排序
冒泡排序
捞中捞,时间复杂度O(n^2)
void bubble_sort(vector<int>& vec)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size() - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < vec.size() - i - 1; j++)
{
if (vec[j + 1] < vec[j])
::swap(vec[j + 1], vec[j]);
}
}
}
快速排序

void quick_sort(vector<int> &vec, int l, int r)
{
// 递归终止条件 当只有一个元素时已不需要排序 直接返回
if (l >= r) return;
// 取数组中[l]作为随机点x的值
int i = l - 1, j = r + 1, x = vec[l];
// 调整区间的操作 令左侧的数都 < x 且右侧的数都 > x
while (i < j)
{
while (vec[++i] < x);
while (vec[--j] > x);
// 调整后i和j所在的位置就是不满足while条件的位置
// 如果i在j的左边 证明i是大于j的(由上述while循环的条件得到) 则需要交换
if (i < j)
::swap(vec[i], vec[j]);
}
// 递归处理两边 以j为分界线(此时的i要么与j相等,要么比j大1)
quick_sort(vec, l, j);
quick_sort(vec, j + 1, r);
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
quick_sort(v, 0, v.size() - 1);
for (int i : v)
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
归并排序

void merge_sort(vector<int>& vec, int l, int r, vector<int>& cachedVec)
{
// 递归终止条件 当只有一个元素时已不需要排序 直接返回
if (l >= r) return;
// 右移一位 代表除以2 (左移3位则代表乘以2^3) 由于运算优先级 优点是可以少打一个括号
int mid = l + r >> 1;
// 递归左边和右边
merge_sort(vec, l, mid, cachedVec);
merge_sort(vec, mid + 1, r, cachedVec);
// 归并操作 i代表左半边数组的起点 j代表右半边数组的起点 cachedIndex代表缓存数组的起点
int i = l, j = mid + 1, cachedIndex = 0;
// 从两半边数组中选一个小的数放入缓存数组 然后"指针"推进
while (i <= mid && j <= r)
{
if (vec[i] <= vec[j])
cachedVec[cachedIndex++] = vec[i++];
else
cachedVec[cachedIndex++] = vec[j++];
}
// TIPS:不可能出现左右都有剩下的情况
// 如果左边的指针还没移动到底 则将剩下的数搬过去
while (i <= mid)
cachedVec[cachedIndex++] = vec[i++];
// 如果右边的指针还没移动到底 则将剩下的数据搬过去
while (j <= r)
cachedVec[cachedIndex++] = vec[j++];
// 根据本次归并的范围 将缓存数组中的数据搬到原数组对应的位置(缓存数组从头开始搬)
for (i = l, j = 0; i <= r; i++, j++)
vec[i] = cachedVec[j];
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
vector<int> cachedVec(v.size());
merge_sort(v, 0, v.size() - 1, cachedVec);
for (int i : v)
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
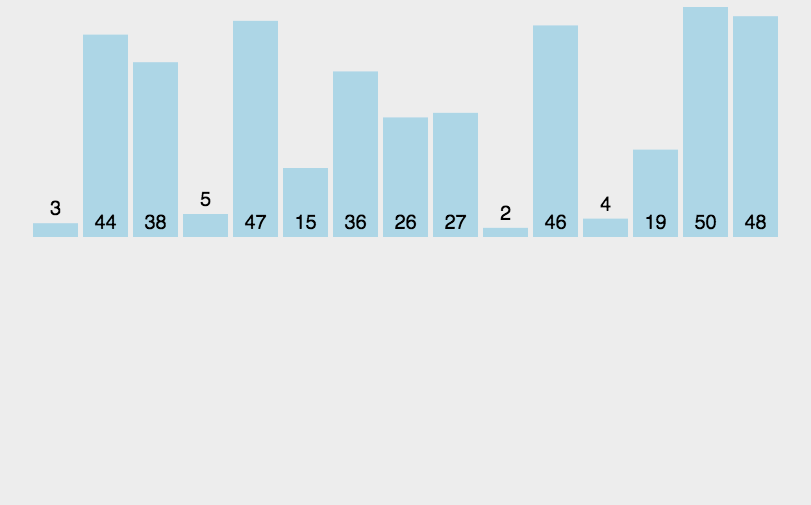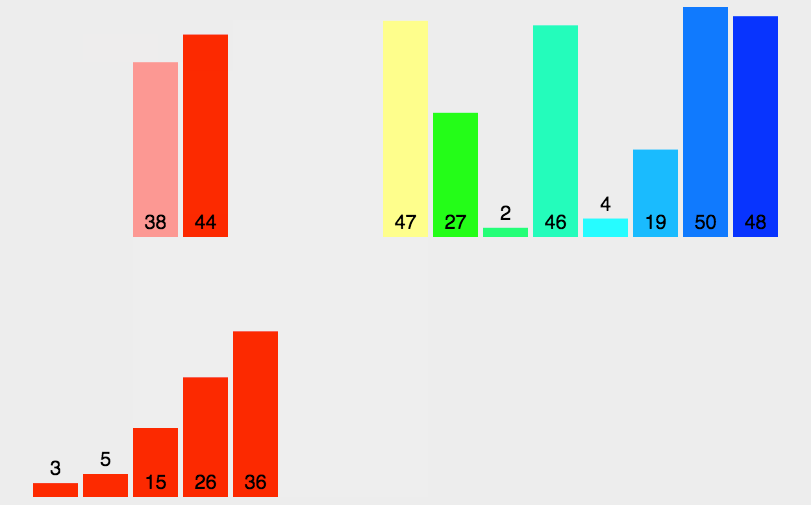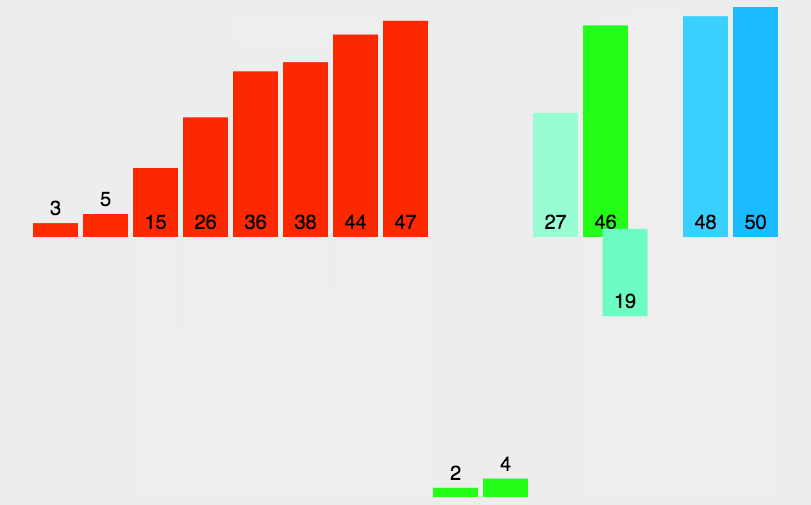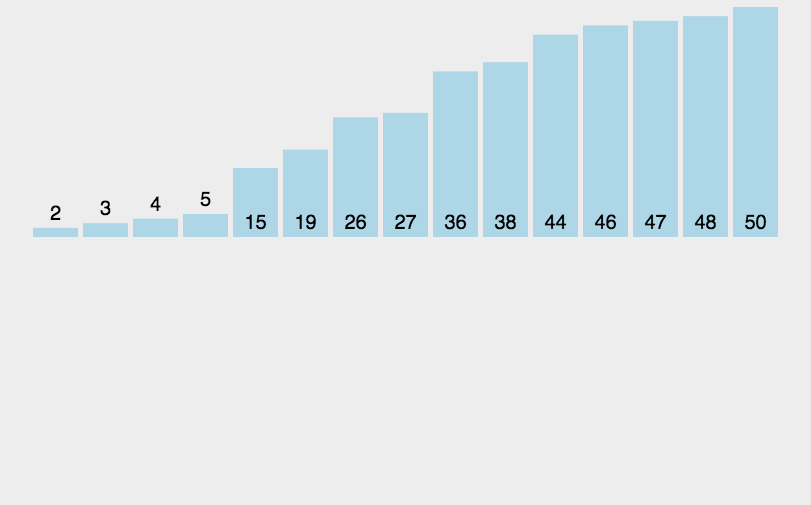
个人对归并过程的小图解
实际过程的由l和r框起来的一小段其实是小于等于cachedVec的,cachedVec与整段v等长。而每次缓存都会从cachedVec的头开始,而不是从与l对齐的位置开始
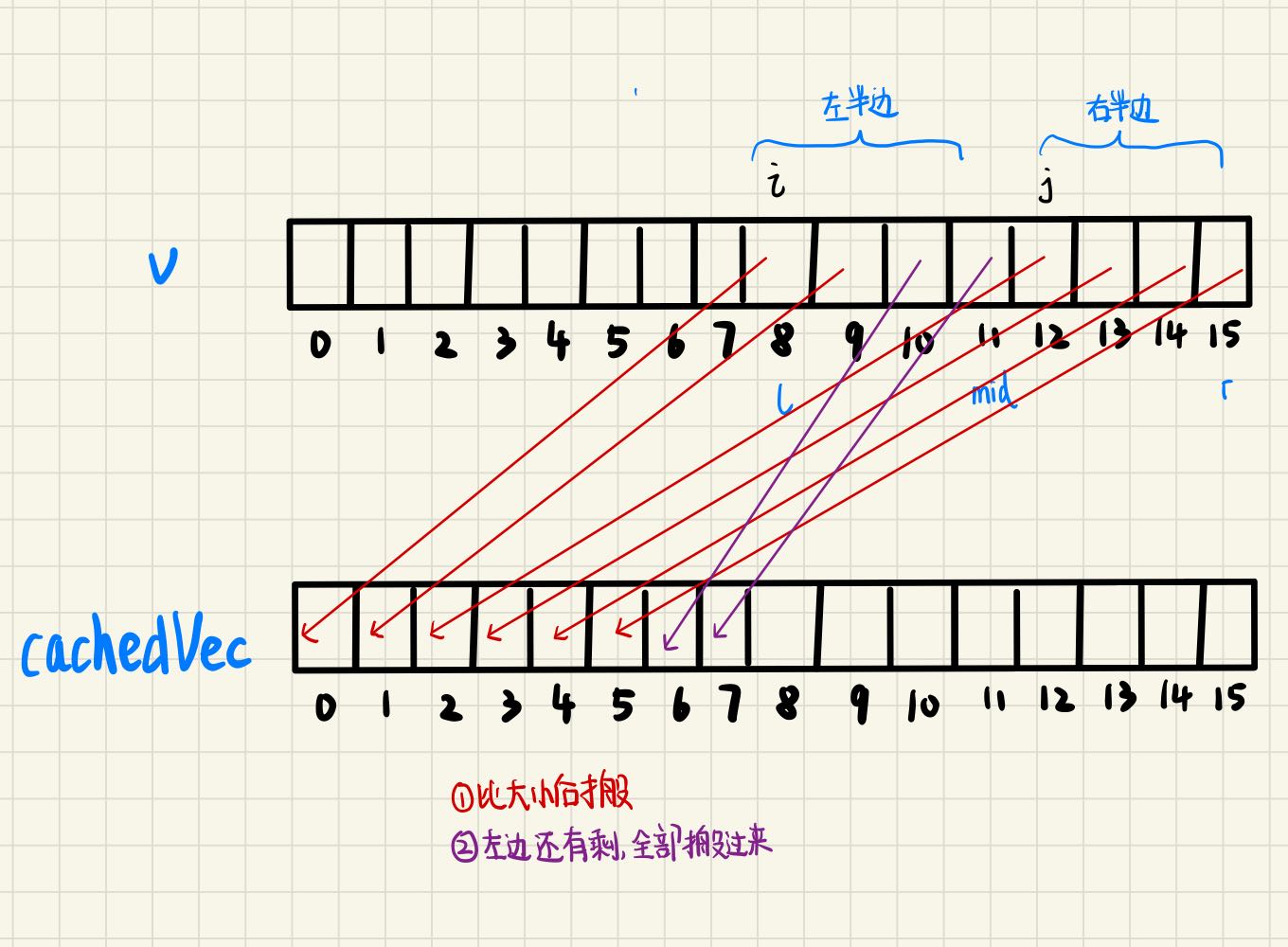
动图解析 该动图的缓存数组表示的不直观 缓存数组并不是一直都与l对齐的
插入排序(待完成)
桶排序(待完成)
二分
整数二分查找的模板
int bSearch(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 2;
if (check(x)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int bSearch(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (check(x)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
注解:
- 在答案取不到值的时候,函数返回的值是第一个/最后一个满足
check(x)条件的值 - 在
while循环结束后,l的值与r相等,所以返回哪个都可以 check(x)包含取等的情况
以上的注解可能看起来有点抽象,来看这个简单的二分查找例子
vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 5, 6, 9};
int midSearchFirst(int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
// 走左边
if (x <= vec[mid]) r = mid;
// 走右边
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int midSearchLast(int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r + 1) / 2;
// 走右边
if (x >= vec[mid]) l = mid;
// 走左边
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
- 查找数字3,
midSearchFirst找到的是2号位的3,midSearchLast找到的是4号位的3 - 查找数组4,
midSearchFirst返回4号位的3,midSearchLast返回五号位的5
在STL中,有lower_bound和upper_bound两种,两者默认操作升序数组(默认为less<T>())
vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 5, 6, 9};
int main()
{
// 找大于等于
cout << *lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 5) << endl; // 5
// 找大于
cout << *upper_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 5) << endl; // 6
}
- 如果找的是数3,那么
lower_bound会返回指向第一个3的指针,upper_bound会返回指向最后一个3的指针 - 如果找的是数4,那么
lower_bound,upper_bound都会返回指向数字5的指针 - 如果找的是数-100,那么两者都会返回指向数组第一个元素的指针;如果找的是数100,那么两者都会返回
vec.end()。因此在查找的时候应该把数据限制在该数组的最大最小范围内
// 找小于等于
lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 5, greater<int>());
// 找小于
upper_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 5, greater<int>());
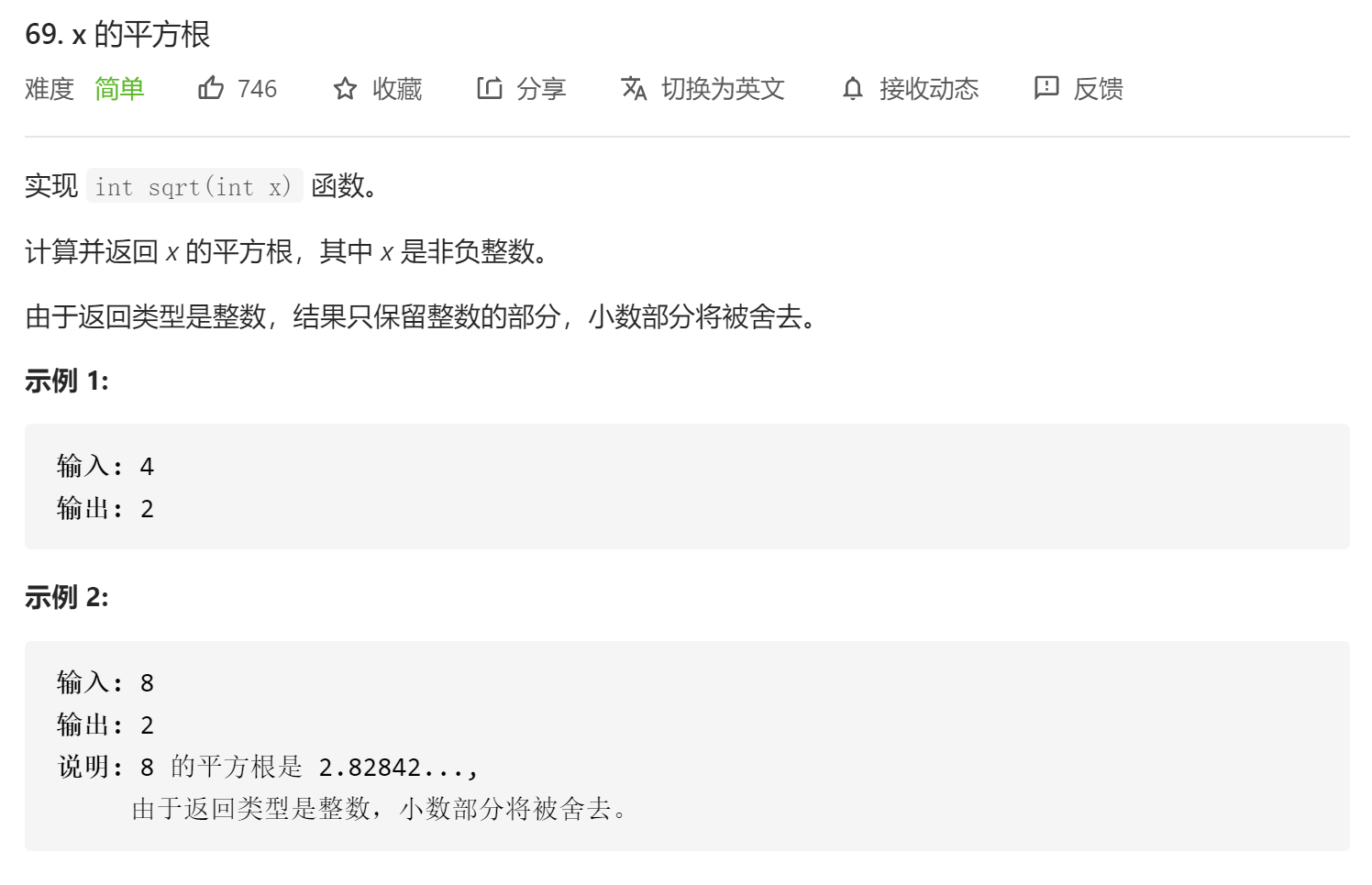
数的平方根
class Solution
{
public:
long long mySqrt(long long x)
{
// 定义边界 从 0-x 开始分
long long l = 0, r = x;
while (l < r)
{
long long mid = (l + r + 1) / 2;
// 当x等于5时,要求result为2 也就是说2是满足5 > 2 * 2最后的一个值,因为5 < 3 * 3
// 所以选用 x >= mid * mid 作为判定条件而不是 x <= mid * mid
if (x / mid >= mid)
l = mid;
else
r = mid - 1;
}
// 返回l或者返回r都行
return l;
}
};
按权重随机选择
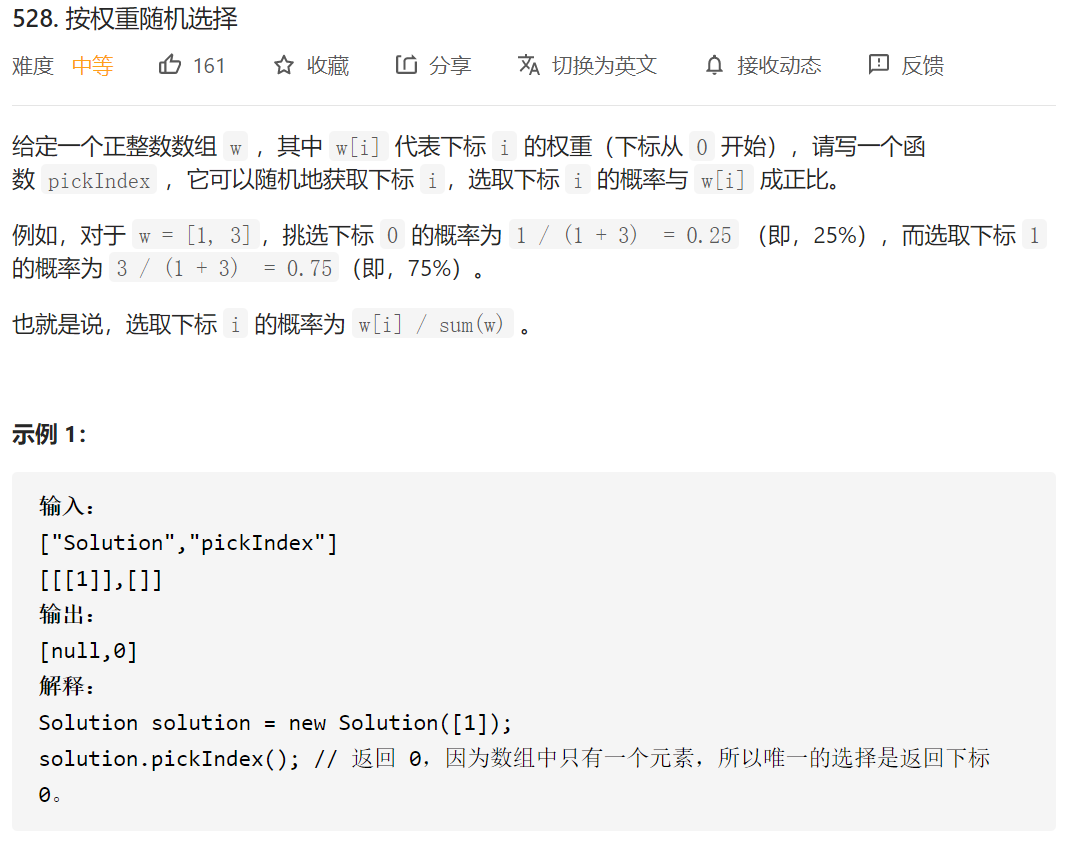
利用前缀和+随机数充当概率模拟,利用二分加快index查找
#include<random>
class Solution {
public:
default_random_engine e;
uniform_int_distribution<int> u;
vector<int> sumVec;
Solution(vector<int>& w) : sumVec(w.size() + 1), e()
{
sumVec[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < sumVec.size(); i++)
sumVec[i] = sumVec[i - 1] + w[i - 1];
u = uniform_int_distribution<int>(0, sumVec[w.size()] - 1);
}
int midSearch(int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r + 1) / 2;
if (x >= sumVec[mid])
l = mid;
else
r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
int pickIndex() {
return midSearch(0, sumVec.size() - 1, u(e));
}
};
使用STL自带的二分查找
#include<random>
class Solution {
public:
default_random_engine e;
uniform_int_distribution<int> u;
vector<int> sumVec;
Solution(vector<int>& w) : sumVec(w.size() + 1), e()
{
sumVec[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < sumVec.size(); i++)
sumVec[i] = sumVec[i - 1] + w[i - 1];
u = uniform_int_distribution<int>(0, sumVec[w.size()] - 1);
}
int pickIndex() {
int randomNum = u(e);
auto iterator = lower_bound(sumVec.begin(), sumVec.end(), randomNum);
if (*iterator != randomNum)
iterator--;
int index = iterator - sumVec.begin();
return index;
}
};
数学问题
快速幂
long long quick_power(int a, int k, int p)
{
int result = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1)
result = result * a % p;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % p;
}
return result;
}
动态规划
递归的时间复杂度计算 = 递归调用的次数 * 递归函数本身的复杂度
本人对动态规划的理解
- 先写原始递归解法,此时递归开销大,进行了许多重复操作
- 优化为带备忘录的递归解法(对原递归树进行剪枝操作),此时算法思路仍为自顶向下
- 由于备忘录中记录的数据与
dp数组中记录的一致,故此时将算法思路转为自底向上,就是动态规划解法
斐波那契数列

