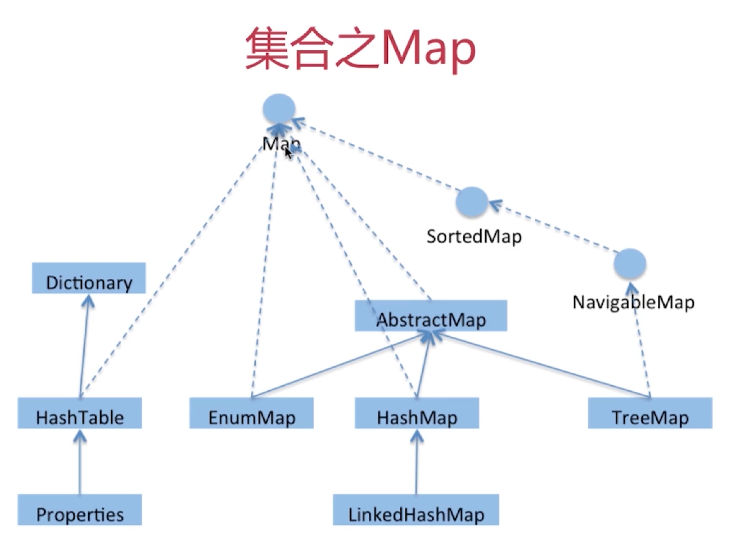
问题:HashMap 、HashTable、ConccurentHashMap的区别?
-----》
hashMap(JAVA8以前):数组+链
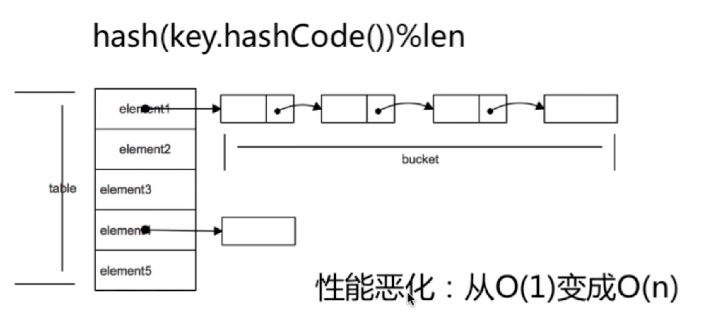
每个数据中保存的是,链表的头节点。实际上hashMap是通过位运算来获取头部信息,比hash算法的效率高。
HashMap(Java9及以后):数组+链表+红黑色
下面是HashMap的部分源码,put方法里面的
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
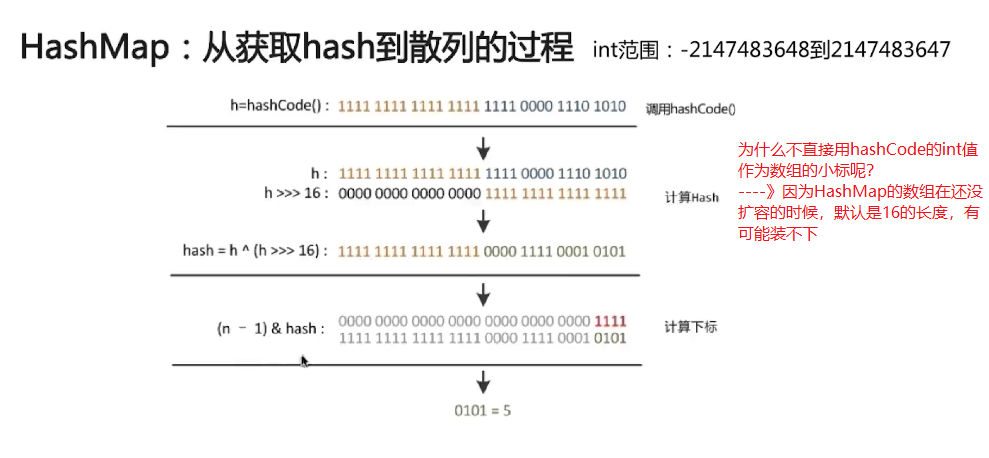
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // 这里的hash值,可以去看看具体算法,位和与运算出来的hash值
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);// 创建新节点
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 检查是否已经树化
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { // 没树化的话,则遍历
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 树化操作
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}

碰撞:就是key的hash算法之后的值,是相同,就发生碰撞
最低数化容量:64
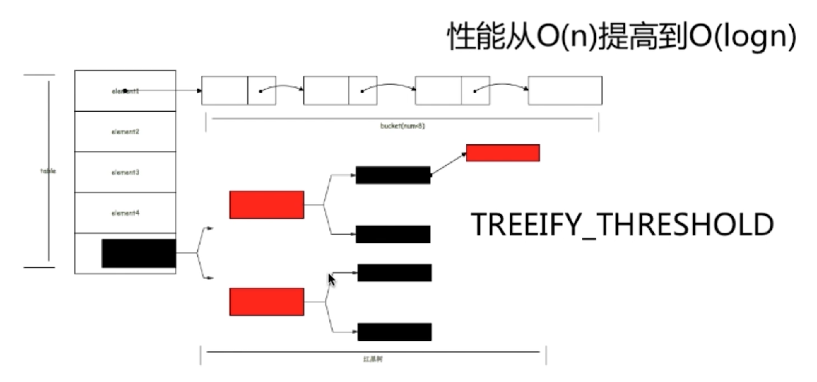
问题:HashMap什么时候转用红黑树?
---》当桶的容量超过8,而且整个HashMap的元素超过64,就会将链表转为红黑树
当桶的容量超过8,而且整个HashMap的元素不超过64,不会树化,只会扩容
问题:HashMap如何有效减少碰撞?
-----》
1、扰动函数:促使元素位置分布均价,减少碰撞几率
2、使用final对象,并采用合适的equals() 和 HashCode()方法
HashMap:扩容的问题
1、多线程环境下,调整大小会存在条件竞争,容易造成死锁
2、rehashing是一个比较耗时的过程
HashMap 知识点回归
1、成员变量:数据结构,树化阀值
2、构造函数:延迟创建
3、put和get的流程
4、哈希算法,扩容,性能