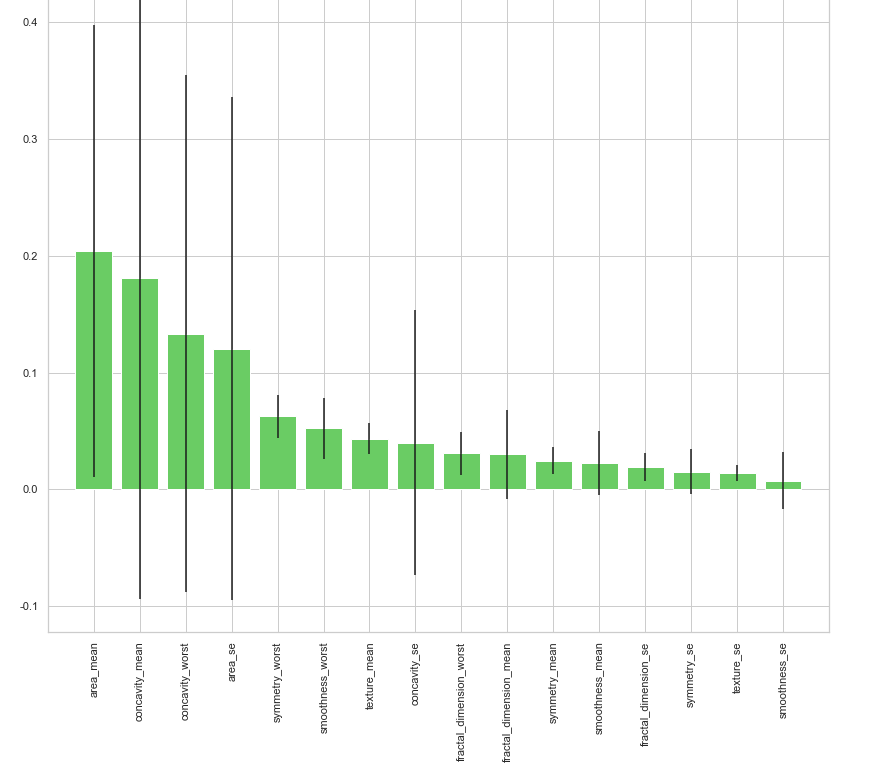
clf_rf_5 = RandomForestClassifier() clr_rf_5 = clf_rf_5.fit(x_train,y_train) importances = clr_rf_5.feature_importances_ std = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in clf_rf.estimators_], axis=0) indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1] # Print the feature ranking print("Feature ranking:") for f in range(x_train.shape[1]): print("%d. feature %d (%f)" % (f + 1, indices[f], importances[indices[f]])) # Plot the feature importances of the forest plt.figure(1, figsize=(14, 13)) plt.title("Feature importances") plt.bar(range(x_train.shape[1]), importances[indices], color="g", yerr=std[indices], align="center") plt.xticks(range(x_train.shape[1]), x_train.columns[indices],rotation=90) plt.xlim([-1, x_train.shape[1]]) plt.show()

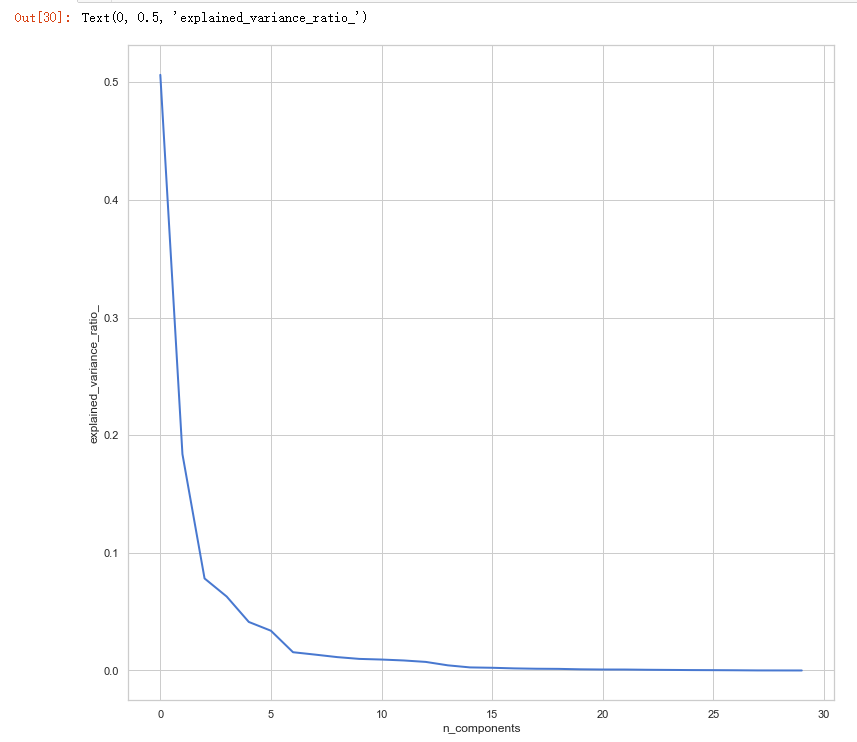
# split data train 70 % and test 30 % x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42) #normalization x_train_N = (x_train-x_train.mean())/(x_train.max()-x_train.min()) x_test_N = (x_test-x_test.mean())/(x_test.max()-x_test.min()) from sklearn.decomposition import PCA pca = PCA() pca.fit(x_train_N) plt.figure(1, figsize=(14, 13)) plt.clf() plt.axes([.2, .2, .7, .7]) plt.plot(pca.explained_variance_ratio_, linewidth=2) plt.axis('tight') plt.xlabel('n_components') plt.ylabel('explained_variance_ratio_')