原始递归解法,复杂度为 2^n * 1
class Solution
{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
return (fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)) % 1000000007;
}
};
这种解法具有很多的冗余操作,比如重复计算(递归)的41和40等等,此时利用备忘录能够避免不必要的递归
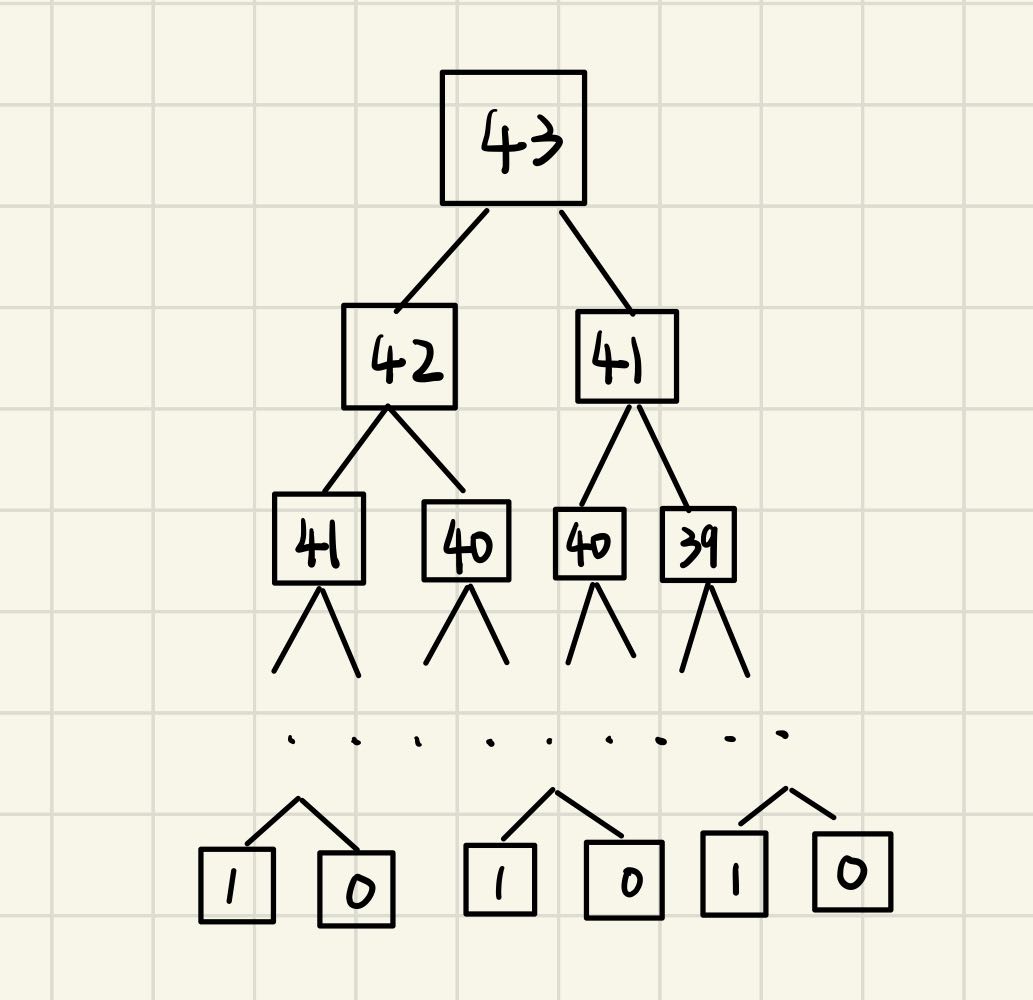
带备忘录的递归解法,相当于对原递归树做了剪枝操作,时间复杂度为o(n)
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> cachedVec;
int fib(int n)
{
cachedVec = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
cachedVec[0] = 0;
cachedVec[1] = 1;
return dp(n);
}
int dp(int n)
{
if (cachedVec[n] != -1) return cachedVec[n];
cachedVec[n] = (dp(n - 1) + dp(n - 2)) % 1000000007;
return cachedVec[n];
}
};

