# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python # For example, here's several helpful packages to load in import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import statsmodels.tsa.seasonal as smt import numpy as np # linear algebra import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv) import random import datetime as dt from sklearn import linear_model from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error import plotly # import the relevant Keras modules from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Activation, Dense from keras.layers import LSTM from keras.layers import Dropout # Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory. # For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory from subprocess import check_output
import os os.chdir('F:\kaggleDataSet\price-volume\Stocks')
#read data # kernels let us navigate through the zipfile as if it were a directory # trying to read a file of size zero will throw an error, so skip them # filenames = [x for x in os.listdir() if x.endswith('.txt') and os.path.getsize(x) > 0] # filenames = random.sample(filenames,1) filenames = ['prk.us.txt', 'bgr.us.txt', 'jci.us.txt', 'aa.us.txt', 'fr.us.txt', 'star.us.txt', 'sons.us.txt', 'ipl_d.us.txt', 'sna.us.txt', 'utg.us.txt'] filenames = [filenames[1]] print(filenames) data = [] for filename in filenames: df = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=',') label, _, _ = filename.split(sep='.') df['Label'] = filename df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date']) data.append(df)

traces = [] for df in data: clr = str(r()) + str(r()) + str(r()) df = df.sort_values('Date') label = df['Label'].iloc[0] trace = plotly.graph_objs.Scattergl(x=df['Date'],y=df['Close']) traces.append(trace) layout = plotly.graph_objs.Layout(title='Plot',) fig = plotly.graph_objs.Figure(data=traces, layout=layout) plotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True) plotly.offline.iplot(fig, filename='dataplot')

df = data[0] window_len = 10 #Create a data point (i.e. a date) which splits the training and testing set split_date = list(data[0]["Date"][-(2*window_len+1):])[0] #Split the training and test set training_set, test_set = df[df['Date'] < split_date], df[df['Date'] >= split_date] training_set = training_set.drop(['Date','Label', 'OpenInt'], 1) test_set = test_set.drop(['Date','Label','OpenInt'], 1) #Create windows for training LSTM_training_inputs = [] for i in range(len(training_set)-window_len): temp_set = training_set[i:(i+window_len)].copy() for col in list(temp_set): temp_set[col] = temp_set[col]/temp_set[col].iloc[0] - 1 LSTM_training_inputs.append(temp_set) LSTM_training_outputs = (training_set['Close'][window_len:].values/training_set['Close'][:-window_len].values)-1 LSTM_training_inputs = [np.array(LSTM_training_input) for LSTM_training_input in LSTM_training_inputs] LSTM_training_inputs = np.array(LSTM_training_inputs) #Create windows for testing LSTM_test_inputs = [] for i in range(len(test_set)-window_len): temp_set = test_set[i:(i+window_len)].copy() for col in list(temp_set): temp_set[col] = temp_set[col]/temp_set[col].iloc[0] - 1 LSTM_test_inputs.append(temp_set) LSTM_test_outputs = (test_set['Close'][window_len:].values/test_set['Close'][:-window_len].values)-1 LSTM_test_inputs = [np.array(LSTM_test_inputs) for LSTM_test_inputs in LSTM_test_inputs] LSTM_test_inputs = np.array(LSTM_test_inputs)
def build_model(inputs, output_size, neurons, activ_func="linear",dropout=0.10, loss="mae", optimizer="adam"): model = Sequential() model.add(LSTM(neurons, input_shape=(inputs.shape[1], inputs.shape[2]))) model.add(Dropout(dropout)) model.add(Dense(units=output_size)) model.add(Activation(activ_func)) model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer=optimizer) return model
# initialise model architecture nn_model = build_model(LSTM_training_inputs, output_size=1, neurons = 32) # model output is next price normalised to 10th previous closing price # train model on data # note: eth_history contains information on the training error per epoch nn_history = nn_model.fit(LSTM_training_inputs, LSTM_training_outputs, epochs=5, batch_size=1, verbose=2, shuffle=True)

plt.plot(LSTM_test_outputs, label = "actual") plt.plot(nn_model.predict(LSTM_test_inputs), label = "predicted") plt.legend() plt.show() MAE = mean_absolute_error(LSTM_test_outputs, nn_model.predict(LSTM_test_inputs)) print('The Mean Absolute Error is: {}'.format(MAE))

#https://github.com/llSourcell/How-to-Predict-Stock-Prices-Easily-Demo/blob/master/lstm.py def predict_sequence_full(model, data, window_size): #Shift the window by 1 new prediction each time, re-run predictions on new window curr_frame = data[0] predicted = [] for i in range(len(data)): predicted.append(model.predict(curr_frame[np.newaxis,:,:])[0,0]) curr_frame = curr_frame[1:] curr_frame = np.insert(curr_frame, [window_size-1], predicted[-1], axis=0) return predicted predictions = predict_sequence_full(nn_model, LSTM_test_inputs, 10) plt.plot(LSTM_test_outputs, label="actual") plt.plot(predictions, label="predicted") plt.legend() plt.show() MAE = mean_absolute_error(LSTM_test_outputs, predictions) print('The Mean Absolute Error is: {}'.format(MAE))
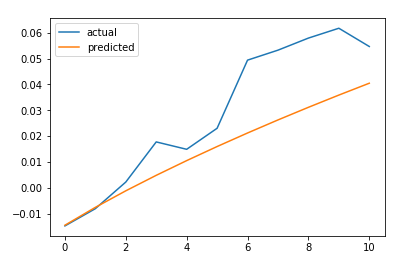
结论
LSTM不能解决时间序列预测问题。对一个时间步长的预测并不比滞后模型好多少。如果我们增加预测的时间步长,性能下降的速度就不会像其他更传统的方法那么快。然而,在这种情况下,我们的误差增加了大约4.5倍。它随着我们试图预测的时间步长呈超线性增长。