分类是数据挖掘中十分重要的组成部分.分类作为一种无监督学习方式被广泛的使用.
之前关于"数据挖掘中十大经典算法"中,基于ID3核心思想的分类算法C4.5榜上有名.所以不难看出ID3在
数据分类中是多么的重要了.
ID3又称为决策树算法,虽然现在广义的决策树算法不止ID3一种,但是由于ID3的重要性,习惯是还是把ID3
和决策树算法等价起来.
另外无监督学习方式我还要多说两句.无监督学习方式包括决策树算法,基于规则的分类,神经网络等.这些分
类方式是初始分类已知,将样本分为训练样本和测试样本,训练样本用于根据特定的输入输出关系训练出特定
的分类映射关系.然后通过此映射关系将测试样本映射到相应的类别上.
这里先引用http://blog.163.com/zhoulili1987619@126/blog/static/353082012013113083417956/的一个例子
先让大家对决策树算法有个直观的印象.
例如下:
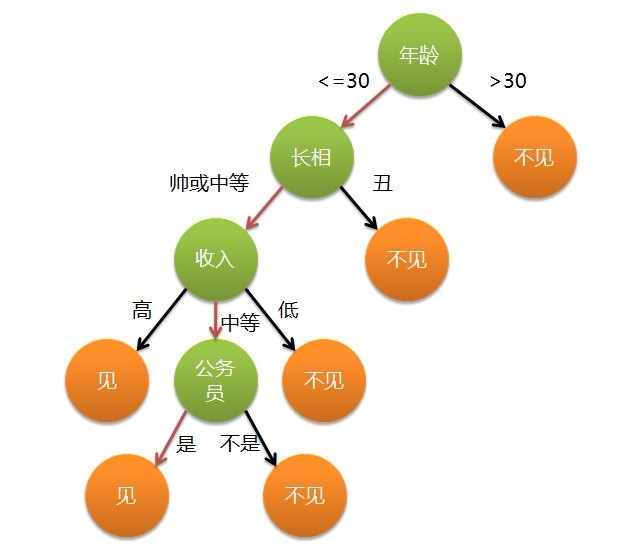
套用俗语,决策树分类的思想类似于找对象。现想象一个女孩的母亲要给这个女孩介绍男朋友,于是有了下面的对话:
女儿:多大年纪了?
母亲:26。
女儿:长的帅不帅?
母亲:挺帅的。
女儿:收入高不?
母亲:不算很高,中等情况。
女儿:是公务员不?
母亲:是,在税务局上班呢。
女儿:那好,我去见见。
这个女孩的决策过程就是典型的分类树决策。相当于通过年龄、长相、收入和是否公务员对将男人分为两个类别:
见和不见。假设这个女孩对男人的要求是:30岁以下、长相中等以上并且是高收入者或中等以上收入的公务员,那
么这个可以用下图表示女孩的决策逻辑:
图-1
不难看出女儿选老公是通过一个一个条件逐步决策的.这些条件包括年龄,长相,收入,是否公务员.而如何选取这些条
件的优先级呢,意思是女儿选老公的条件是如何排序的呢,显然首先考虑的是年龄.其次是长相.再次是收入,最后才是
是不是公务员.如何说一个男人的年龄超过了30岁那么一开始就被排除在外了.那么我们如何确定这些条件的优先级
,所以这就是决策树算法必须的一个过程-----训练通过已知的样本来确定条件属性在决策中的优先级,进而达到样本目
标分类的结果.
那么这个条件属性的优先级到底是如何定量的呢?所以这里不得不提到的一个概念就是信息熵.信息熵是度量数据中包
含的信息,概率的度量.信息熵是信息论中的概念,可以这样理解.变量的不确定性越大,信息熵越大.一组数据越有序,其包
含的信息量越小,信息熵越小.一组数据越无序,越混乱,其包含的信息量越大,信息熵越大
比如一组数据{x1,x2,x3.....xn};其和是sum,那么这组数据的信息熵
H(X)=-∑(x1/sum)*log(x1/sum);
而决策树算法中训练样本就是通过计算信息增益来决定条件属性的优先权的.
下面我还是用一个例子来说明如何通过信息熵来选取条件属性的决策优先权.
通过上面训练出来的决策树我们不难得到下面这样一个训练前的表格:
| 年龄 | 长相 | 收入 | 公务员 | 见/不见 |
| >30 | 丑 | 低 | 是 | 不见 |
| <=30 | 丑 | 高 | 不是 | 不见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 低 | 不是 | 不见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 高 | 是 | 见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 中等 | 是 | 见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 中等 | 不是 | 不见 |
表中红色字体部分为补充部分,即表示对生成决策树没有影响,可以随意填.
那么现在上面表格共有五个属性列,其中前四列(年龄,长相,收入,公务员)为条件属性,而最后一列为目标属性.