此时的解法已经和动态规划很接近了,区别就在于思路是自顶向下还是自底向上
原先我计算43的时候,需要递归去找42和41,计算42的话,需要去找41和40,这就是自顶向下
而自底向上的思路是,当我知道0和1的时候,就能推出2,而知道了1和2,就能推出3,这是一种自底向上的迭代解法
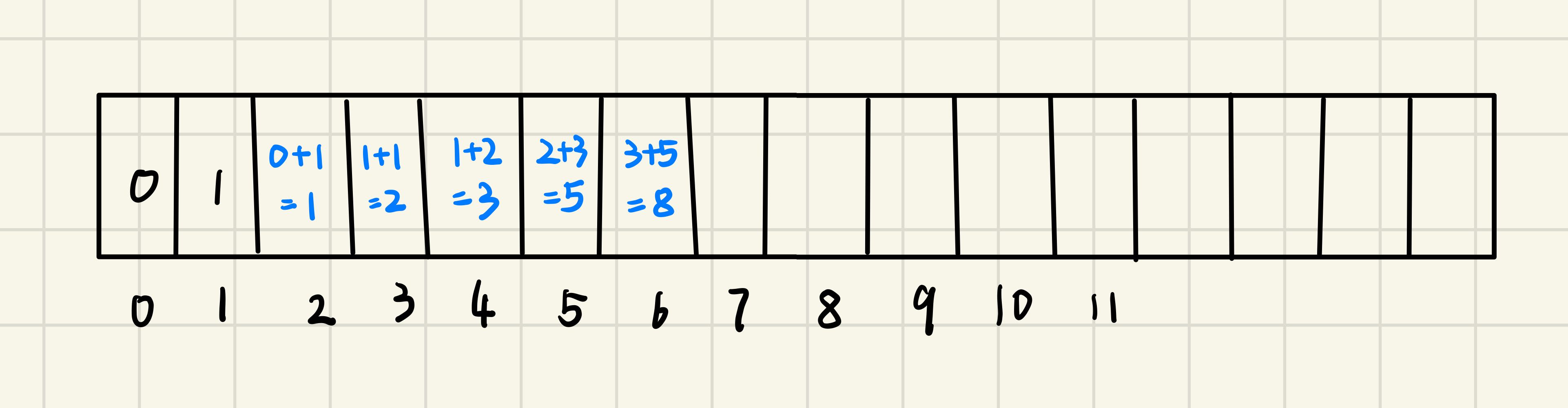
class Solution
{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
vector<int> dp(n + 1, -1);
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) % 1000000007;
}
return dp[n];
}
};
而又由于此题每当更新dp数组的值的时候,只需要用到前两个槽的值,所以可以进一步优化,省略掉整个数组,用三个int值代替
class Solution
{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
int a = 0, b = 1, result = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// F(n) = F(n - 2) + F(n - 1);
result = (a + b) % 1000000007;
// 往前移
a = b;
b = result;
}
return result;
}
};
跳台阶
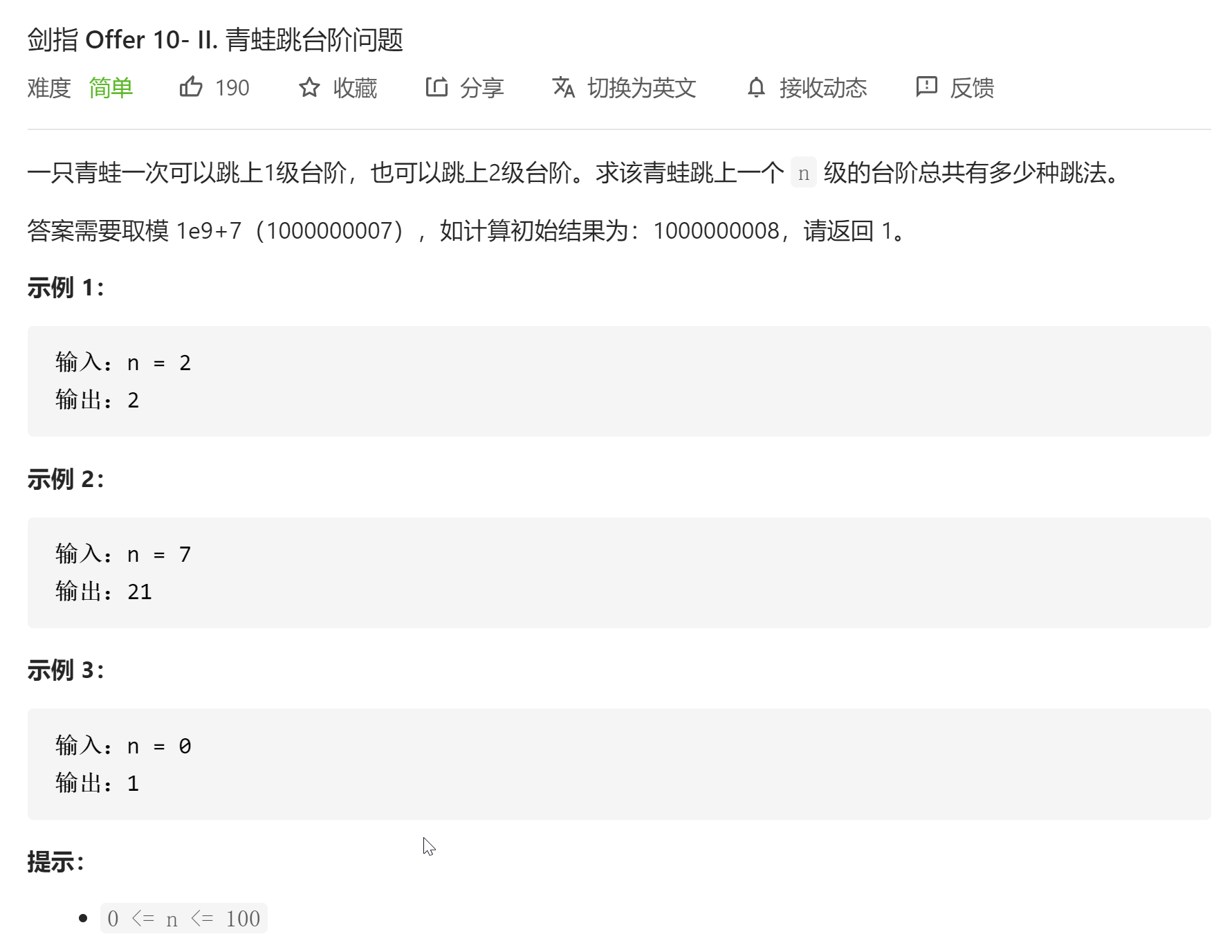
题目分析:小青蛙有两种跳法,要么一次跳一格,要么一次跳两格。假设它需要跳上两格高的楼梯,那么它有两种选择,一次性跳两格高(F(n - 2)),达到终点,F(0) = 1;要么跳一格(F(n - 1)),距离终点还剩下1格,F(1) = 1。
同理,小青蛙想跳三格高的楼梯,一开始也有两种选择,跳2或者跳1,也就是说它跳3格的跳法数量是跳2格的跳法数量 + 跳1格的跳法数量,即F(3) = F(3 - 2) + F(3 - 1)
所以通项为F(n) = F(n - 2) + F(n - 1),特殊值为F(0) = 1,F(1) = 1
class Solution
{
public:
int numWays(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n == 1) return 1;
int a = 1, b = 1, result = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
result = (a + b) % 1000000007;
a = b;
b = result;
}
return result;
}
};
最大子序和

由题意,先建立一个与nums等长的dp数组, 用来记录nums数组中的最大子序和,然后给dp[0]赋特殊值为nums[0],作为第一个连续子数组的和,同时设置result,用于记录dp数组中的最大值

然后逐个遍历dp数组,比较dp数组中储存的值与nums中下一位的值的和,如果新连续数组的和较小,则终止连续,立nums下一位元素为新连续数组的首位;若和计算结果较大,则连续继续
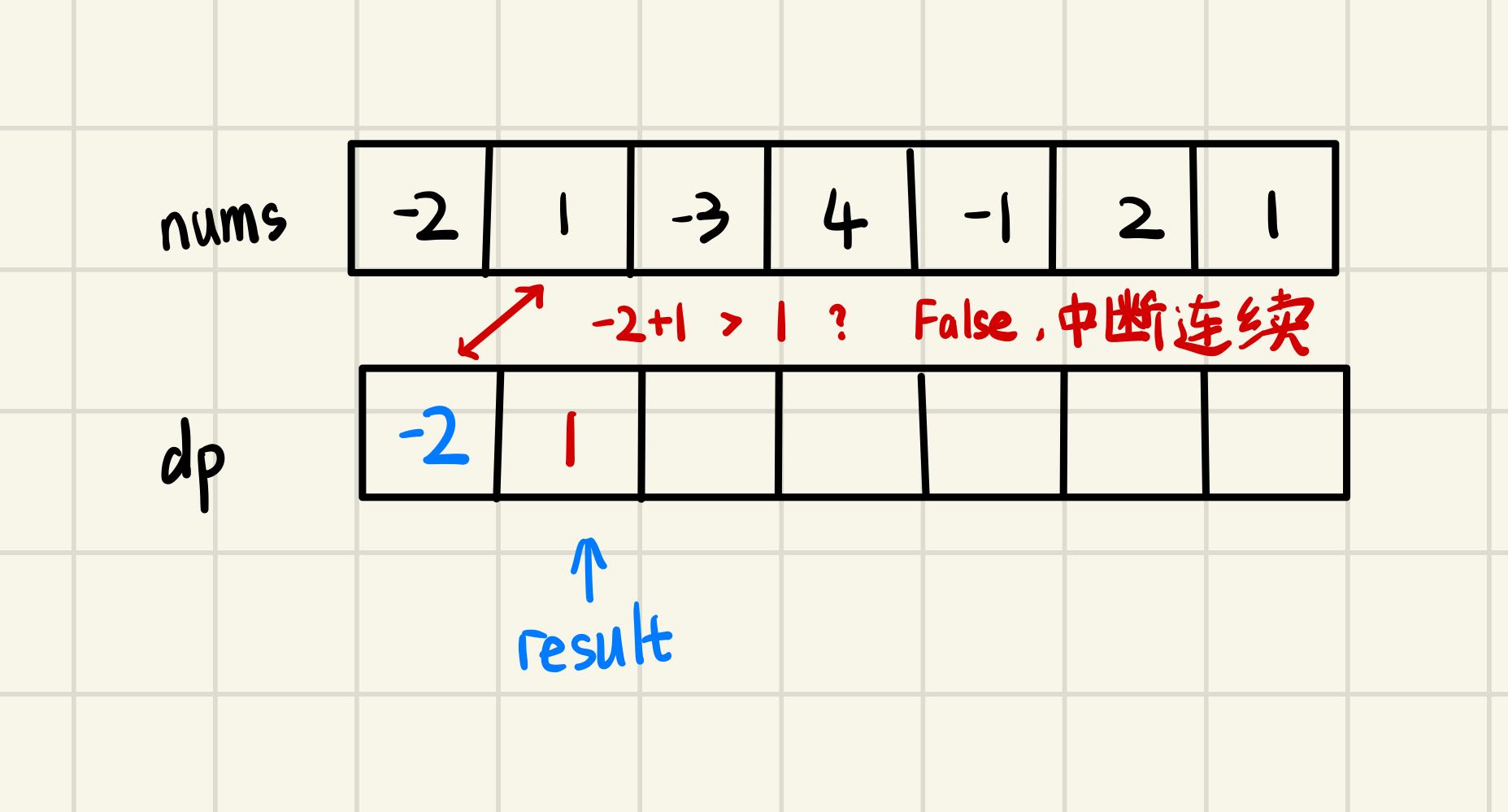

遍历结束时的result就是题目的解
class Solution
{
public:
int maxSubArray(const vector<int>& nums)
{
auto vecSize = nums.size();
if (vecSize == 0) return 0;
int dp = nums[0];
int result = dp;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
dp = ::max(dp + nums[i], nums[i]);
result = ::max(result, dp);
}
return result;
}
};
零钱兑换

纯递归解法
class Solution
{
public:
int coinChange(const vector<int>& coins, int amount)
{
// 零钱太少 不够用
if (amount < 0) return -1;
// 刚刚好换完
if (amount == 0) return 0;
int result = INT32_MAX;
for (int coin : coins)
{
int subResult = coinChange(coins, amount - coin);
if (subResult < 0) continue;
result = ::min(result, subResult + 1);
}
// 如果都被continue了 则result仍然是INT32_MAX 也就是说结果是无法兑换
return result == INT32_MAX ? -1 : result;
}
};
使用带备忘录的递归解法
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> cachedVec;
const int defaultValue = -2;
int coinChange(const vector<int>& coins, int amount)
{
cachedVec = vector<int>(amount + 1, defaultValue);
cachedVec[0] = 0;
return dp(coins, amount);
}
int dp(const vector<int>& coins, int amount)
{
if (amount < 0) return -1;
if (cachedVec[amount] != defaultValue)
return cachedVec[amount];
int subAmount = INT32_MAX;
for (int coin : coins)
{
// 检测缓存数组中是否已经存有数据
int subResult = dp(coins, amount - coin);
if (subResult == -1) continue;
subAmount = ::min(subAmount, subResult + 1);
}
cachedVec[amount] = subAmount == INT32_MAX ? -1 : subAmount;
return cachedVec[amount];
}
};
动态规划解法
class Solution
{
public:
int coinChange(const vector<int>& coins, int amount)
{
vector<int> dp(amount + 1, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < dp.size(); i++)
{
for (int coin : coins)
{
if (i - coin < 0) continue;
dp[i] = ::min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] == amount + 1 ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
};
数据结构
单调栈
主要题型
给定一个序列,求在这个序列中每一个数左边/右边,离他最近的数但比他小/大的数是什么
下一个更大元素

