回归与分类
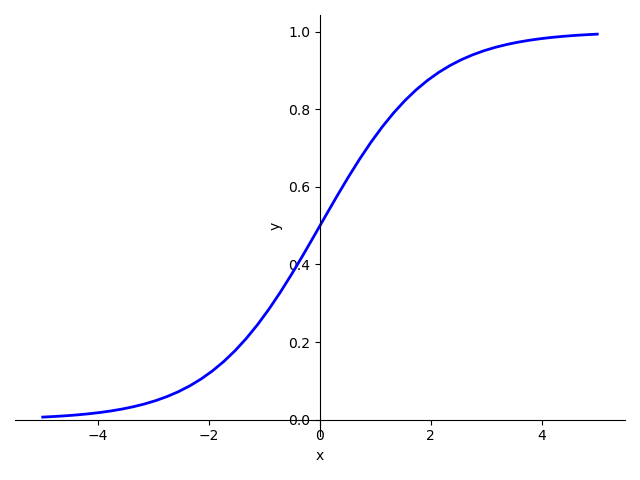
- 回归->分类:将实数空间(R)映射到([0,1])
- Logistic函数(y=frac{1}{1+e^{-x}})
损失函数
线性回归的损失函数
[loss = (hat{y}-y)^{2}=(x*omega-y)^{2}
]
二分类的损失函数(交叉熵)
[loss = -(yloghat{y}+(1-y)log(1-hat{y}))
]
Mini-Batch损失函数
对二分类的损失函数求均值
[loss = -frac{1}{N}sum_{n=1}^N(y_{n}loghat{y_n}+(1-y_{n}log(1-hat{y_n})))
]
与线性回归的区别
- 在前馈中多了一个sigmoid的处理
- 损失函数不再是MSELoss,而是BSELoss以求交叉熵
代码实现
训练数据是x表示学习时间,y表示是否合格(0不合格,1合格)
from abc import ABC
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = torch.Tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.Tensor([[0], [0], [1]])
class LogisticRegressionModel(torch.nn.Module, ABC):
def __init__(self):
super(LogisticRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(self.linear(x))
return y_pred
model = LogisticRegressionModel()
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(size_average=False)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss_list = []
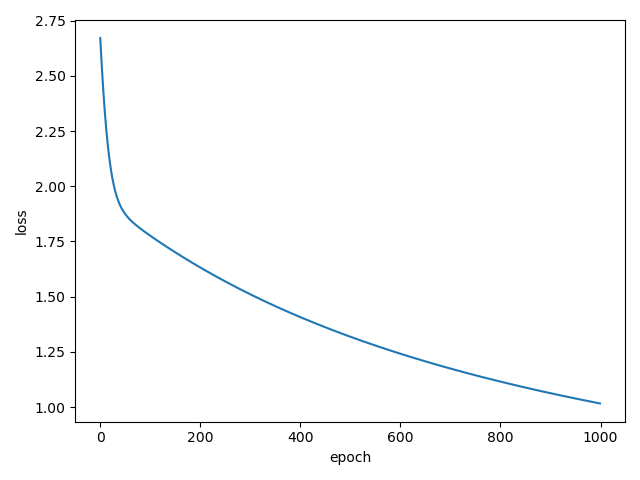
for epoch in range(1000):
y_pred = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data)
print(epoch, loss.item())
loss_list.append(loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_list = list(range(1000))
plt.plot(epoch_list, loss_list)
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("loss")
plt.show()
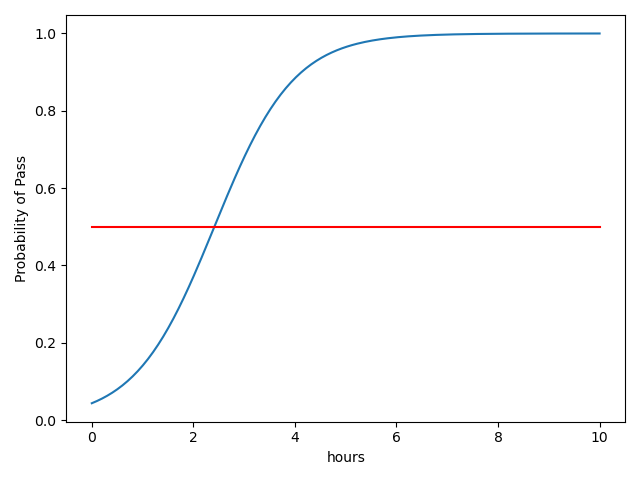
测试
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 200)
x_test = torch.Tensor(x).view(200, 1) # reshape 200行 1列
y_test = model(x_test)
y = y_test.data.numpy()
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.plot([0, 10], [0.5, 0.5], c='r')
plt.xlabel("hours")
plt.ylabel('Probability of Pass')
plt.show()