(一)1.如何绘制散点图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 如何绘制散点图# 先随机生成数据x = np.array(range(100))y = np.sin(x)# 直接输入x和y便可绘制相应的散点图plt.scatter(x, y)# 不要忘了这句话,表示让图像显示plt.show() |
可以看到类似于正弦曲线一样的点
(一)2.如何给散点图加上样式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.array(range(0, 100, 5))y = 3 * x + 2# scatter里面的参数有很多,不过我们主要使用四种# 1:s,表示点的面积,注意是面积。# 2:c,颜色,不指定默认为蓝色# 3:marker:点的形状,不指定默认为点# 4:alpha:透明度,不指定默认为1,表示透明度为0plt.scatter(x, y, s=100, c="green", marker="<", alpha=0.1)plt.show() |
(二)1.如何绘制折线图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)y = x ** 2plt.plot(x, y)# 此外还有一个plt.plot_date()函数,专门用来绘制有一个轴是日期格式的数据plt.show() |
(二)2.如何给折线图加上样式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.linspace(-10, 10, 20)y = x ** 2z = x * 2 + 1# 关于样式的参数有很多# linestyle:表示线段的样式# color:表示颜色# marker:表示点的样式plt.plot(x, y, linestyle="-", color="green", marker="o")plt.plot(x, z, linestyle="--", color="red", marker="<")plt.show() |
(三)1.如何绘制条形图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 还记得每一个图对应的每一个函数吗?# 散点图:scatter# 折线图:plot# 条形图:bar# 这个函数可以只接收两个参数,分别是条形图中每一条的索引和高度plt.bar(x=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], height=[11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66])plt.show() |
(三)2.如何给条形图加上样式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# color:颜色# width:线条宽度plt.bar(x=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], height=[11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66], color="green", width=0.2)plt.show() |
(三)3.如何绘制横向的条形图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 如果绘制横向的条形图# 那么bottom相当于之前的x,width相当于之前的heightplt.bar(x=0, bottom=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], width=[11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66], color="green", height=0.2, orientation="horizontal")# 还有一个plt.barh(),表示花水平的条形图,不用显示的指定orientation="horizontal",但其他的参数还是要有的plt.show() |
(四)1.如何绘制直方图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltmu = 100sigma = 20x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(2000)# 设置直方图# bins:表示要分成多少个区间# normed:表示是否进行标准化,标准化之后,那么纵坐标不在是个数,而是频率。plt.hist(x, bins=30, color="red", density=True)plt.show() |
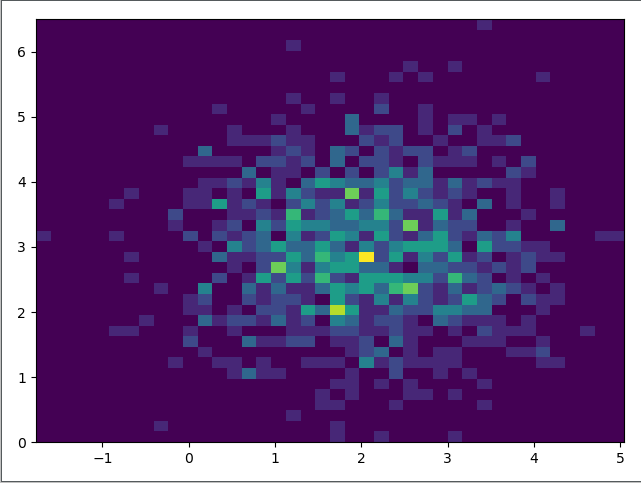
(四)2.如何绘制双变量直方图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.random.randn(1000)+2y = np.random.randn(1000)+3plt.hist2d(x, y, bins=40)plt.show() |
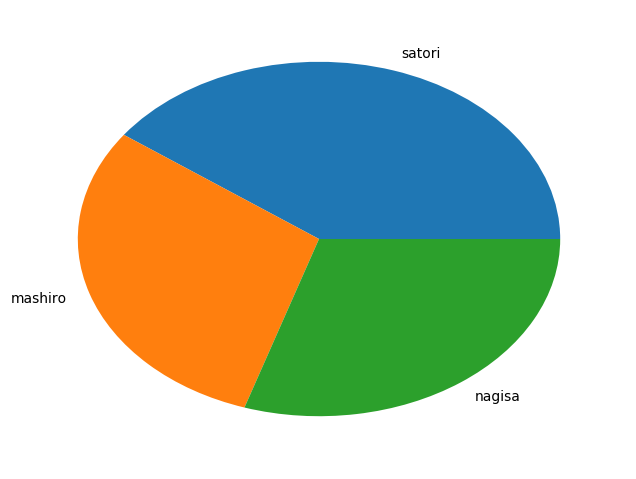
(五)1.如何绘制饼图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltlabels = ["satori", "mashiro", "nagisa"]fracs = [40, 30, 30]# 最重要的两个参数# x:所占的份额# labels:对应的标签plt.pie(x=fracs, labels=labels)plt.show() |
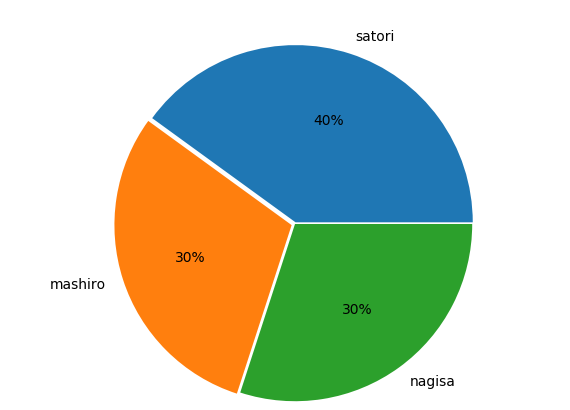
细心地哲学♂家可能回好奇,为什么是一个椭圆,这是因为我们这里少了一句话
而且每一块上面光秃秃的,每个部分都贴在了一块,也不好看,我们也可以设置一些参数,让其变得好看一些
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltlabels = ["satori", "mashiro", "nagisa"]fracs = [40, 30, 30]# 加上这句话表示x和y轴的比例是一比一# 因此图形就变成了圆形plt.axes(aspect=1)# autopct:表示每一块的比例# explode:突出显示,每个部分不会贴在一块<br><br># shadow:表示加上一层阴影,指定为True即可 |
|
1
|
plt.pie(x=fracs, labels=labels, autopct="%.0f%%", explode=[0.01, 0.02, 0]) plt.show() |
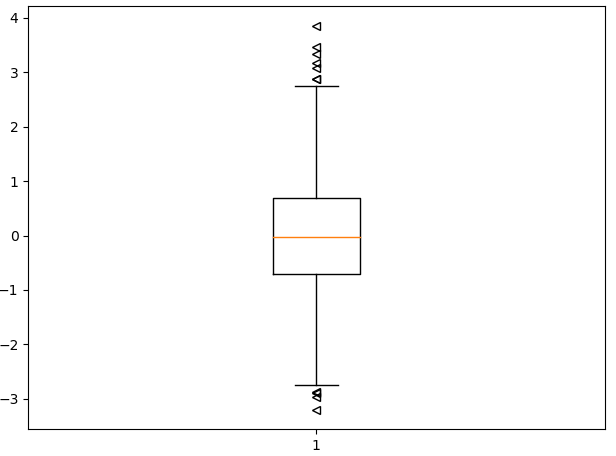
(六)1.如何绘制箱形图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npnp.random.seed(100)data = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=1000)# sym:形状,表示异常值的形状# whis:表示虚线的长度,可以控制异常值显示的多少,越大虚线越长plt.boxplot(data, sym="<", whis=1.5)plt.show() |
(七)颜色和样式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
蓝色 - 'b'绿色 - 'g'红色 - 'r'青色 - 'c'品红 - 'm'黄色 - 'y'黑色 - 'k' 白色 - 'w' |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
'.' point marker',' pixel marker'o' circle marker'v' triangle_down marker'^' triangle_up marker'<' triangle_left marker'>' triangle_right marker'1' tri_down marker'2' tri_up marker'3' tri_left marker'4' tri_right marker's' square marker'p' pentagon marker'*' star marker'h' hexagon1 marker'H' hexagon2 marker'+' plus marker'x' x marker'D' diamond marker'd' thin_diamond marker'|' vline marker'_' hline marker |
|
1
2
3
4
|
'-' solid line style'--' dashed line style'-.' dash-dot line style':' dotted line style |
输入样式的时候还有一个简便的方法,cx--,c是青色,x是点的样式,--是线的样式
(八)1.如何绘制子图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(0, 100, 5)# 生成一个画布fig = plt.figure()# 往画布上添加对象# 这里的221表示,生成一个2X2的画布,并处于第一个位置s1 = fig.add_subplot(221)s2 = fig.add_subplot(222)s3 = fig.add_subplot(223)s4 = fig.add_subplot(224)y1 = np.exp(x)y2 = np.sin(x)y3 = np.cos(x)y4 = x ** 2s1.plot(x, y1, "cx--")s2.plot(x, y2, "bo-.")s3.plot(x, y3, "g<--")s4.plot(x, y4, "y>-.")# 最后显示要用fig,因为它是我们创建出来的画布,必须要让它显示fig.show() |
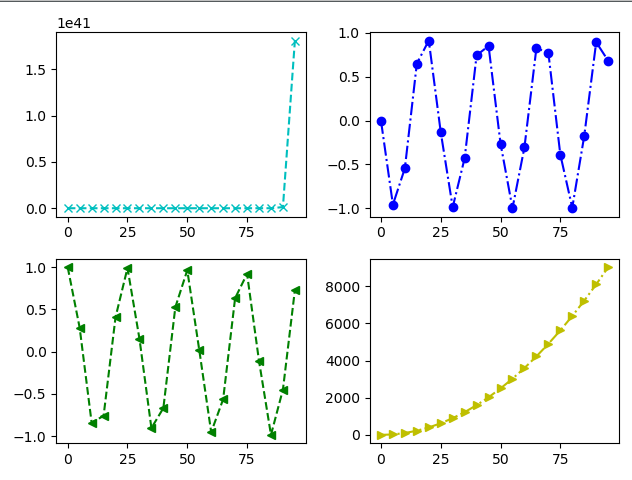
(八)2.如何绘制子图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(0, 100, 5)plt.subplot(221)plt.plot(x, np.exp(x))plt.subplot(222)plt.plot(x, np.sin(x))plt.subplot(223)plt.plot(x, np.cos(x))plt.subplot(224)plt.plot(x, x**2)plt.show() |
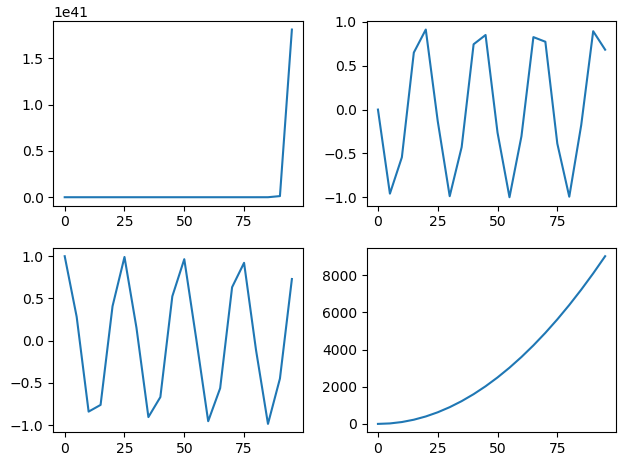
(九)如何绘制网格
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(0, 100, 5)# 绘制出格子plt.grid(x, color="green")# 绘制线段plt.plot(x, x, "cx--")plt.show() |
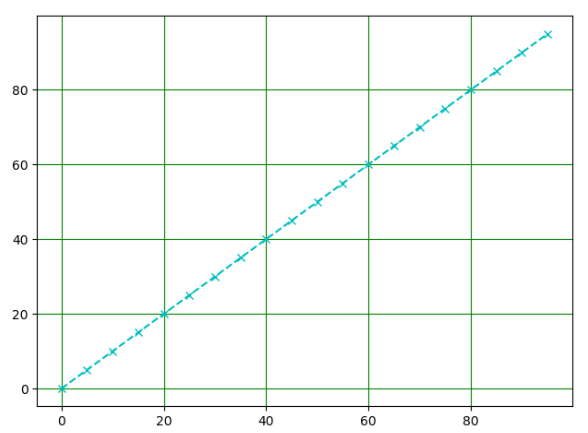
(十)如何给图像带上标记
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