简单分析:
- 先从
nums2数组中找出每一个数右边第一个比它大的数(使用单调栈) - 遍历
nums1找到其存在于nums2中的元素并进行答案输出(使用哈希表)
假设有7, 22, 20, 8这样的数列,从右往左遍历。8入栈后,遍历到20这个元素。因为20比8大,所以比8小的数一定比20小(满足题目求的下一个大数字的条件),且20比8更近,也就是说这个8一点用也没有了,一切风头都被20占了去,所以8出栈。
......
当遍历到22,依照上方描述,20也出栈,栈空了,此时代表22的右边没有比它大的数,所以返回-1。最后22入栈
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
// 创建哈希表 记录num2中的元素Key和其对应的右边最大数Value
unordered_map<int, int> hash;
// 创建单调栈 栈中存的是比 当前遍历到的元素 大的数
stack<int> stk;
// 因为是从右边开始找 所以逆序遍历数组
for (int i = nums2.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
// 找出比它大的数 == 求栈顶元素
// 因为数组的遍历顺序是逐渐往左走 所以如果遍历到了一个更大的数 就说明这个数不仅能满足条件而且满足优先级更高(更近)的条件
// 题目中给出了数互不相同的条件 所以无需 >=
while (!stk.empty() && nums2[i] > stk.top())
stk.pop();
// 栈不空 证明有结果 将对应的结果存入哈希表
if (!stk.empty())
hash.insert(make_pair(nums2[i], stk.top()));
else
hash.insert(make_pair(nums2[i], -1));
// 遍历到的元素入栈
stk.push(nums2[i]);
}
// 将nums1中的数和哈希表中的比对 有记录则输出结果
int nums1Size = nums1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < nums1Size; ++i)
{
auto iterator = hash.find(nums1[i]);
// nums1再利用 节省空间
if (iterator != hash.end())
nums1[i] = iterator->second;
}
return nums1;
}
};
每日温度
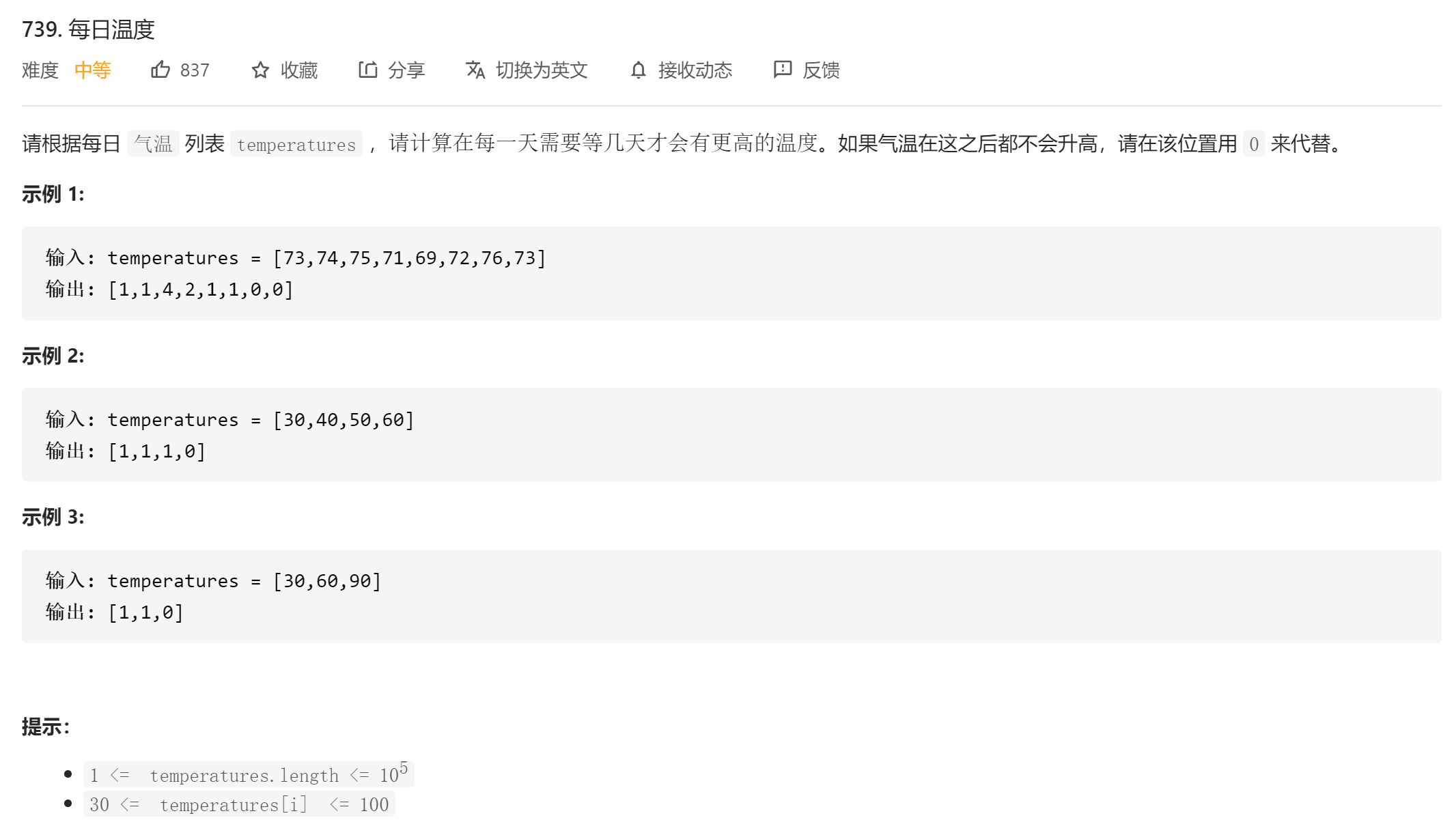
题目分析:题目要求的是某一个数的右边第一个比它大的数
所以使用单调栈,逆序遍历数组
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(const vector<int>& temperatures) {
// 单调栈中存的是数的index
stack<int> stk;
vector<int> result(temperatures.size());
for (int i = temperatures.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
// 将不可能用到的元素出栈
while (!stk.empty() && temperatures[i] >= temperatures[stk.top()])
stk.pop();
// 计算结果
result[i] = stk.empty() ? 0 : stk.top() - i;
// 将遍历到的元素的index入栈
stk.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
小技巧
-
如果是求某个数左边,那么正序遍历数组;如果求的是右边,那么逆序遍历数组
-
出栈的条件为:
栈非空且大于或小于如何判断大于还是小于,把遍历到的那个数写在左边,栈顶的数写在右边,中间的符号为题目给的要求(例如求右边第一个比他大的数,那么符号为
>);是否写等于号根据题意判断temperatures[i] >= temperatures[stk.top()]
单调队列
滑动窗口
class Solution {
public:
void slidingWindow(const vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
list<int> q;
int numsSize = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)
{
// 检测队头是否已经滑出滑动窗口
if (!q.empty() && i - k == q.front())
q.pop_front();
// 扩充活动窗口
q.push_back(i);
// 输出窗口内容
for (auto item : q)
cout << nums[item] << ends;
cout << endl;
}
}
};
使用list模拟queue,目的是遍历方便,适合Debug
int main()
{
Solution s;
// 窗口大小为3
s.slidingWindow({1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7}, 3);
return 0;
}
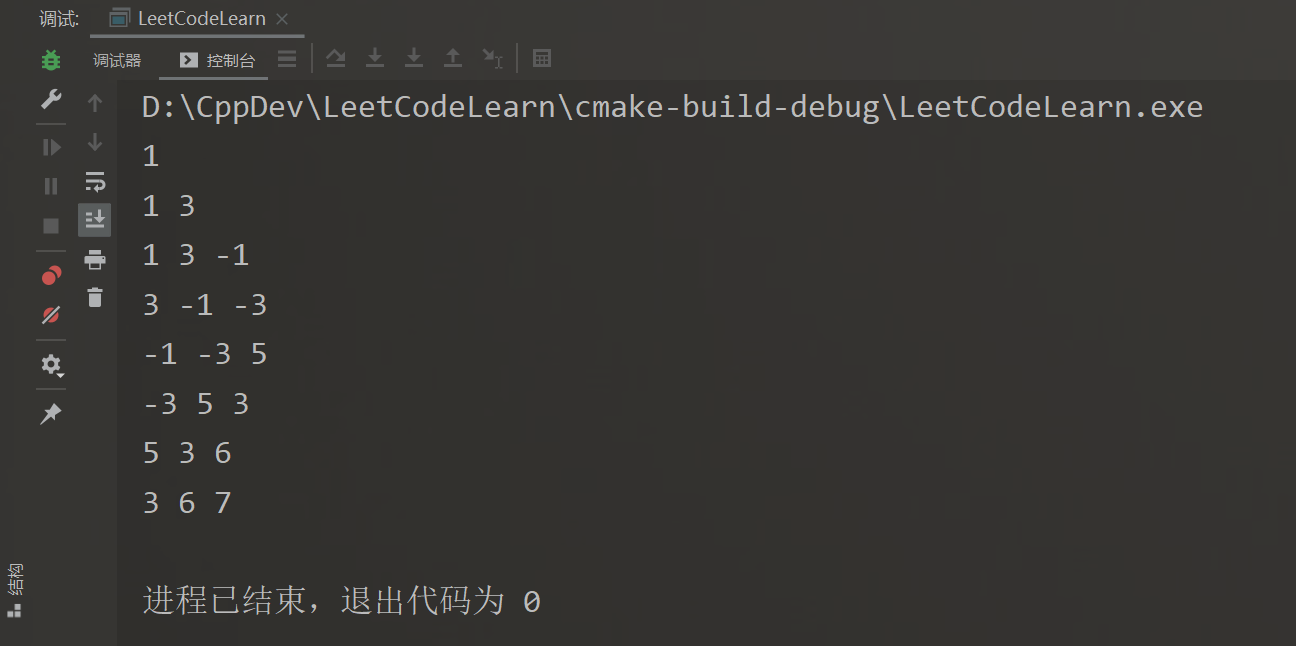
但是一般情况下,我们通常使用右标识来控制滑动窗口。因为实际做题下,双端队列一般优化为单调队列,记录的数据不一定完全按着窗口顺序来
class Solution {
public:
void maxSlidingWindow(const vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
// 用于Debug输出值才使用的双向链表 实际会使用双端队列
list<int> l;
for (int right = 0; right < nums.size(); right++)
{
// 加入新元素
l.push_back(right);
// 当队列不为空 且滑动窗口的大小超出了界限时 才需要出队
int left = right - k + 1;
if (!l.empty() && l.front() < left)
l.pop_front();
// 遍历输出
for (int i = l.front(); i <= right; i++)
cout << nums[i] << ends;
cout << endl;
}
}
};
滑动窗口最大值
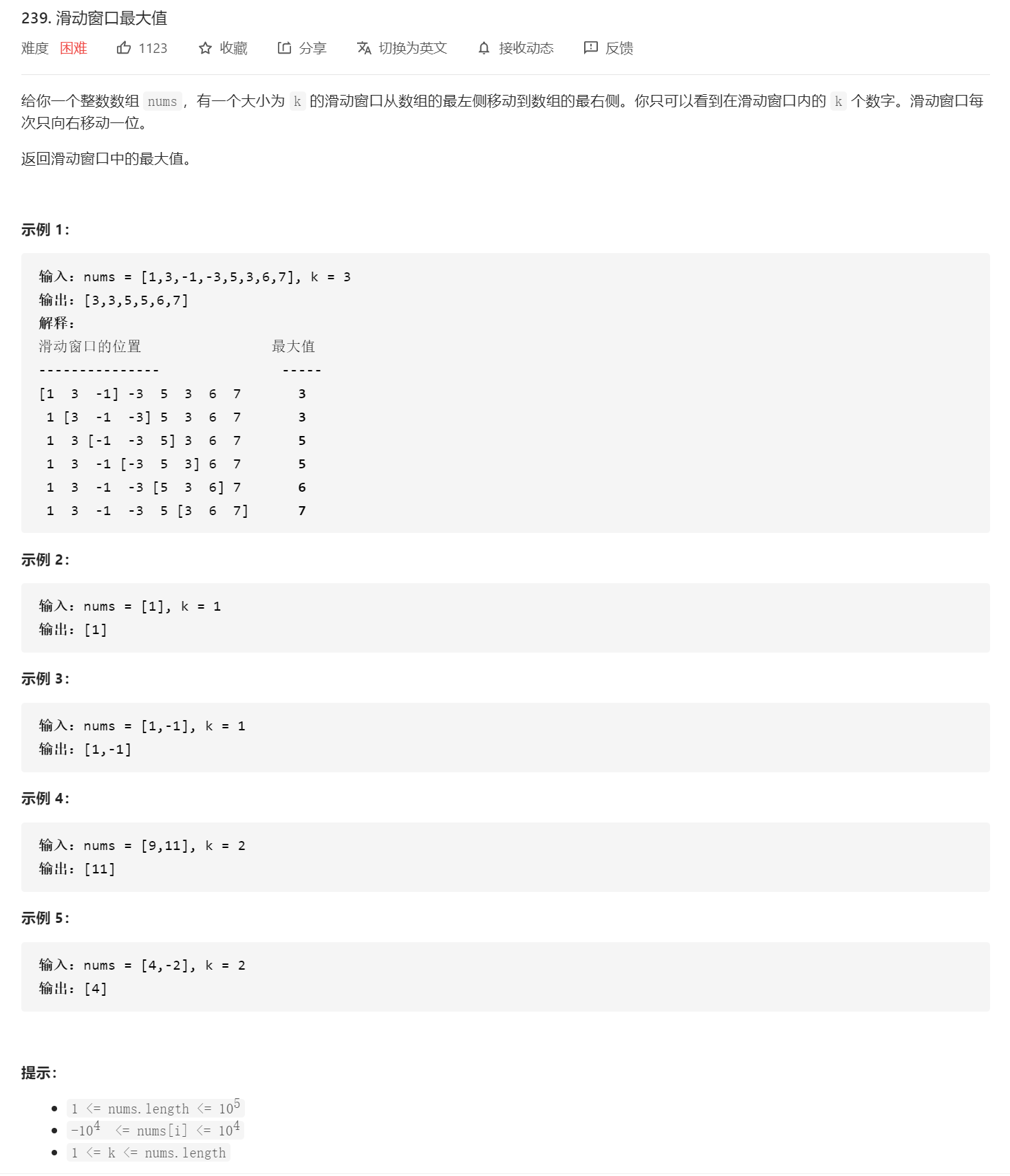
单纯的从滑动窗口的角度出发,每次窗口移动时遍历其中元素,找出最大值,这种是暴力做法
而采用单调队列的方法能够优化滑动窗口问题,降低时间复杂度
- 先判断是否需要循环出队尾,使
deque满足单调性 - 新元素入队(窗口的增长)
- 窗口过长部分裁剪
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(const vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// 求最大数 == 求单调队列的队头 => 单调队列为递减队列
// 单调队列中存放的是index
deque<int> dq;
int numsSize = nums.size();
vector<int> result(numsSize - k + 1);
for (int right = 0; right < numsSize; right++)
{
// 确保队列是单调队列 如果即将加入的元素比队尾的元素要大 则循环出队尾
while (!dq.empty() && nums[right] >= nums[dq.back()])
dq.pop_back();
// 新元素入队
dq.push_back(right);
// 当队列不为空 且滑动窗口的大小超出了界限时 才需要出队
int left = right - k + 1;
if (!dq.empty() && dq.front() < left)
dq.pop_front();
// 当滑动窗口大小增长至k时 才开始记录结果
// 队头的元素就是最大值的index
if (right + 1 >= k)
result[right - k + 1] = nums[dq.front()];
}
return result;
}
};
Trie树-字典树
用来快速存储字符串集合的数据结构
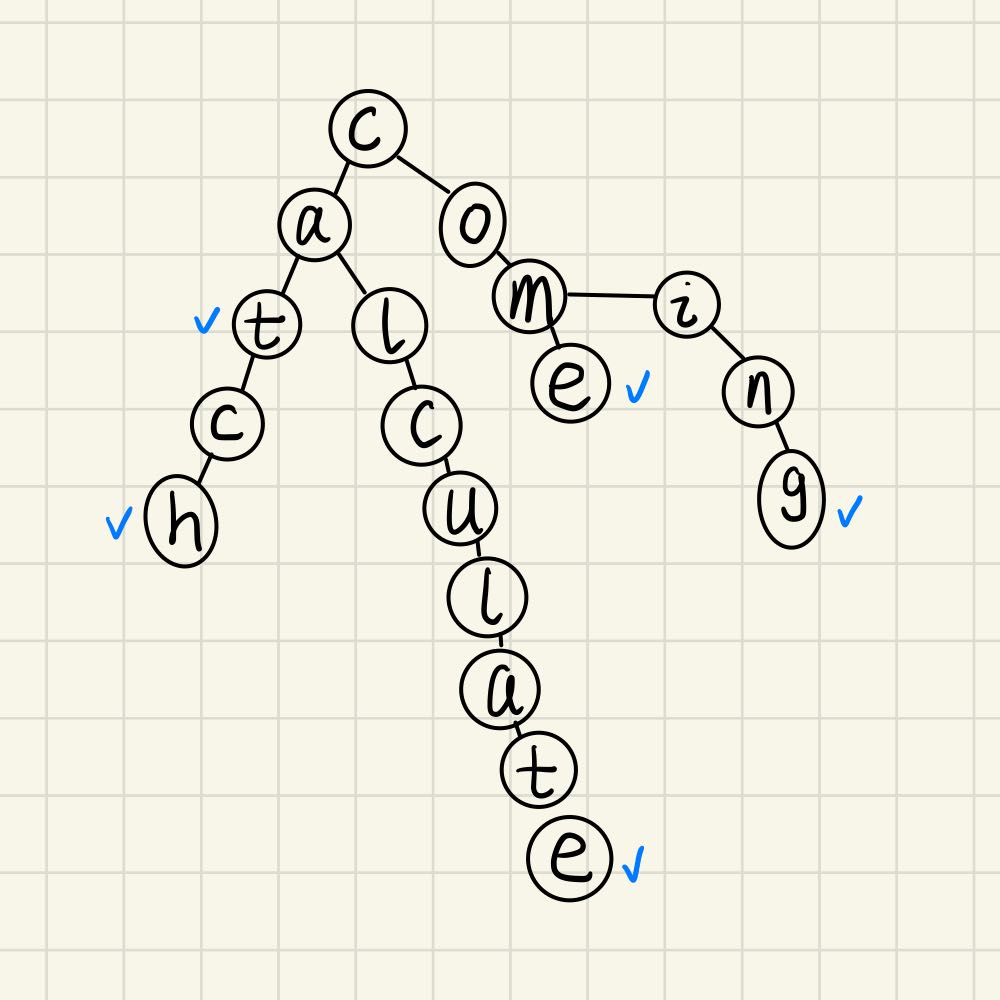
假设只存储小写字母,那么一个节点最多会有26个子节点,那么在初始化的时候先分配这26个空间,但是先置为nullptr
class Trie
{
private:
struct TrieNode
{
bool isEnd;
vector<shared_ptr<TrieNode>> children;
TrieNode() : isEnd(false), children(26) {}
};
shared_ptr<TrieNode> root;
shared_ptr<TrieNode> searchPrefix(const string& prefix)
{
shared_ptr<TrieNode> current = root;
for (const char& c : prefix)
{
int index = c - 'a';
if (current->children[index] == nullptr)
return nullptr;
current = current->children[index];
}
return current;
}
public:
Trie() : root(make_shared<TrieNode>()) {}
void insert(const string& word)
{
shared_ptr<TrieNode> current = root;
for (const char& c : word)
{
int index = c - 'a';
if (current->children[index] == nullptr)
current->children[index] = make_shared<TrieNode>();
current = current->children[index];
}
current->isEnd = true;
}
bool search(const string& word)
{
shared_ptr<TrieNode> p = searchPrefix(word);
return p != nullptr && p->isEnd == true;
}
bool startsWith(const string& prefix)
{
shared_ptr<TrieNode> p = searchPrefix(prefix);
return p != nullptr;
}
};
并查集
简单的示例代码,不考虑合并或者查找的树不在集合中的情况
class UnionFindSet
{
private:
unordered_map<int, int> parent;
unordered_map<int, int> size;
public:
void add(int x)
{
parent[x] = x;
size[x] = 1;
}
int find(int x)
{
// 路径压缩
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
int rootSize(int x)
{
return size[find(x)];
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
// 如果二者是不同集合的元素
if (xRoot != yRoot)
{
// yRoot成为新的父
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
size[yRoot] += size[xRoot];
}
}
};
二叉堆
堆是一个数据集合,是一颗完全二叉树
- 插入一个数
- 求集合中的最小值
- 删除最小值
- 删除任意一个元素
- 修改任意一个元素
小根堆
up操作接受一个index,小根堆中直接将该位置和父节点比较,如果比父节点小,则说明优先级更高,和父节点互换,称作上浮down操作接受一个index,小根堆中先和两个孩子比较(如果有的话),然后选出一个最小的进行互换(除了是自己),和子节点互换,称作下沉
struct MyData
{
int data;
MyData(int num) : data(num) {}
MyData(const MyData& other) { this->data = other.data;}
bool operator<(const MyData& other) const
{
return this->data < other.data;
}
};
class Heap
{
private:
vector<MyData> heap; // 小根堆
public:
Heap() : heap(1, INT32_MIN) {}
Heap(const initializer_list<MyData>& tempList) : Heap()
{
heap.reserve(tempList.size() + 1);
for (const auto& num : tempList)
heap.push_back(num);
// 建堆
for (int i = (heap.size() - 1) / 2; i >= 1; i--)
down(i);
}
int size() { return heap.size() - 1; }
void insert(int num)
{
// 在末端插入
heap.push_back(num);
// 末端元素上浮
up(heap.size() - 1);
}
const MyData& front()
{
if (heap.size() < 2)
throw exception("Heap is Empty");
