工作中消失而面试却长存的算法与数据结构
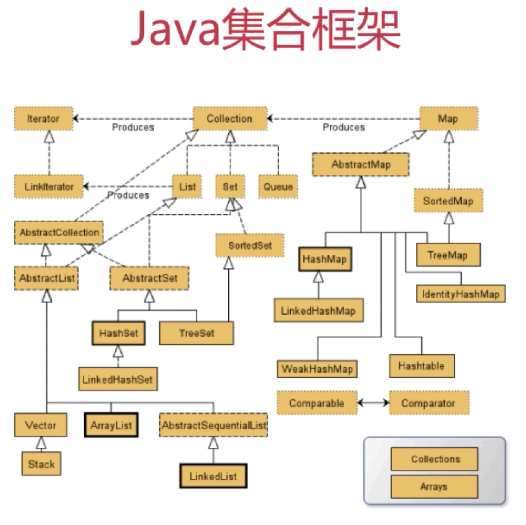
1、优秀的算法和数据结构被封装到了Java的集合框架之中
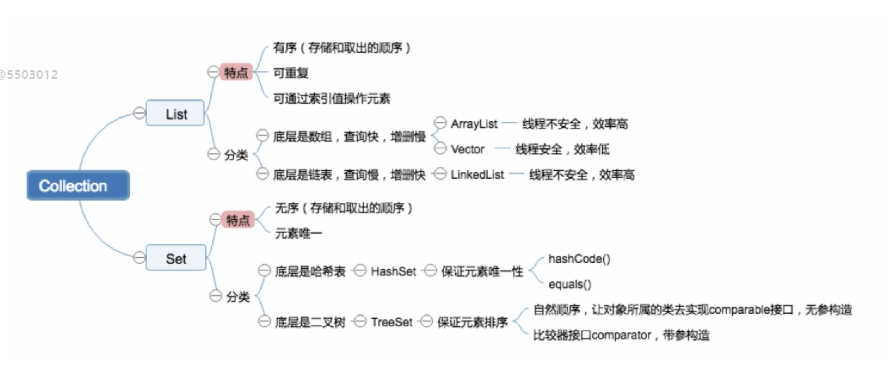
数据结构考点:
1、数组和链表的区别
2、链表的操作,如反转,链表环路检测,双向链表,循环链表相关操作
3、队列,栈的应用
4、二叉树的遍历方式以其递归和非递归的实现
5、红黑色的旋转
算法考点:
1、内部排序:如递归排序、交换排序(冒泡、块排)、选择排序、插入排序
2、外部排序:应掌握如何利用有限的内存配合海量的外部存储来处理超大的数据集,写不出来也要有相关的思路
考点扩展:
1、哪些排序是不稳定,稳定意味着什么
2、不同数据集,各种排序最好或最差的情况
3、如何优化算法
注意:1、TreeSet的底层是TreeMap
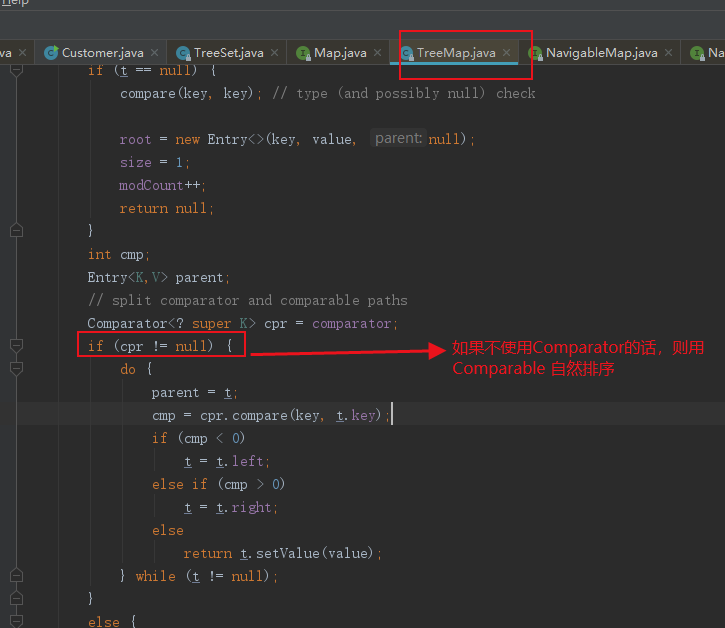
2、Comparable 是自然排序,Comparator 是客户化排序,当用户用了自然排序和客户化排序的话,最终是使用客户化排序。具体可以看看源码。
public class Customer implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Customer(String name, int age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (!(obj instanceof Customer))
return false;
final Customer other = (Customer) obj;
if (this.name.equals(other.getName()) && this.age == other.getAge())
return true;
else
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result;
result = (name == null ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = 29 * result + age;
return result;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Customer other = (Customer) o;
// 先按照name属性排序
if (this.name.compareTo(other.getName()) > 0)
return 1;
if (this.name.compareTo(other.getName()) < 0)
return -1;
// 在按照age属性排序
if (this.age > other.getAge())
return 1;
if (this.age < other.getAge())
return -1;
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Customer> set = new TreeSet<Customer>();
Customer customer1 = new Customer("Tom", 16);
Customer customer2 = new Customer("Tom", 15);
Customer customer3 = new Customer("Tom", 15);
set.add(customer1);
set.add(customer2);
set.add(customer3);
for(Customer c : set){
System.out.println(c.name + " " + c.age);
}
// 重写了equals,必须重写hashcode方法,
// 为什么要重写equals和hashCode方法呢?
// ----》这看你是怎么比较了,如果只是比较其中对象的属性则不用重写的,如果是判断两个对象是不是同一个对象则要重写的
System.out.println(customer1.hashCode()); // 重写了HashCode方法,则内容一样的对象,Hash算法出来的值都是一样的!!!
System.out.println(customer2.hashCode());
System.out.println(customer3.hashCode());
}
}