遍历
N叉树的遍历
树的遍历
一棵二叉树可以按照前序、中序、后序或者层序来进行遍历。在这些遍历方法中,前序遍历、后序遍历和层序遍历同样可以运用到N叉树中。
回顾 - 二叉树的遍历
- 前序遍历 - 首先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树;
- 中序遍历 - 首先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树;
- 后序遍历 - 首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点;
- 层序遍历 - 按照从左到右的顺序,逐层遍历各个节点。
请注意,N叉树的中序遍历没有标准定义,中序遍历只有在二叉树中有明确的定义。尽管我们可以通过几种不同的方法来定义N叉树的中序遍历,但是这些描述都不是特别贴切,并且在实践中也不常用到,所以我们暂且跳过N叉树中序遍历的部分。
把上述关于二叉树遍历转换为N叉树遍历,我们只需把如下表述:
遍历左子树... 遍历右子树...
变为:
对于每个子节点:
通过递归地调用遍历函数来遍历以该子节点为根的子树
我们假设for循环将会按照各个节点在数据结构中的顺序进行遍历:通常按照从左到右的顺序,如下所示。
N叉树遍历示例
我们用如图所示的三叉树来举例说明:
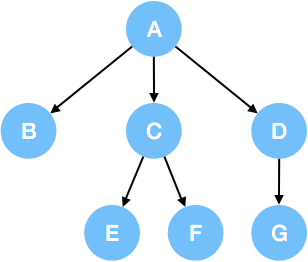
1.前序遍历
在N叉树中,前序遍历指先访问根节点,然后逐个遍历以其子节点为根的子树。
例如,上述三叉树的前序遍历是: A->B->C->E->F->D->G.
2.后序遍历
在N叉树中,后序遍历指前先逐个遍历以根节点的子节点为根的子树,最后访问根节点。
例如,上述三叉树的后序遍历是: B->E->F->C->G->D->A.
3.层序遍历
N叉树的层序遍历与二叉树的一致。通常,当我们在树中进行广度优先搜索时,我们将按层序的顺序进行遍历。
例如,上述三叉树的层序遍历是: A->B->C->D->E->F->G.
练习
接下来,我们将为你提供几道与N叉树相关的习题。
N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
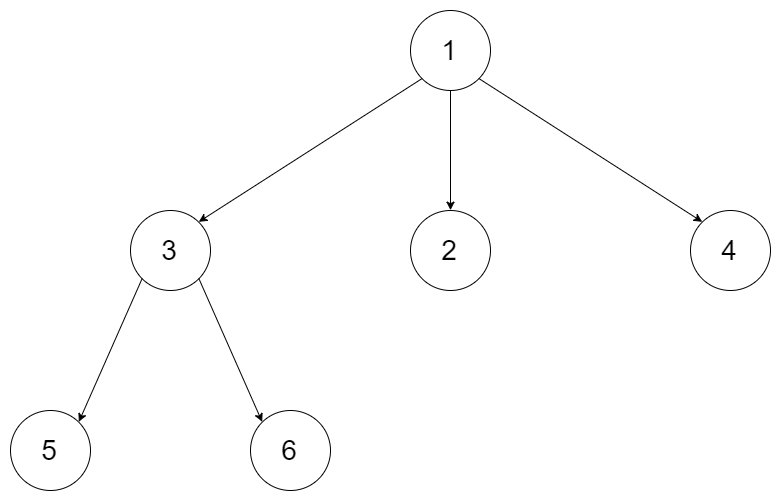
返回其前序遍历: [1,3,5,6,2,4]。
说明: 递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node(){}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*>_children){
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
/// Recursion
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(h)
class SolutionA{
public:
vector<int> preorder(Node* root){
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
private:
void dfs(Node* node, vector<int>& res){
if(!node)
return;
res.push_back(node->val);
for(Node* next: node->children)
dfs(next, res);
}
};
/// Non-Recursion
/// Using stack
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(h)
class SolutionB{
public:
vector<int> preorder(Node* root){
vector<int> res;
if(!root)
return res;
stack<Node*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
Node* cur = stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
for(vector<Node*>::reverse_iterator iter = cur->children.rbegin();
iter != cur->children.rend(); iter++)
stack.push(*iter);
}
return res;
}
};
int main(){
return 0;
}
N-ary Tree Postorder Traversal
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的后序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
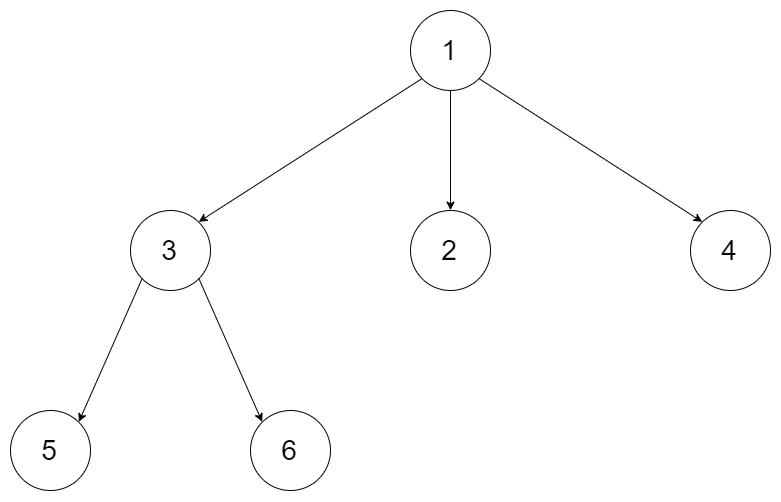
返回其后序遍历: [5,6,3,2,4,1].
说明: 递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node(){}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children){
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
/// Recursion
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(h)
class SolutionA{
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root){
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
private:
void dfs(Node* node, vector<int>& res){
if(!node)
return;
for(Node* next: node->children)
dfs(next, res);
res.push_back(node->val);
}
};
/// Non-Recursion
/// Using stack
///
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(h)
class SolutionB{
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root){
vector<int> res;
if(!root)
return res;
stack<Node*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
Node* cur = stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
for(Node* next: cur->children)
stack.push(next);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
int main(){
return 0;
}
N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
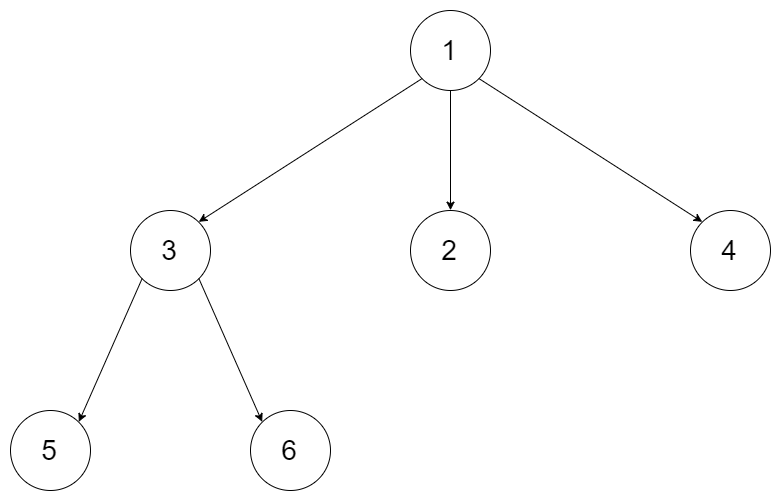
返回其层序遍历:
[
[1],
[3,2,4],
[5,6]
]
说明:
- 树的深度不会超过
1000。 - 树的节点总数不会超过
5000。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int val = NULL;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
/// BFS
/// Store step in the queue
///
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(n)
class SolutionA{
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root){
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root)
return res;
queue<pair<Node*, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while(!q.empty()){
Node* cur = q.front().first;
int step = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(step == res.size())
res.push_back({cur->val});
else
res[step].push_back(cur->val);
for(Node* next: cur->children)
q.push(make_pair(next, step + 1));
}
return res;
}
};
int main(){
return 0;
}
递归
N叉树的经典递归解法
经典递归法
我们在之前的章节中讲过如何运用递归法解决二叉树问题。在这篇文章中,我们着重介绍如何将这个思想引入到N叉树中。
在阅读以下内容之前,请确保你已阅读过 运用递归解决树的问题 这篇文章。
- "自顶向下"的解决方案
"自顶向下"意味着在每个递归层次上,我们首先访问节点以获得一些值,然后在调用递归函数时,将这些值传给其子节点。
一个典型的 "自顶向下" 函数 top_down(root, params) 的工作原理如下:
1. 对于 null 节点返回一个特定值
2. 如果有需要,对当前答案 answer 进行更新 // answer <-- params
3. for each child node root.children[k]:
4. ans[k] = top_down(root.children[k], new_params[k]) // new_params <-- root.val, params
5. 如果有需要,返回答案 answer // answer <-- all ans[k]
- "自底向上"的解决方案
"自底向上" 意味着在每个递归层次上,我们首先为每个子节点递归地调用函数,然后根据返回值和根节点本身的值给出相应结果。
一个典型的 "自底向上" 函数 bottom_up(root) 的工作原理如下:
1.对于 null 节点返回一个特定值
2.for each child node root.children[k]:
3. ans[k] = bottom_up(root.children[k]) // 为每个子节点递归地调用函数
4. 返回答案 answer // answer <- root.val, all ans[k]
Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
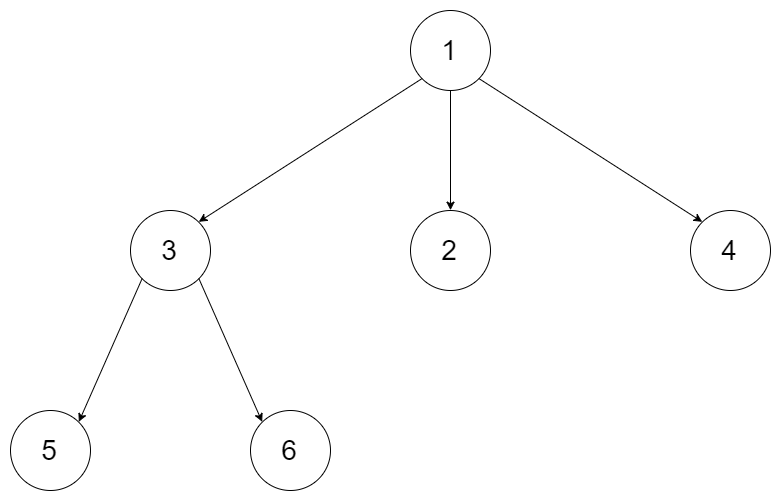
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
说明:
- 树的深度不会超过
1000。 - 树的节点总不会超过
5000。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/// DFS
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(n)
/// Definition for a Node.
class Node{
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node(){}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children){
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
class Solution{
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root){
if(!root)
return 0;
int res = 1;
for(Node* child: root->children)
res = max(res, 1 + maxDepth(child));
return res;
}
};
int main(){
return 0;
}
小结
这张卡旨在介绍N叉树的基本思想。 实际上,二叉树只是N叉树的一种特殊形式,N叉树相关问题的解决方案与二叉树的解法十分相似。 因此,我们可以把在二叉树中学到的知识扩展到N叉树中。
我们提供了一些经典的N叉树习题,以便进一步帮助你理解本章中N叉树的概念。