return heap[1];
}
void pop_front()
{
if (heap.size() < 2)
throw exception("Heap is Empty");
// 让最顶层的和最底层的交换
heap[1] = heap[heap.size() - 1];
heap.pop_back();
// 让顶层元素下沉
down(1);
}
private:
void up(int index)
{
int father = index / 2;
// 直接和根节点比较
if (father > 0 && heap[father] > heap[index])
{
// 互换
::swap(heap[father], heap[index]);
up(father);
}
}
void down(int index)
{
int minIndex = index;
// 判断根节点和左节点的大小
if (index * 2 < heap.size() && heap[index * 2] < heap[minIndex])
minIndex = index * 2;
// 判断根节点和右节点的大小
if (index * 2 + 1 < heap.size() && heap[index * 2 + 1] < heap[minIndex])
minIndex = index * 2 + 1;
// 如果和左右节点的比较有结果
if (minIndex != index)
{
// 互换
::swap(heap[minIndex], heap[index]);
down(minIndex);
}
}
};
int main()
{
Heap h({1, 2, 3 ,4 ,2, -1});
int heapSize = h.size();
for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++)
{
cout << h.front().data << ends;
h.pop_front();
}
}
大根堆和小根堆的实现可以说是一样的,只是在down和up操作时将每个节点的比较颠倒一下就可以,又或者有这个究极偷懒方法
bool operator<(const MyData& other) const
{
// 反向比较
return this->data > other.data;
}
优先队列
这里实现一个int类型的,队头为大元素的优先队列(其实就是大根堆,几乎和上面的代码一摸一样)
class PriorityQueue
{
private:
vector<int> heap;
void down(int index)
{
int maxIndex = index;
if (index * 2 < heap.size() && heap[index * 2] > heap[maxIndex])
maxIndex = index * 2;
if (index * 2 + 1 < heap.size() && heap[index * 2 + 1] > heap[maxIndex])
maxIndex = index * 2 + 1;
if (maxIndex == index)
return;
::swap(heap[index], heap[maxIndex]);
down(maxIndex);
}
void up(int index)
{
int father = index / 2;
if (father > 0 && heap[father] < heap[index])
{
::swap(heap[father], heap[index]);
up(father);
}
}
public:
PriorityQueue() : heap(1, INT32_MAX) {}
void push_back(int data)
{
heap.push_back(data);
up(heap.size() - 1);
}
void pop_front()
{
// 将最后一个数和队头的元素互换 然后移除最后一个数
if (heap.size() <= 1) return;
heap[1] = heap[heap.size() - 1];
heap.pop_back();
down(1);
}
const int& top()
{
if (heap.size() > 1)
return heap[1];
throw exception("out of range");
}
int size()
{
return heap.size() - 1;
}
bool empty()
{
return size() == 0;
}
};
哈希表
哈希表基类
template<typename realType, typename storeType = realType>
class BaseHashSet
{
protected:
// 储存int类型的数据
vector<vector<storeType>> hashVec;
inline virtual int get_hash_code(const realType& data) = 0;
inline virtual storeType get_mapping_value(const realType& data) = 0;
public:
BaseHashSet() = default;
void insert(realType data)
{
int code = get_hash_code(data);
hashVec[code].push_back(get_mapping_value(data));
}
bool find(realType data)
{
int code = get_hash_code(data);
return any_of(hashVec[code].begin(), hashVec[code].end(), [&data, this](const storeType& i)
{
return i == get_mapping_value(data);
});
}
};
template<typename T>
class HashSet : public BaseHashSet<T>
{
};
int类型的哈希表
说是哈希表,其实是简陋到家的unordered_set<int>,采用链地址法解决冲突。modValue的取值遵循以下几点
- 最好是质数,且离2^n越远越好
movValue的值不能过大也不能过小(大概是当前数量级的一半?例如109和105)- 哈希数组的大小和
modValue的大小一致
template<>
class HashSet<int> : public BaseHashSet<int>
{
private:
int modValue;
protected:
inline virtual int get_hash_code(const int& data) override
{
return (data % modValue + modValue) % modValue;
}
inline virtual int get_mapping_value(const int& data) override
{
return data;
}
public:
HashSet(int _modValue = 13) : modValue(_modValue), hashVec(_modValue) {}
};
string类型的哈希表
先将string映射为unsigned long long,当种子取质数133时,可以近似认为映射得来的数是独一无二的。然后再将映射后的值取模求index,最后存入哈希数组中
template<>
class HashSet<string> : public BaseHashSet<string, unsigned long long>
{
private:
const int seed = 133;
int modValue;
protected:
inline virtual int get_hash_code(const string& data) override
{
// 将映射值取模后存入哈希表中
unsigned long long mappingValue = get_mapping_value(data);
return (int)(mappingValue % modValue);
}
inline virtual unsigned long long get_mapping_value(const string& data) override
{
// 映射为unsigned long long
unsigned long long result = 0;
for (const char& c : data)
result = result * seed + c;
return result;
}
public:
HashSet(int _modValue = 13) : modValue(_modValue), hashVec(_modValue) {}
};
树
二叉树
遍历
二叉树的解题模板基本都是围绕三种遍历方式展开的,用的最多的是先序遍历和后序遍历。递归遍历的代码很简单,这里就不演示了,需要掌握的是各种遍历方式究竟能遍历个什么东西出来
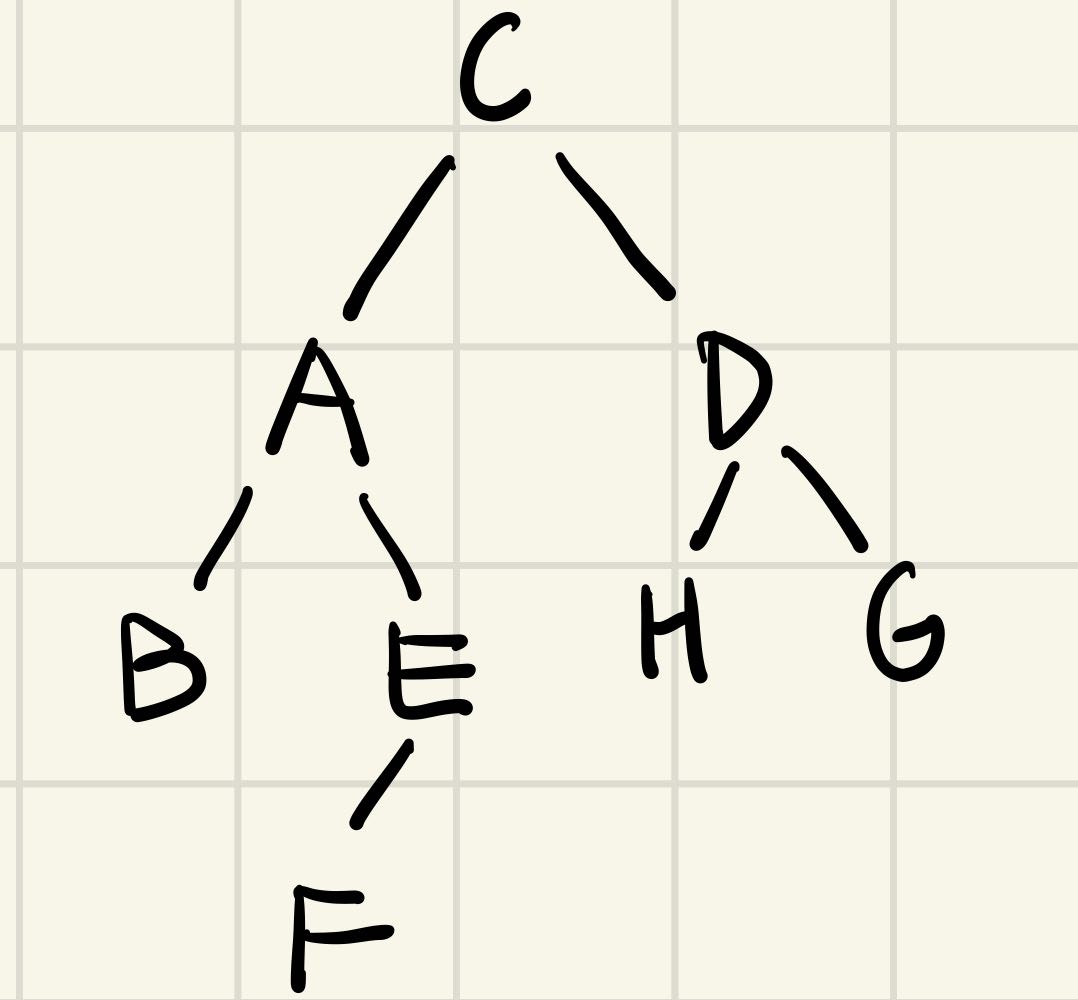
- 前序遍历:C A B E F D H G (根左右)
- 中序遍历:B A F E C H D G (左根右)
- 后序遍历:B F E A H G D C (左右根)
根据前中序遍历构建树
两个知识点
- 前序遍历的第一位是根节点,后续遍历最后一位是根节点
- 中序遍历中某个节点将其左右两端分为左右子树
设有前序遍历为ACDEFHGB,中序遍历为DECAHFBG树,将它构建出来
- 首先前序遍历的第一位是A,所以根节点是A
- 然后在中序中找到A,观察它的左右两边,分别为左右两个子树(左子树的元素有DEC,右子树的元素有HFBG,不分顺序)
- 在左右两个子树的元素中,找到最先在前序遍历中出现的,为子树的根(DEC三者中C最先在前序中出现,HFBG中F最先出现)
- 循环第二第三步骤
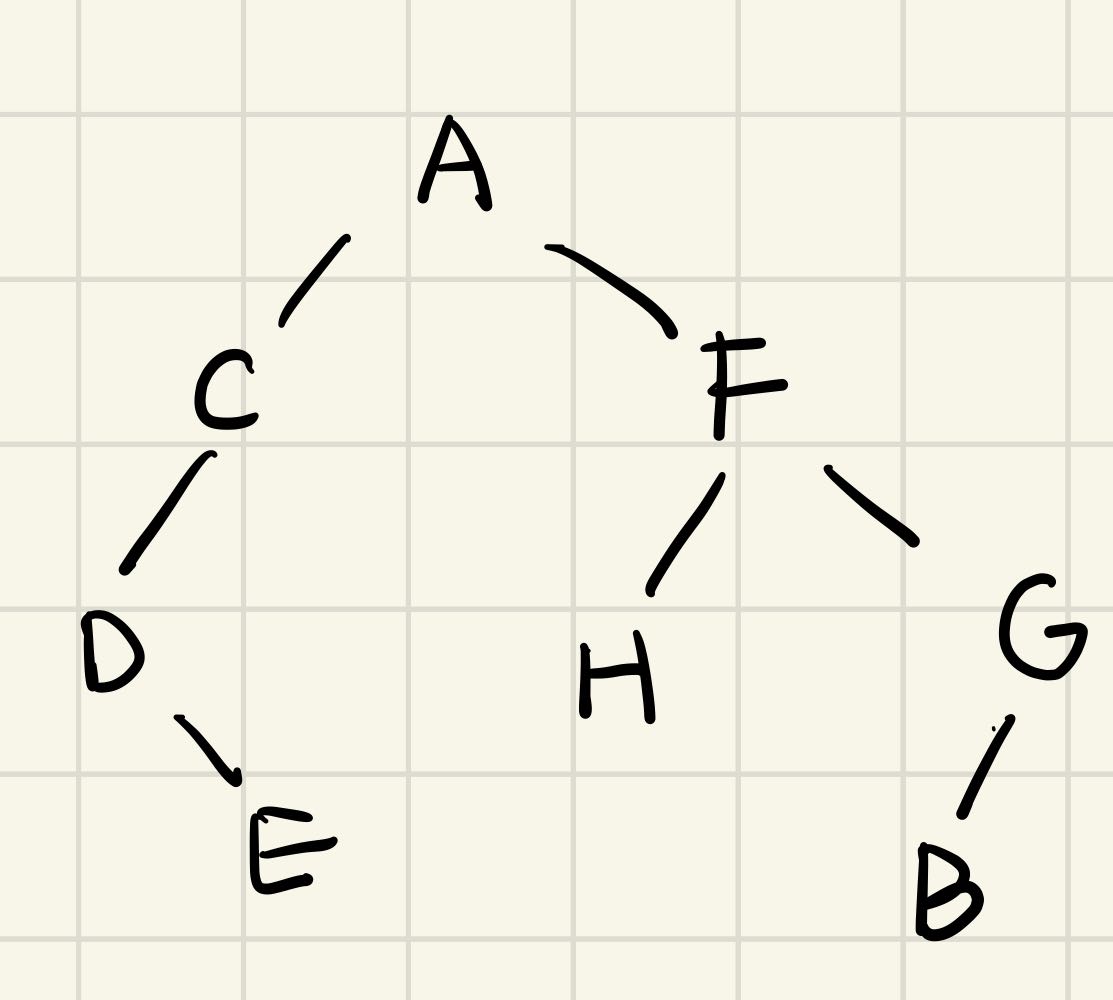
且后序遍历为:EDCHBGFA
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, int> inorderMap;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int inorderSize = inorder.size();
// 记录中序遍历索引
for (int i = 0; i < inorderSize; i++)
inorderMap.insert(make_pair(inorder[i], i));
return build(preorder, 0, inorderSize - 1, inorder, 0, inorderSize - 1);
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
vector<int>& inorder, int inStart, int inEnd)
{
if (preStart > preEnd)
return nullptr;
int rootValue = preorder[preStart];
int rootValueIndex = inorderMap[rootValue];
TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(rootValue);
int leftChildNum = rootValueIndex - inStart;
int rightChildNum = inEnd - rootValueIndex;
newNode->left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftChildNum, inorder, inStart, rootValueIndex - 1);
int newPreEnd = preStart + leftChildNum;
newNode->right = build(preorder, newPreEnd + 1, newPreEnd + rightChildNum, inorder, rootValueIndex + 1, inEnd);
return newNode;
}
};
刷题
框架规划很简单,分为两个步骤
- 分清需要使用哪种遍历方式。前序是不知道孩子节点的情况的;而后序是知道孩子节点的情况的。前序访问的第一个点为根节点
- 两行递归的前/后写出的代码是针对”根节点“的操作,具体是哪里的”根“,要看递归的深度
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<string, int> cachedMap;
vector<TreeNode*> result;
vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) {
Traverse(root);
return result;
}
string Traverse(TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return "#";
string leftStr = Traverse(node->left);
string rightStr = Traverse(node->right);
string newTree = to_string(node->val) + "," + leftStr + "," + rightStr;
auto it = cachedMap.find(newTree);
if (it != cachedMap.end())
{
if (it->second == 1)
result.push_back(node);
it->second++;
}
else
cachedMap.insert(make_pair(newTree, 1));
return newTree;
}
};
这种做法是将树转换为字符串的形式储存在哈希表中,记录的信息为:

优化解法为
class Solution {
public:
int index = 1;
unordered_map<string, int> str2Index;
unordered_map<int, int> index2Num;
vector<TreeNode*> result;
vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) {
Traverse(root);
return result;
}
int Traverse(TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftIndex = Traverse(node->left);
int rightIndex = Traverse(node->right);
string str = to_string(node->val) + to_string(leftIndex) + to_string(rightIndex);
// 树第一次出现
if (str2Index.find(str) == str2Index.end())
str2Index.insert(make_pair(str, index++));
// 获取树的编号
int oldIndex = str2Index[str];
if (index2Num.find(oldIndex) == index2Num.end())
index2Num.insert(make_pair(oldIndex, 0));
if (++index2Num[oldIndex] == 2)
result.push_back(node);
return oldIndex;
}
};
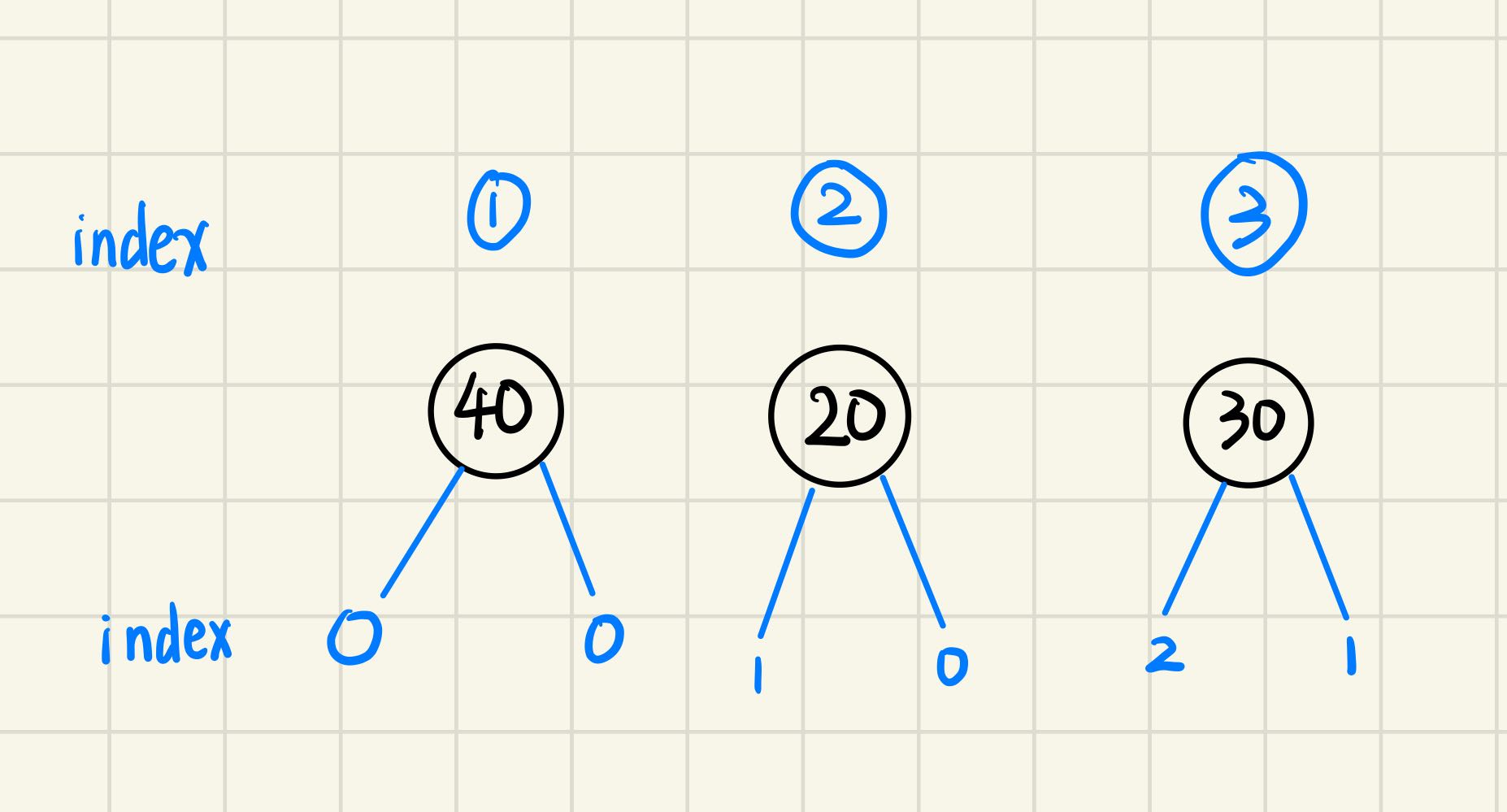
假设有这么一颗树
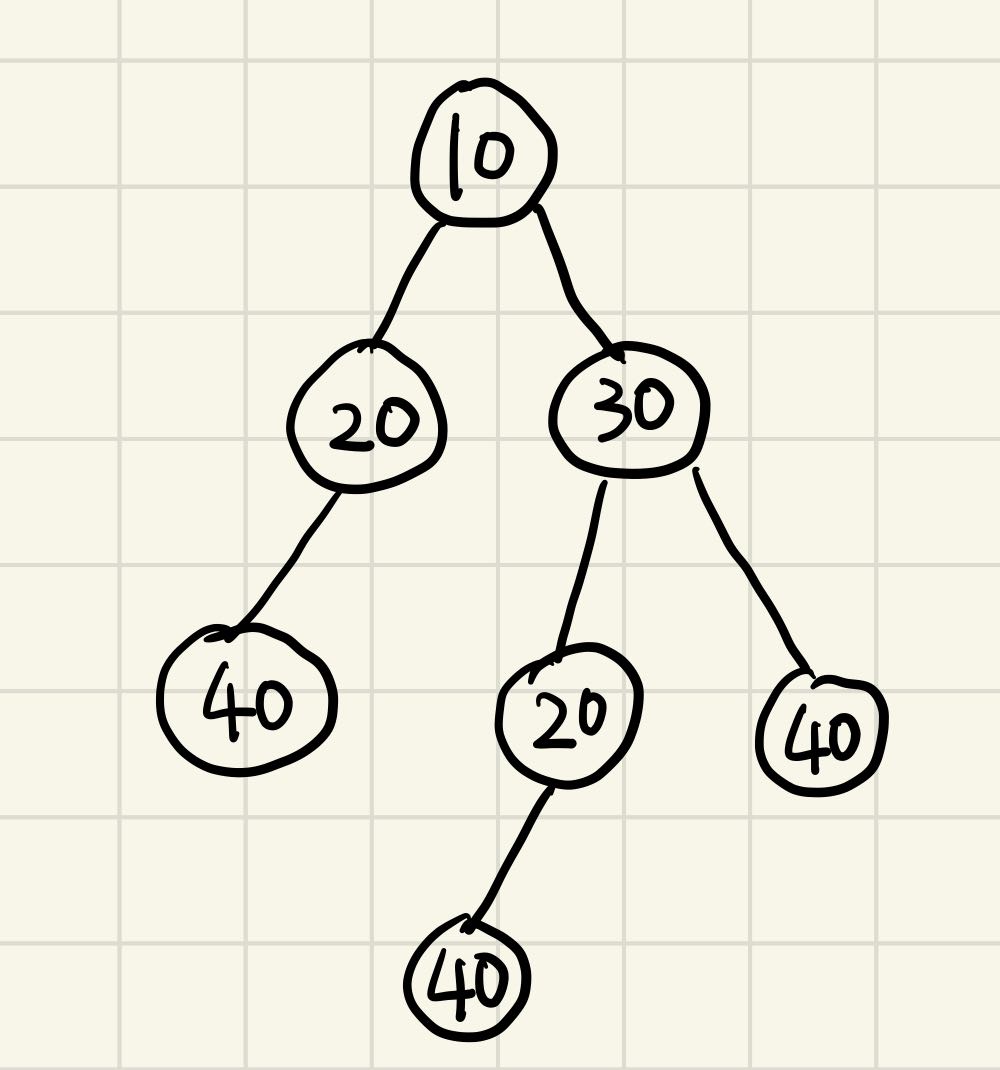
经过遍历后,哈希表中存的数据编程一个“3位的int值”,同时value为该树的编号。比如二号树,它的根节点为值20,左孩子为编号为1的树,右孩子为编号为0的树,即没有右孩子
二叉搜索树(BST)
Binary-Search-Tree
对于任意一个节点来说,它的值必须大于左子树所有的节点,且必须小于右子树所有的节点。并且整棵树中没有相同的数据
拓展性质:
- 从某根节点沿着左下方一直延申,数据越来越小;沿着右下方一直延申,数据越来越大
- 任何子树都是BST
- BST进行中序遍历将会得到有序数列(升序)
验证树是二叉树

class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
// 使用long防止被卡数据
return isValid(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);
}
bool isValid(TreeNode* root, long min, long max)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
if (root->val <= min || root->val >= max)
return false;
return isValid(root->left, min, root->val) && isValid(root->right, root->val, max);
}
};
删除操作
- 如果是叶子节点则直接删除
- 如果只有一个节点则直接将子节点替换上去
- 如果有两个节点则通过中序遍历找到待删除节点的下一个节点,然后替换
查找操作
- 最好的情况:该树为二叉平衡搜索树,搜索时间复杂度为O(logn),与二分查找相同
- 最坏的情况:该树为链表(所有节点只有一个孩子),搜索时间复杂度为O(n)
二叉平衡搜索树(AVL树)(待完成)
AVL树中所有的节点的左右子树的高度差不超过1
LRU结构
少壮不努力老大徒伤悲,LRU结构使用双向链表和哈希表来实现。通过维护节点顺序来列出最久未使用节点,通过哈希表加速链表的访问,以空间换时间

使用STL中的容器实现,不管是速度还是空间上表现都比较一般
class LRUCache {
public:
struct MyData
{
int key;
int value;
MyData() : key(0), value(0) {}
MyData(int _key, int _value) : key(_key), value(_value) {}
};
list<MyData> cacheList;
unordered_map<int, list<MyData>::iterator> key2ListMap;
int cacheSize;
LRUCache(int capacity) : cacheSize(capacity) {}
int get(int key)
{
if (key2ListMap.find(key) != key2ListMap.end())
{
// 调用到数据 优先级上升 插到队头
auto& pData = key2ListMap[key];
cacheList.emplace_front(pData->key, pData->value);
cacheList.erase(pData);
pData = cacheList.begin();
return pData->value;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
// 已经在列表中 更新值 移动到队尾
if (key2ListMap.find(key) != key2ListMap.end())
{
auto& pData = key2ListMap[key];
pData->value = value;
cacheList.emplace_front(pData->key, pData->value);
cacheList.erase(pData);
pData = cacheList.begin();
}
else
{
// 还有空间
if (cacheList.size() < cacheSize)
{
cacheList.emplace_front(key, value);
key2ListMap[key] = cacheList.begin();
}
// 没有空间
else
{
// 链表队尾的为最久未使用的元素
key2ListMap.erase(cacheList.back().key);
cacheList.pop_back();
cacheList.emplace_front(key, value);
key2ListMap[key] = cacheList.begin();
}
}
}
};
使用自建的数据结构实现,哈希表的执行速率和占用空间都不如STL自带的。因此推荐自己重写双向链表,然后用STL的unordered_map
双向链表的设计使用了“虚拟”的头尾节点,在插入和删除的时候方便很多
struct LRUData
{
int key;
int value;
LRUData() = default;
LRUData(int _key, int _value) : key(_key), value(_value) {}
LRUData(LRUData&& _lruData) : key(_lruData.key), value(_lruData.value) {}
};
template<typename T>
struct DoubleLinkNode
{
T data;
DoubleLinkNode* next;
DoubleLinkNode* pre;
DoubleLinkNode() = default;
explicit DoubleLinkNode(T&& _data, DoubleLinkNode* _next = nullptr, DoubleLinkNode* _pre = nullptr) :
data(std::move(_data)), next(_next), pre(_pre) {}
};
template<typename T>
class DoubleLinkList
{
public:
using Node = DoubleLinkNode<T>;
private:
int listSize;
Node* begin;
Node* end;
public:
DoubleLinkList() : listSize(0), begin(new Node()), end(new Node())
{
begin->next = end;
end->pre = begin;
}
~DoubleLinkList()
{
Node* pCurrent = begin;
while (pCurrent->next != nullptr)
{
pCurrent = pCurrent->next;
delete pCurrent->pre;
}
delete end;
}
inline int size() { return listSize; }
void move_to_front(Node* node)
{
if (begin->next == node)
return;
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
node->next = begin->next;
node->pre = begin;
begin->next->pre = node;
begin->next = node;
}
Node* push_front(T&& data)
{
Node* pInsertNode = new Node(std::move(data), begin->next, begin);
listSize++;
pInsertNode->next->pre = pInsertNode;
begin->next = pInsertNode;
return pInsertNode;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (listSize == 0)
return;
Node* pDeleteNode = end->pre;
// 上一节点指向结尾
pDeleteNode->pre->next = end;
// 结尾指向上一节点
end->pre = pDeleteNode->pre;
listSize--;
delete pDeleteNode;
}
T& back()
{
// 判断节点数量
if (listSize > 0)
return end->pre->data;
throw exception();
}
};
template<typename T>
class HashMap
{
private:
int modValue;
vector<forward_list<pair<int, T>>> hashVec;
inline int get_hash_code(int key)
{
return (key % modValue + modValue) % modValue;
}
public:
explicit HashMap(int _modValue = 53) : modValue(_modValue), hashVec(_modValue) {}
bool find(int key)
{
int hashCode = get_hash_code(key);
return any_of(hashVec[hashCode].begin(), hashVec[hashCode].end(), [&key](const pair<int, T>& dataPair)
{
return dataPair.first == key;
});
}
void erase(int key)
{
int hashCode = get_hash_code(key);
typename forward_list<pair<int, T>>::iterator p = hashVec[hashCode].before_begin();
for (auto iterator = hashVec[hashCode].begin(); iterator != hashVec[hashCode].end(); ++iterator)
{
if (iterator->first == key)
{
hashVec[hashCode].erase_after(p);
return;
}
p++;
}
}
void insert(int key, T value)
{
int hashCode = get_hash_code(key);
hashVec[hashCode].emplace_front(key, value);
}
T& operator[](int key)
{
for (pair<int, T>& dataPair : hashVec[get_hash_code(key)])
{
if (dataPair.first == key)
return dataPair.second;
}
throw exception();
}
};
class LRUCache {
public:
DoubleLinkList<LRUData> linkList;
HashMap<DoubleLinkNode<LRUData>*> key2PointerMap;
int maxCapacity;
LRUCache(int capacity) : maxCapacity(capacity), linkList(), key2PointerMap(503) {}
int get(int key)
{
if (key2PointerMap.find(key) == true)
{
// 将该数据更新为最近刚刚使用过
linkList.move_to_front(key2PointerMap[key]);
// 返回找到的数据
return key2PointerMap[key]->data.value;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
if (key2PointerMap.find(key) == true)
{
// 数据更新
key2PointerMap[key]->data.value = value;
// 将该数据更新为最近刚刚使用过
linkList.move_to_front(key2PointerMap[key]);
}
else
{
// 最新数据 插入到链表头
key2PointerMap.insert(key, linkList.push_front(LRUData(key, value)));
// 判断是否过长
if (linkList.size() > maxCapacity)
{
// 删除标记
key2PointerMap.erase(linkList.back().key);
// 删除尾部元素
linkList.pop_back();
}
}
}
};
DFS/BFS
| 数据结构 | 空间 | 特点 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DFS | stack | O(H)和高度成正比 | 不具备最短路 |
| BFS | queue | O(2^n)随深度增加指数增长 | 最短路 |
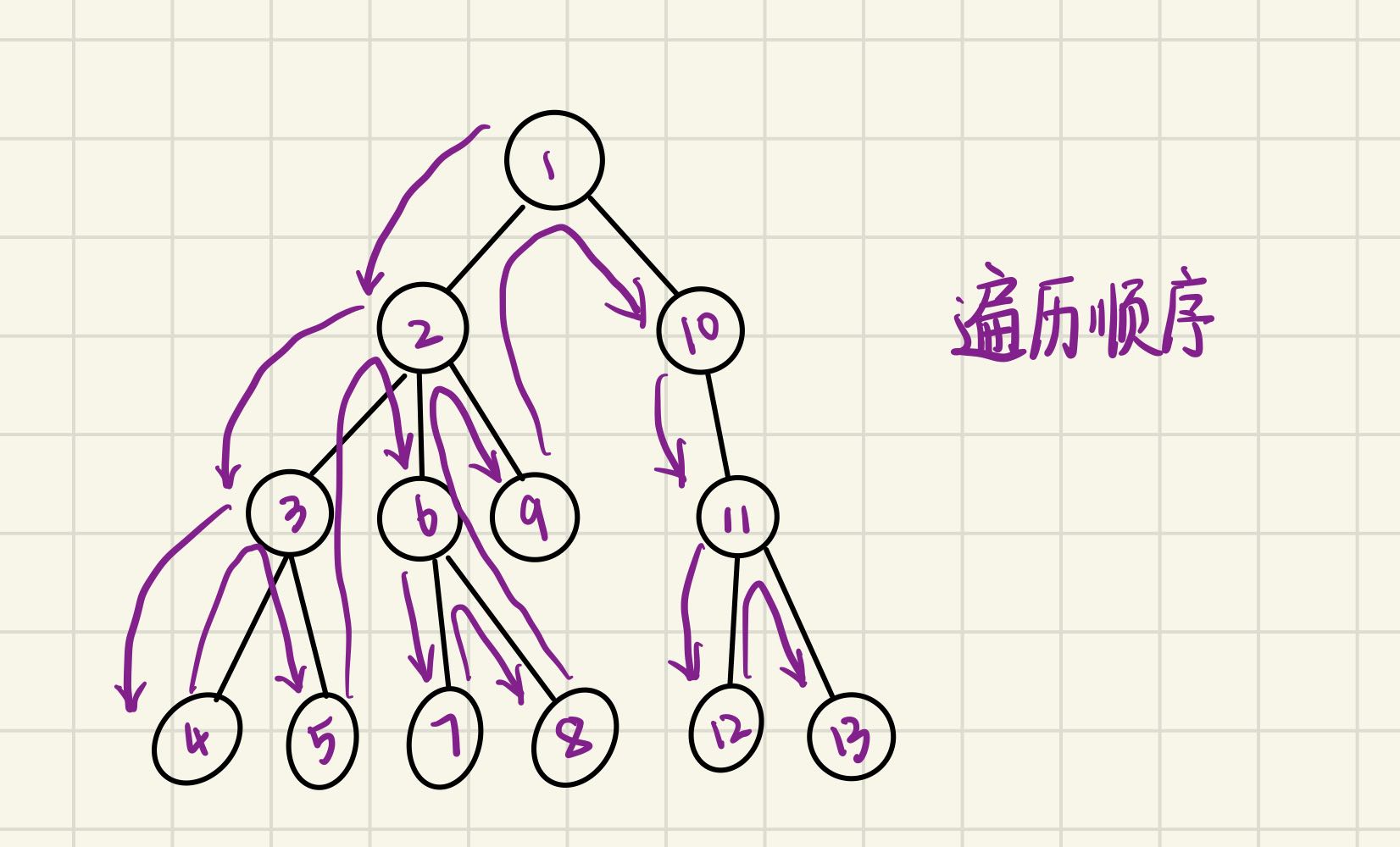
深度优先搜索
看起来有点像前序遍历
排列数字

使用unordered_map的原因是为了让代码更容易看懂,本题只用vector也可以
class Solution
{
public:
unordered_map<int, bool> markMap;
vector<int> sortVec;
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<vector<int>> sortNum(int n)
{
sortVec.resize(n);
dfs(0, n);
return result;
}
void dfs(int index, int n)
{
// 递归结束条件
if (index == n)
{
result.push_back(sortVec);
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// 若i不存在则默认为false
if (markMap[i] == true)
continue;
// 记录并修改标志位
sortVec[index] = i;
markMap[i] = true;
// 往下一层递归
dfs(index + 1, n);
// 回溯操作 复原现场
markMap[i] = false;
}
}
};
还可以使用STL进行求解,由于要求的是所有的排列方案,所需需要将数组的初始值定为123
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> sortNum(int n)
{
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> sequence;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
sequence.push_back(i);
do
result.push_back(sequence);
while (next_permutation(sequence.begin(), sequence.end()));
return result;
}
};
字典序排数

思路是先假设有9棵十叉树,开始时分别对九棵树进行DFS。每棵树有10个节点(0-9),且深度每进一层,节点的值翻十倍
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> result;
vector<int> lexicalOrder(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
dfs(i, n);
return result;
}
void dfs(int current, int max)
{
if (current > max) return;
result.push_back(current);
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
dfs(current * 10 + i, max);
}
};
n-皇后问题

方法一,逐个检查法
class CheckSolution
{
public:
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> board;
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n)
{
board = vector<string>(n, string(n, '.'));
dfs(0);
return result;
}
void dfs(int lineIndex)
{
// 递归结束条件 将棋盘放入结果数组中
if (lineIndex == board.size())
result.push_back(board);
else
{
// 当前行逐个遍历
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++)
{
// 检查是否符合皇后放置条件
if (!canPlace(lineIndex, i))
continue;
// 符合条件 放置皇后
board[lineIndex][i] = 'Q';
// 递归进入下一行
dfs(lineIndex + 1);
// 恢复现场
board[lineIndex][i] = '.';
}
}
}
bool canPlace(int lineIndex, int columnIndex)
{
//检查正上方
for (int i = 0; i < lineIndex; i++)
if (board[i][columnIndex] == 'Q')
return false;
//检查右斜上方
for (int i = lineIndex - 1, j = columnIndex + 1; i >= 0 && j < board.size(); i--, j++)
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
//检查左斜上方
for (int i = lineIndex - 1, j = columnIndex - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
// 只需要检查上方部分的棋盘 并且同行不需要检测 因为一行只有一个棋子
return true;
}
};
方法二,标记法
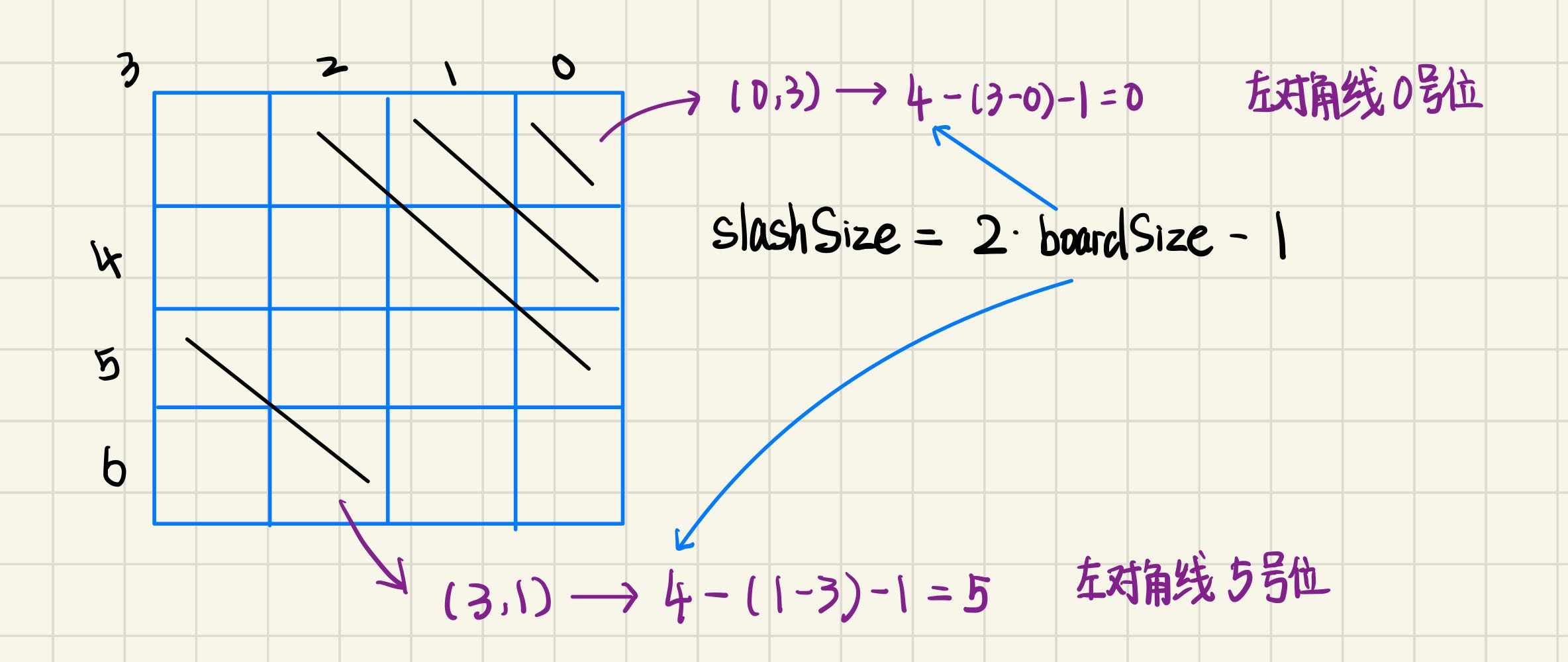
class MarkSolution
{
public:
vector<bool> column, leftSlash, rightSlash;
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> board;
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n)
{
// 初始化列
column = vector<bool>(n, true);
// 初始化左对角线和右对角线
leftSlash = rightSlash = vector<bool>(2 * n - 1, true);
board = vector<string>(n, string(n, '.'));
dfs(0);
return result;
}
void dfs(int line)
{
int boardSize = board.size();
if (line == boardSize)
result.push_back(board);
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; i++)
{
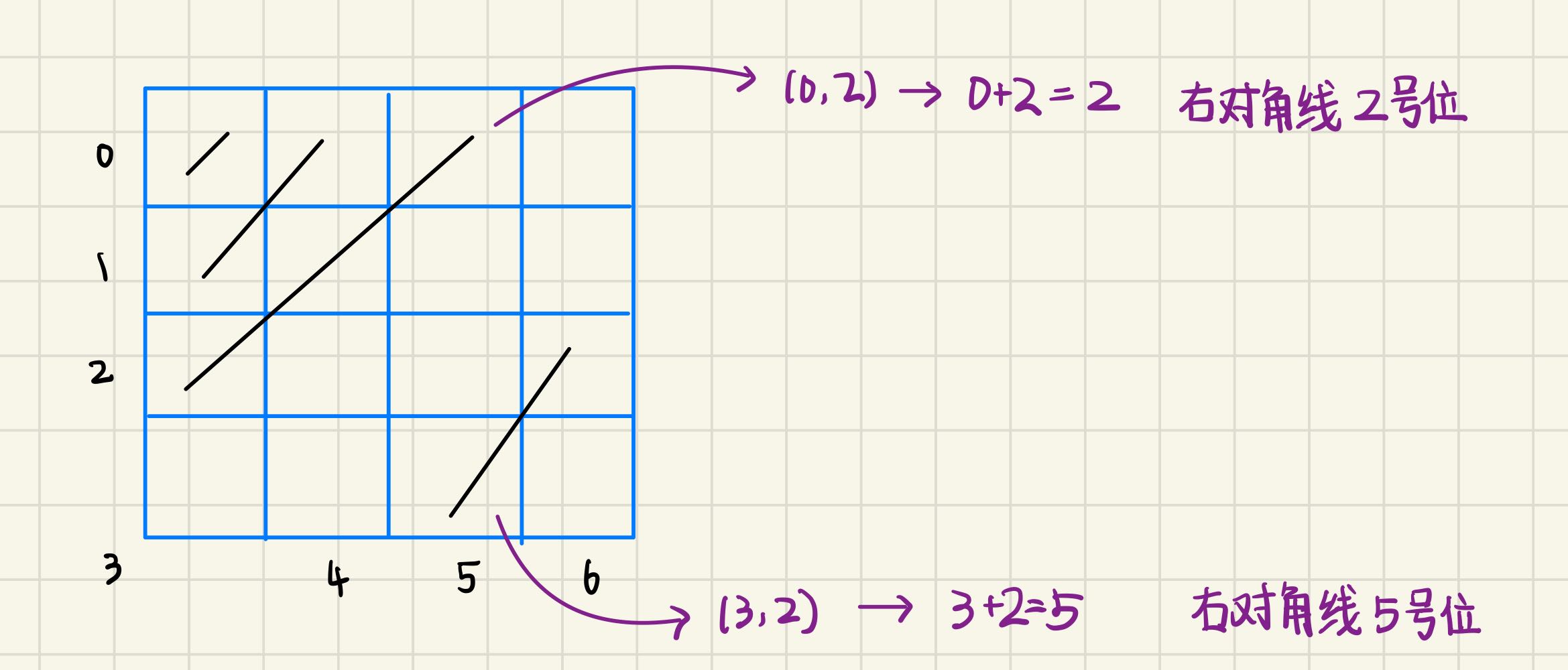
int leftIndex = boardSize - line + i - 1;
int rightIndex = line + i;
// 判断是否能放置
if (column[i] && rightSlash[rightIndex] && leftSlash[leftIndex])
{
board[line][i] = 'Q';
column[i] = rightSlash[rightIndex] = leftSlash[leftIndex] = false;
dfs(line + 1);
board[line][i] = '.';
column[i] = rightSlash[rightIndex] = leftSlash[leftIndex] = true;
}
}
}
}
};
执行速率对比

广度优先搜索
看起来有点像层序遍历
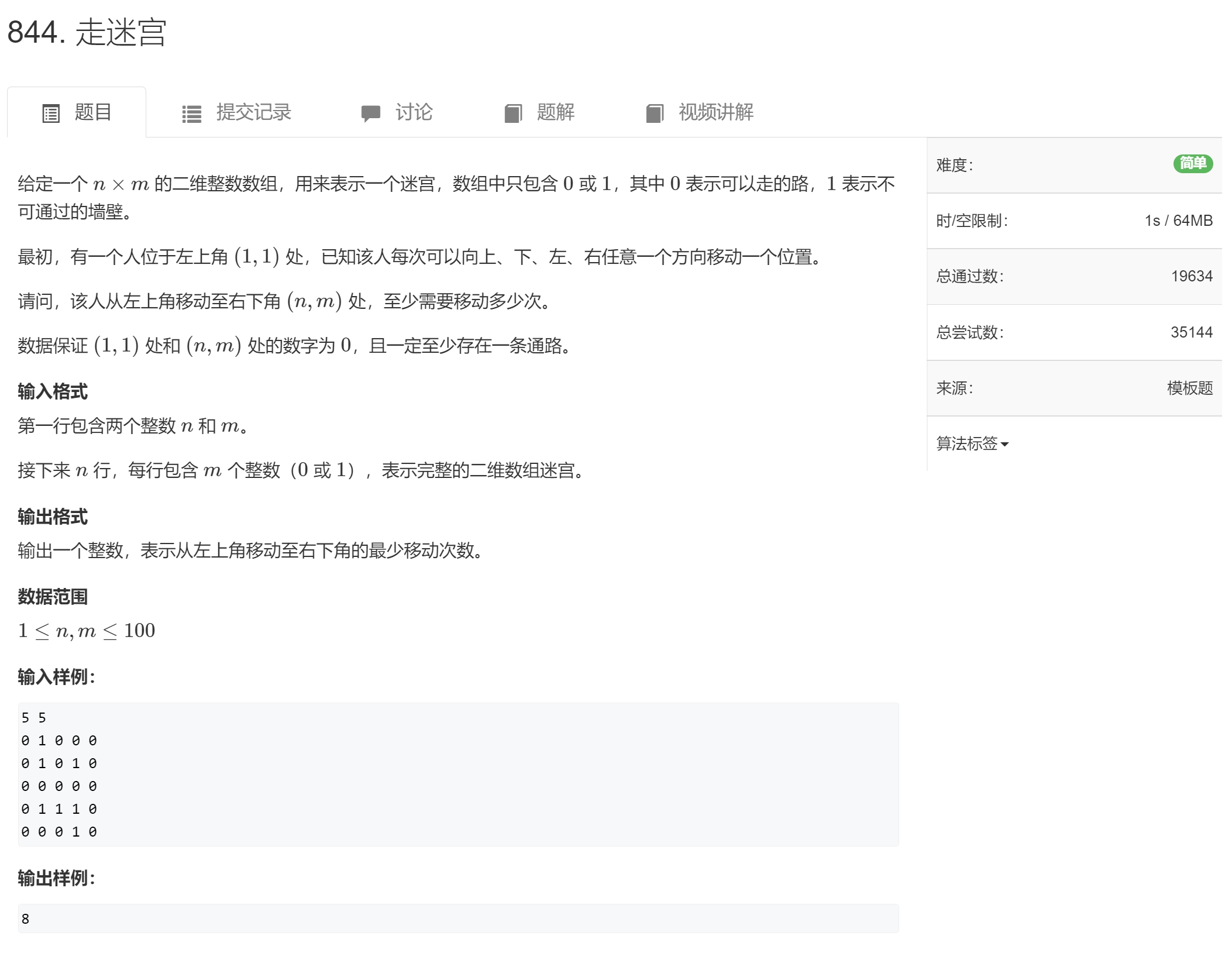
走迷宫
因为LeetCode的题是收费的所以...
class Solution
{
public:
int walkMaze(vector<vector<int>> maze)
{
// 初始化行 列
int lineSize = maze.size();
int columnSize = maze[0].size();
// 初始化距离二维数组为-1
vector<vector<int>> distance = vector<vector<int>>(lineSize, vector<int>(columnSize, -1));
// 深度遍历队列
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
// 设置遍历的初始值 从左上角开始遍历
distance[0][0] = 0;
q.push(make_pair(0, 0));
// 设置环顾方向 左 下 右 上
int moveX[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int moveY[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
// 入队与出队处理
while (!q.empty())
{
auto pos = q.front();
q.pop();
// 检测周围是否有元素能入队
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nextLineIndex = pos.first + moveY[i];
int nextColumnIndex = pos.second + moveX[i];
// 判断是否超出边界
if (nextLineIndex >= 0 && nextColumnIndex >= 0 && nextLineIndex < lineSize && nextColumnIndex < columnSize)
{
// 只走没走过的路 且 不被障碍物堵住
if (distance[nextLineIndex][nextColumnIndex] == -1 && maze[nextLineIndex][nextColumnIndex] != -1)
{
q.push(make_pair(nextLineIndex, nextColumnIndex));
distance[nextLineIndex][nextColumnIndex] = distance[pos.first][pos.second] + 1;
}
}
}
}
return distance[lineSize - 1][columnSize - 1];
}
};