我们的目的是通过条件属性的信息熵来得出信息熵的优先级,进而推出之前图-1的决策树.
首先计算出目标属性--见/不见的信息熵.见/不见属性有两种取值情况:见,不见.其中见有两次,不见有四次.
那么目标属性的信息熵为:H(D)=-(2/6)*log(2/6)-(4/6)*log(4/6)=0.639;(log取e为底)
接下来求各个条件属性取不同值熵(以年龄为例):
H(年龄>30)=0;
H(年龄<=30)=-(3/5)log(3/5)-(2/5)log(2/5)=0.672;
接下来求年龄属性的信息熵:H(年龄)=-(1/6)*0-(5/6)*0.672=0.558;
类似的求出长相属性的信息熵:H(长相)=0.457
类似的求出收入属性的信息熵:H(收入)=0.457
类似的求出是否公务员的信息熵:H(公务员)=0.318
下面引入信息增益(information gain)这个概念,用Gain(D)表示,
该概念是指信息熵的有效减少量,该量越高,表明目标属性在该参考属性那失去的信息熵越多,
那么该属性越应该在决策树的上层.
所以Gain(年龄)=H(D)-H(年龄)=0.114
Gain(长相)=H(D)-H(长相)=0.215
Gain(收入)=H(D)-H(年龄)=0.215
Gain(公务员=H(D)-H(公务员)=0.354
所以先按照条件属性年龄将数据分为:
| 年龄 | 长相 | 收入 | 公务员 | 见/不见 |
| >30 | 丑 | 低 | 是 | 不见 |
表-2
| 年龄 | 长相 | 收入 | 公务员 | 见/不见 |
| <=30 | 丑 | 高 | 不是 | 不见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 低 | 不是 | 不见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 高 | 是 | 见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 中等 | 是 | 见 |
| <=30 | 帅或中等 | 中等 | 不是 | 不见 |
表-3
对表3还是按上述方式计算信息熵,再进行决策分类.只不过,这时候不考虑表三的年龄属性.一直这样递
归,直到当分到某类时目标属性全是一个值的时候,这时候.由训练样本训练的决策树或者说决策树规则
就产生了.接下来对需要分类的数据运用此决策树规则分类即可.
下面引自博客http://blog.csdn.net/cxf7394373/article/details/6665968关于决策树算法的C++实现.
代码太长了,每时间读,转载过来大家共享.
下表为训练样本数据:
C++源代码如下所示:
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <math.h> #include <string> using namespace std; #define ROW 14 #define COL 5 #define log2 0.69314718055 typedef struct TNode { char data[15]; char weight[15]; TNode * firstchild,*nextsibling; }*tree; typedef struct LNode { char OutLook[15]; char Temperature[15]; char Humidity[15]; char Wind[15]; char PlayTennis[5]; LNode *next; }*link; typedef struct AttrNode { char attributes[15];//属性 int attr_Num;//属性的个数 AttrNode *next; }*Attributes; char * Examples[ROW][COL] = {//"OverCast","Cool","High","Strong","No", // "Rain","Hot","Normal","Strong","Yes", "Sunny","Hot","High","Weak","No", "Sunny","Hot","High","Strong","No", "OverCast","Hot","High","Weak","Yes", "Rain","Mild","High","Weak","Yes", "Rain","Cool","Normal","Weak","Yes", "Rain","Cool","Normal","Strong","No", "OverCast","Cool","Normal","Strong","Yes", "Sunny","Mild","High","Weak","No", "Sunny","Cool","Normal","Weak","Yes", "Rain","Mild","Normal","Weak","Yes", "Sunny","Mild","Normal","Strong","Yes", "OverCast","Mild","Normal","Strong","Yes", "OverCast","Hot","Normal","Weak","Yes", "Rain","Mild","High","Strong","No" }; char * Attributes_kind[4] = {"OutLook","Temperature","Humidity","Wind"}; int Attr_kind[4] = {3,3,2,2}; char * OutLook_kind[3] = {"Sunny","OverCast","Rain"}; char * Temperature_kind[3] = {"Hot","Mild","Cool"}; char * Humidity_kind[2] = {"High","Normal"}; char * Wind_kind[2] = {"Weak","Strong"}; /*int i_Exampple[14][5] = {0,0,0,0,1, 0,0,0,1,1, 1,0,0,1,0, 2,1,0,0,0, 2,2,1,0,0, 2,2,1,1,1, 1,2,1,1,0, 0,1,0,0,1, 0,2,1,0,0, 2,1,1,0,0, 0,1,1,1,0, 1,1,1,1,0, 1,1,1,0,0, 2,1,0,0,1 };*/ void treelists(tree T); void InitAttr(Attributes &attr_link,char * Attributes_kind[],int Attr_kind[]); void InitLink(link &L,char * Examples[][COL]); void ID3(tree &T,link L,link Target_Attr,Attributes attr); void PN_Num(link L,int &positve,int &negative); double Gain(int positive,int negative,char * atrribute,link L,Attributes attr_L); void main() { link LL,p; Attributes attr_L,q; tree T; T = new TNode; T->firstchild = T->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(T->weight,""); strcpy(T->data,""); attr_L = new AttrNode; attr_L->next = NULL; LL = new LNode; LL->next = NULL; //成功建立两个链表 InitLink(LL,Examples); InitAttr(attr_L,Attributes_kind,Attr_kind); ID3(T,LL,NULL,attr_L); cout<<"决策树以广义表形式输出如下:"<<endl; treelists(T);//以广义表的形式输出树 // cout<<Gain(9,5,"OutLook",LL,attr_L)<<endl; cout<<endl; } //以广义表的形式输出树 void treelists(tree T) { tree p; if(!T) return; cout<<"{"<<T->weight<<"}"; cout<<T->data; p = T->firstchild; if (p) { cout<<"("; while (p) { treelists(p); p = p->nextsibling; if (p)cout<<','; } cout<<")"; } } void InitAttr(Attributes &attr_link,char * Attributes_kind[],int Attr_kind[]) { Attributes p; for (int i =0;i < 4;i++) { p = new AttrNode; p->next = NULL; strcpy(p->attributes,Attributes_kind[i]); p->attr_Num = Attr_kind[i]; p->next = attr_link->next; attr_link->next = p; } } void InitLink(link &LL,char * Examples[][COL]) { link p; for (int i = 0;i < ROW;i++) { p = new LNode; p->next = NULL; strcpy(p->OutLook,Examples[i][0]); strcpy(p->Temperature,Examples[i][1]); strcpy(p->Humidity,Examples[i][2]); strcpy(p->Wind,Examples[i][3]); strcpy(p->PlayTennis,Examples[i][4]); p->next = LL->next; LL->next = p; } } void PN_Num(link L,int &positve,int &negative) { positve = 0; negative = 0; link p; p = L->next; while (p) { if (strcmp(p->PlayTennis,"No") == 0) negative++; else if(strcmp(p->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0) positve++; p = p->next; } } //计算信息增益 //link L: 样本集合S //attr_L:属性集合 double Gain(int positive,int negative,char * atrribute,link L,Attributes attr_L) { int atrr_kinds;//每个属性中的值的个数 Attributes p = attr_L->next; link q = L->next; int attr_th = 0;//第几个属性 while (p) { if (strcmp(p->attributes,atrribute) == 0) { atrr_kinds = p->attr_Num; break; } p = p->next; attr_th++; } double entropy,gain=0; double p1 = 1.0*positive/(positive + negative); double p2 = 1.0*negative/(positive + negative); entropy = -p1*log(p1)/log2 - p2*log(p2)/log2;//集合熵 gain = entropy; //获取每个属性值在训练样本中出现的个数 //获取每个属性值所对应的正例和反例的个数 //声明一个3*atrr_kinds的数组 int ** kinds= new int * [3]; for (int j =0;j < 3;j++) { kinds[j] = new int[atrr_kinds];//保存每个属性值在训练样本中出现的个数 } //初始化 for (j = 0;j< 3;j++) { for (int i =0;i < atrr_kinds;i++) { kinds[j][i] = 0; } } while (q) { if (strcmp("OutLook",atrribute) == 0) { for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++) { if(strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[i]) == 0) { kinds[0][i]++; if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0) kinds[1][i]++; else kinds[2][i]++; } } } else if (strcmp("Temperature",atrribute) == 0) { for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++) { if(strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[i]) == 0) { kinds[0][i]++; if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0) kinds[1][i]++; else kinds[2][i]++; } } } else if (strcmp("Humidity",atrribute) == 0) { for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++) { if(strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[i]) == 0) { kinds[0][i]++; if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0) kinds[1][i]++;// else kinds[2][i]++; } } } else if (strcmp("Wind",atrribute) == 0) { for (int i = 0;i < atrr_kinds;i++) { if(strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[i]) == 0) { kinds[0][i]++; if(strcmp(q->PlayTennis,"Yes") == 0) kinds[1][i]++; else kinds[2][i]++; } } } q = q->next; } //计算信息增益 double * gain_kind = new double[atrr_kinds]; int positive_kind = 0,negative_kind = 0; for (j = 0;j < atrr_kinds;j++) { if (kinds[0][j] != 0 && kinds[1][j] != 0 && kinds[2][j] != 0) { p1 = 1.0*kinds[1][j]/kinds[0][j]; p2 = 1.0*kinds[2][j]/kinds[0][j]; gain_kind[j] = -p1*log(p1)/log2-p2*log(p2)/log2; gain = gain - (1.0*kinds[0][j]/(positive + negative))*gain_kind[j]; } else gain_kind[j] = 0; } return gain; } //在ID3算法中的训练样本子集合与属性子集合的链表需要进行清空 void FreeLink(link &Link) { link p,q; p = Link->next; Link->next = NULL; while (p) { q = p; p = p->next; free(q); } } void ID3(tree &T,link L,link Target_Attr,Attributes attr) { Attributes p,max,attr_child,p1; link q,link_child,q1; tree r,tree_p; int positive =0,negative =0; PN_Num(L,positive,negative); //初始化两个子集合 attr_child = new AttrNode; attr_child->next = NULL; link_child = new LNode; link_child->next = NULL; if (positive == 0)//全是反例 { strcpy(T->data,"No"); return; } else if( negative == 0)//全是正例 { strcpy(T->data,"Yes"); return; } p = attr->next; //属性链表 double gain,g = 