y3 = np.tan(x)
# 加上需要的标签label
plt.plot(x, y1, label="np.sin")
plt.plot(x, y2, label="np.cos")
plt.plot(x, y3, label="np.tan")
# 必须加上这句话,否则标签不显示
# legend里面还有一个location参数,可以指定位置
# 以及ncol可以指定要标签分几列显示
plt.legend()
plt.show()
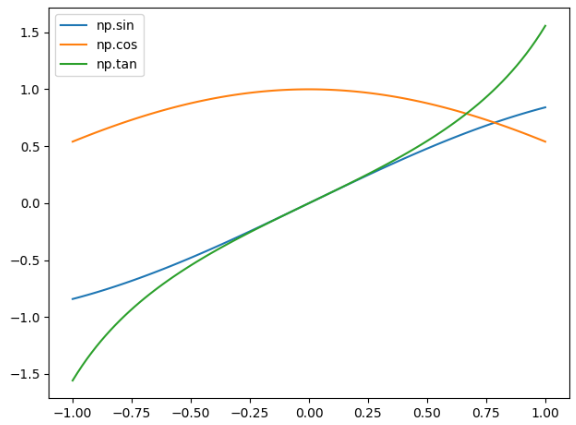
(十一)调整坐标轴范围
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
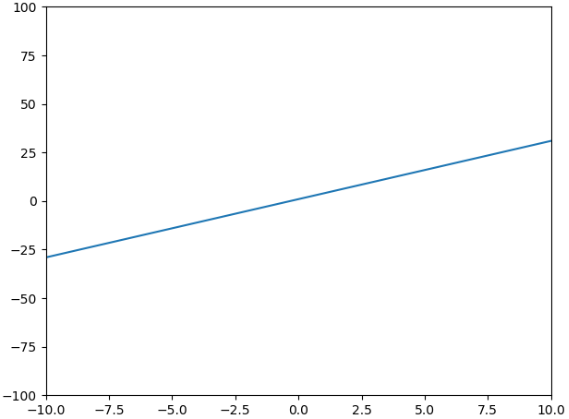
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(-100, 100)y = 3 * x + 1plt.plot(x, y)# 表示x轴从-10到10,y轴-100到100<br># 也可以通过plt.xlim([,])和plt.ylim([,])只调x轴或y轴<br># 如果只想调整一边的话,就直接指定最大或者最小,xlim(xmin=,xmax=),ylim(ymin=,ymax=)plt.axis([-10, 10, -100, 100])plt.show() |
(十二)调整坐标轴刻度
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
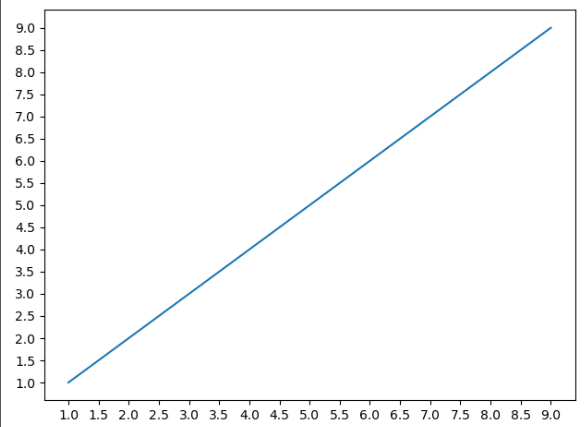
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(1, 10)plt.plot(x, x)# 获取坐标轴属性,get current axisax = plt.gca()# nbins表示有多少间隔,可以看到分成了20份ax.locator_params(nbins=20)# 如果我只想调整某一个轴的话# 指定ax.locator_params("x", nbins=20)plt.show() |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
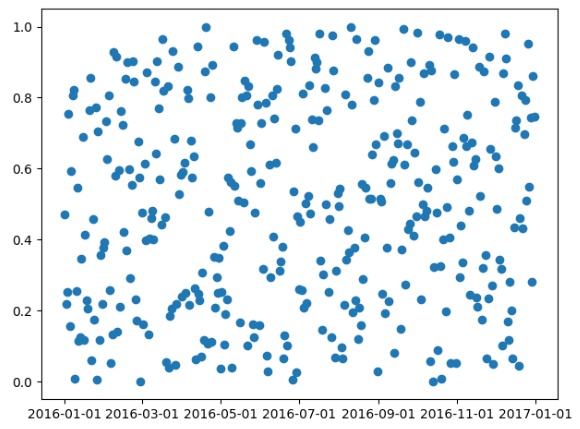
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplimport datetimestart = datetime.date(2016, 1, 1)end = datetime.date(2017, 1, 1)timedelta = datetime.timedelta(days=1)date = mpl.dates.drange(start, end, timedelta)y = np.random.rand(len(date))ax = plt.gca()plt.plot_date(date, y)# 设置时间格式date_format = mpl.dates.DateFormatter("%Y-%m-%d")# 将格式应用到x轴上ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(date_format)plt.show() |
(十三)如何添加坐标轴
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
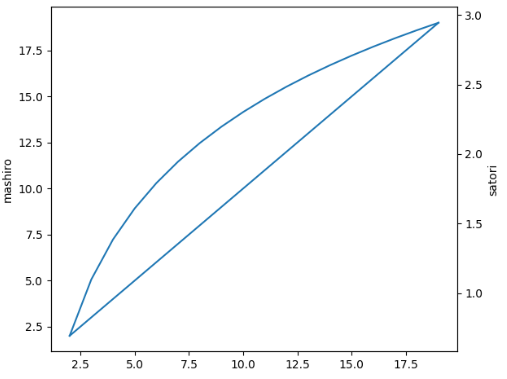
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(2, 20, 1)y1 = xy2 = np.log(x)fig = plt.figure()ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)ax1.plot(x, y1)ax1.set_ylabel("mashiro")# 表示生成一个双胞胎y轴,twinx,表示生成一个y轴ax2 = ax1.twinx()ax2.plot(x, y2)ax2.set_ylabel("satori")fig.show() |
(十四)添加注释
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
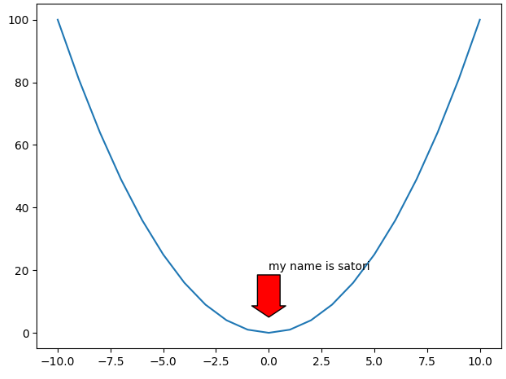
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(-10, 11)y = x ** 2plt.plot(x, y)plt.annotate("my name is satori", xy=(0, 5), # 箭头坐标 xytext=(0, 20), # 文本坐标 arrowprops={"facecolor": "r", # 颜色 "headlength": 10, # 箭头的长度 "headwidth": 30, # 箭头的头的宽度 "width": 20 # 箭头的身体的宽度 } )plt.show() |
(十五)如何绘制3D图形
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
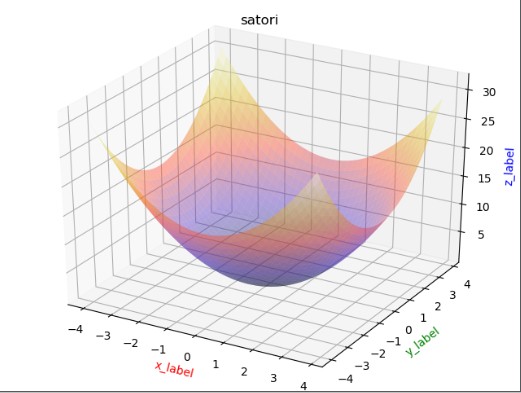
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D as A3fig = plt.figure()ax = A3(fig)x = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.2)y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.2)x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y)z = np.power(x, 2) + np.power(y, 2)plt.title("satori")# rstride,cstride表示行列每隔多少个点建一个面,cmap表示颜色ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.cm.CMRmap, alpha=0.4)ax.set_xlabel('x_label', color='r')ax.set_ylabel('y_label', color='g')ax.set_zlabel('z_label', color='b')plt.show() |
如何解决中文乱码问题
|
1
2
3
4
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 步骤一(替换sans-serif字体)plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 步骤二(解决坐标轴负数的负号显示问题) |
解决子图重合问题
plt.tight_layout()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(1, 100)y = 2 * xplt.plot(x, y)# 调整x,y轴的取值范围plt.xlim(10, 30)plt.ylim(20, 60)# 调整x或y轴的间隔ax = plt.gca()ax.locator_params("x", nbins=40)# 调整x或y轴坐标的倾斜程度plt.xticks(rotation=60)plt.show() |