0; /************************************************************************/ /* 建立属性子集合与训练样本子集合有两个方案: 一:在原来链表的基础上进行删除; 二:另外申请空间进行存储子集合; 采用第二种方法虽然浪费了空间,但也省了很多事情,避免了变量之间的应用混乱 */ /************************************************************************/ if(p) { while (p) { gain = Gain(positive,negative,p->attributes,L,attr); cout<<p->attributes<<" "<<gain<<endl; if(gain > g) { g = gain; max = p;//寻找信息增益最大的属性 } p = p->next; } strcpy(T->data,max->attributes);//增加决策树的节点 cout<<"信息增益最大的属性:max->attributes = "<<max->attributes<<endl<<endl; //下面开始建立决策树 //创建属性子集合 p = attr->next; while (p) { if (strcmp(p->attributes,max->attributes) != 0) { p1 = new AttrNode; strcpy(p1->attributes,p->attributes); p1->attr_Num = p->attr_Num; p1->next = NULL; p1->next = attr_child->next; attr_child->next = p1; } p = p->next; } //需要区分出是哪一种属性 //建立每一层的第一个节点 if (strcmp("OutLook",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,OutLook_kind[0]); T->firstchild = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[0]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Temperature",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Temperature_kind[0]); T->firstchild = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[0]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Humidity",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Humidity_kind[0]); T->firstchild = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[0]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Wind",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Wind_kind[0]); T->firstchild = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[0]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } int p = 0,n = 0; PN_Num(link_child,p,n); if (p != 0 && n != 0) { ID3(T->firstchild,link_child,Target_Attr,attr_child); FreeLink(link_child); } else if(p == 0) { strcpy(T->firstchild->data,"No"); FreeLink(link_child); // strcpy(T->firstchild->data,q1->PlayTennis);//----此处应该需要修改----:) } else if(n == 0) { strcpy(T->firstchild->data,"Yes"); FreeLink(link_child); } //建立每一层上的其他节点 tree_p = T->firstchild; for (int i = 1;i < max->attr_Num;i++) { //需要区分出是哪一种属性 if (strcmp("OutLook",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,OutLook_kind[i]); tree_p->nextsibling = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->OutLook,OutLook_kind[i]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Temperature",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Temperature_kind[i]); tree_p->nextsibling = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Temperature,Temperature_kind[i]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Humidity",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Humidity_kind[i]); tree_p->nextsibling = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Humidity,Humidity_kind[i]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } else if (strcmp("Wind",max->attributes) == 0) { r = new TNode; r->firstchild = r->nextsibling = NULL; strcpy(r->weight,Wind_kind[i]); tree_p->nextsibling = r; //获取与属性值相关的训练样例Example(vi),建立一个新的训练样本链表link_child q = L->next; while (q) { if (strcmp(q->Wind,Wind_kind[i]) == 0) { q1 = new LNode; strcpy(q1->OutLook,q->OutLook); strcpy(q1->Humidity,q->Humidity); strcpy(q1->Temperature,q->Temperature); strcpy(q1->Wind,q->Wind); strcpy(q1->PlayTennis,q->PlayTennis); q1->next = NULL; q1->next = link_child->next; link_child->next = q1; } q = q->next; } } int p = 0,n = 0; PN_Num(link_child,p,n); if (p != 0 && n != 0) { ID3(tree_p->nextsibling,link_child,Target_Attr,attr_child); FreeLink(link_child); } else if(p == 0) { strcpy(tree_p->nextsibling->data,"No"); FreeLink(link_child); } else if(n == 0) { strcpy(tree_p->nextsibling->data,"Yes"); FreeLink(link_child); } tree_p = tree_p->nextsibling;//建立所有的孩子结点 }//建立决策树结束 } else { q = L->next; strcpy(T->data,q->PlayTennis); return;//这个地方要赋以训练样本Example中最普遍的Target_attributes的值 } }
运行结果如下: