面向对象

为什么要面向对象:
1、和函数一样,把算法封装起来,方便复用
2、更好理解自己和别人写的代码
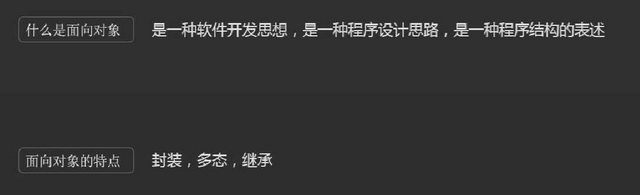
封装:数据、结构、逻辑的封装,方便复用
多态:同一个对象,同一种指令,不同的行为(反应)
继承:



有机物(有生命):人,猫,张阿姨,隔壁老王,向日葵,菊花,荷花
无机物(无生命):机器人,机器,汽车,飞机,太阳,星星
有机物(有生命):动物(会动):人:男人:隔壁老王
:女人:张阿姨
:猫
:植物(不动):水生(菊科):向日葵(向日葵属),菊花(菊属)
:陆生:荷花
无机物(无生命):人造:机器:机器人,汽车,飞机
:自然:天体:太阳,星星

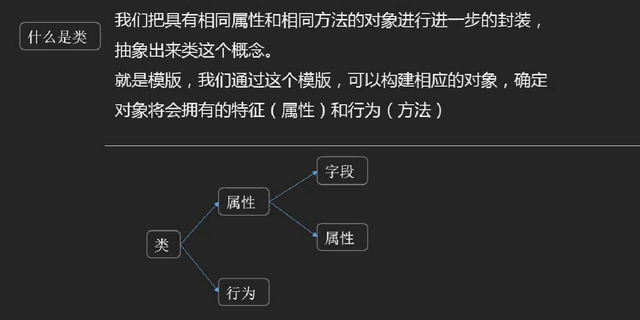
共有属性和共有行为
字段:类或结构中定义的变量和常量,不安全
属性:属性不是字段,但必然和类中的某个或某些字段相联系,属性定义了得到和修改相联系的字段的方法。保护变量,不可修改;根据不同状态,反应不同属性

结构是值类型,存的是值,结构里面不可以包含自己
类是引用类型,存的是地址,类里面可以包含本身


对象


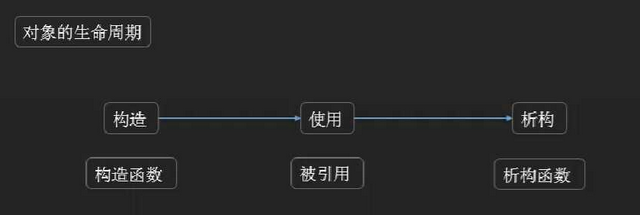
构造函数:在类中,函数名和类名相同的函数称为构造函数。它的作用是在建立一个对象时,作某些初始化的工作(例如对数据赋予初值)。
析构函数:当一个类的对象离开作用域时,析构函数将被调用(系统自动调用)。对一个类来说,只能允许一个析构函数,析构函数不能有参数,并且也没有返回值。析构函数的作用是完成一个清理工作,如释放从堆中分配的内存。
有没有办法在实例化的时候,同时初始化:使用构造函数

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace m1w3d2_class_oop { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 类的定义 //日常生活中的类,是属性和行为的抽象 //程序中的类,是属性和方法的封装 //定义的格式和结构一样,只是关键字不一样用class //成员不一样,类允许使用任意类型的成员 #endregion #region 类到对象 //通过实例化,我们可以将类实例化成某一个具体的对象 //通过 new 关键字 结合构造函数 可以实例化 一个具体的对象 //通过初始化,可以确保这个对象有自己专有的值 //数据类型 变量名 = 初始化值; Student xiaoMing = new Student();//Student()为构造函数,与类名一致 //初始化 为了确保数据的合理性,我们会把数据初始化 //把值保证在合理范围内,这个过程一般交给 构造函数去做 xiaoMing.name = "小明"; xiaoMing.sex = "男"; xiaoMing.age = 18; Student xiaoHua = new Student(); xiaoHua.name = "小花"; xiaoHua.sex = "女"; xiaoHua.age = 18; xiaoMing.desker = xiaoHua; xiaoHua.desker = xiaoMing; //对象方法被调用时,里面使用的不同对象的属性, xiaoMing.SayHello("吴彦祖"); //xiaoMing.GetSorce(); xiaoMing.SaySorce(); xiaoMing.SayDesker(); xiaoHua.SayHello(); xiaoHua.SaySorce(); Console.WriteLine(); Player daXia = new Player(); daXia.name = "无名大侠"; daXia.level = 1; daXia.healthPoint = 100; daXia.magicPoint = 50; daXia.UpGrade(); #endregion #region 将自己抽象成类 // Console.WriteLine(); #endregion #region 对象 //对象是类的一个实例 //我们用this关键指向自己这个对象 //某一个类的对象拥有这个类所有的属性和方法,换言之,一个类的对象和这个类的属性和方法是一致的 //同一个类的对象一般表现为数据不同,而属性和方法是一致的 //构造 - 被使用 - 析构 //构造 //实例化可以将一个类实例化成一个对象 //Student xiaoMing = new Student(); //实例化会在内存中开辟一块空间,然后初始化(对空间中的成员添值,添值的逻辑我们交给构造函数) #endregion #region 构造函数 //构造函数只能写在本类里 //和函数大体一致 //1、没有返回类型 //2、函数名和类名一致 //构造函数允许我们重载 //当你不写构造函数时,会有一个默认构造存在 //一旦重载,默认构造就会消失 //一般情况下,我们会保留默认构造,再写一个默认构造(无参构造) //通过重载构造 我们可以对对象赋予不同的数据 //通过this关键字,我们可以用一个构造函数 调用 另一个构造 //一般情况下有多个构造 我们就用直接指向参数最多的构造 //Student():this("小明",18,"男") Student xiaoming = new Student("小明"); xiaoming.SayHello(); Student xiaohua = new Student("小花",12,"女"); xiaohua.SayHello(); //构造参数的循环调用 Console.WriteLine(); Student1 xiaoMing1 = new Student1("小明"); #endregion } } #region 类的定义 //定义一个学生类 //属性:姓名、性别、年龄、CSharp成绩、Unity成绩 //方法: //一个打招呼:介绍自己叫XX,今年几岁了,是男同学还是女同学 //计算自己总分数和平均分的方法并显示 public class Student//需要外部访问,属性和方法都要加public { //构造函数 public Student(string name) { Console.WriteLine("这是一个构造函数"); this.name = name;//this指的是被实例化出来的对象 age = 18; sex = "男"; } //重载构造函数 public Student(string name,int age,string sex) { Console.WriteLine("这是一个构造函数"); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; } //保留默认构造,再写一个无参构造 public Student() { } //属性,有意义 public Student desker;//和结构体不同,类允许使用自己的类型 public string name; public string sex; public int age; public float unity; public float cSharp; //方法 public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我叫{0},今年{1}岁了,是{2}生", name, age, sex); } public void SayHello(string name)//函数重载,this.name关键字锁定指向对象自身的属性 { Console.WriteLine("我叫{0},今年{1}岁了,是{2}生", this.name, age, sex); } public void GetSorce() { Console.WriteLine("请输入CSharp成绩"); cSharp = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine("请输入Unity成绩"); unity = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); } public void SaySorce() { Console.WriteLine("我的CSharp成绩{0},我的Unity成绩{1}", unity, cSharp); Console.WriteLine("我的总分是{0},我的平均分是{1}", (unity + cSharp), (unity + cSharp)/2); } public void SayDesker() { if (desker == null) { Console.WriteLine("我还没有同桌"); } else { Console.WriteLine("我的同桌是{0},我好喜欢{1}",desker.name, "她"); } } } #endregion #region 将自己抽象成类 public class Player { //属性 public string name; public string sex; public string height; public string weight; public string occupation;//职业 public int level; public int exp; public float healthPoint;//生命 public float magicPoint;//魔法 public float feedDegree;//饱食 public float spiritValue;//精神 public float attack; public float defend; public float money; //方法 public void UpGrade()//升级 { level++; healthPoint += 10; magicPoint += 5; attack += 2; defend += 1; Console.WriteLine($"升级了,等级提高为{level},生命提高为{healthPoint},魔法值提高为{magicPoint},攻击力提高为{attack},防御力提高为{defend}"); } public void battleEnd() { Random roll = new Random(); int input = roll.Next(1, 10); switch (input) { case 1: break; case 2: break; case 3: break; case 4: break; case 5: break; default: break; } } } #endregion #region 构造函数的循环调用 public class Student1 { public Student1(string name) : this(name, 18) { Console.WriteLine("一个参数的构造函数"); } public Student1(string name, int age) : this(name, age, "男") { Console.WriteLine("两个参数的构造函数"); } public Student1(string name, int age, string sex) : this(name, age, sex, null) { Console.WriteLine("三个参数的构造函数"); } public Student1(string name, int age, string sex, Student1 desker) { Console.WriteLine("四个参数的构造函数"); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; this.desker = desker; } public Student1 desker;//和结构体不同,类允许使用自己的类型 public string name; public string sex; public int age; } #endregion }
复习
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace m1w3d2_class_oop_r { //结构体与类的区别 //1、结构体对象属于值类型,类对象属于引用类型 //2、结构体中的字段不能赋初值 类中可以 //3、结构体中不能显式定义无参构造函数,如果是重写了带参的构造函数,那么就需要对所有字段初始化 //4、结构体放在栈里里,读写速度快,类放在堆里 //类一般定义在命名空间下面 //一种模板 这个模板就是用来创建对象的 通过这个模板可以创建对象的属性和方法 class Character { //Field 字段 public int atk = 100; // 成员变量 public int hp = 10; public bool isDeath =false; public Character(int hp, int atk, bool isDeath = false) // 默认值 是常量 或是字面量 { this.hp = hp; this.atk = atk; this.isDeath = isDeath; } //public Character(int _hp, int _atk) // 显式定义构造函数, 默认无参构造函数就没了 //{ // hp = _hp; // atk = _atk; //} public void Attack(ref Character other) //成员方法 { other.hp -= this.atk; if (other.hp <= 0) { other.hp = 0; other.isDeath = true; } } public void ShowInfo() { Console.WriteLine($"hp:{this.hp},atk:{this.atk},isDeath{this.isDeath}"); } } class Program { //类也可以定义在类里面 static void Main(string[] args) { //奥特曼 打小怪兽 //小怪兽群殴奥特曼 //数据结构 //奥特曼 小怪兽 //属性 行为 //血量 攻击力 是否死亡 //攻击行为 //类的对象是属于引用类型,引用类型才能用null //数据初始化 Random roll = new Random(); Character atm = new Character(200, roll.Next(5, 11)); atm.ShowInfo(); Console.WriteLine(atm.hp); //Character monster = new Character(100,5); //monster.ShowInfo(); //Console.WriteLine(monster.hp); //for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) //{ // atm.Attack(monster); //} //monster.ShowInfo(); Character[] monsters = new Character[10]; if (monsters[0] == null) { Console.WriteLine("123"); } for (int i = 0; i < monsters.Length; i++) { monsters[i] = new Character(100, roll.Next(3, 5)); } //游戏运行中 while (true) { bool allDeath = true; foreach (var item in monsters) { if (item.isDeath == false) { allDeath = false; break; } } if (allDeath) break; if (atm.isDeath) break; int selectID =0; while (allDeath == false) { selectID = roll.Next(0, monsters.Length); if (monsters[selectID].isDeath == false) break; } Console.WriteLine($"奥特曼攻击了{selectID}号小怪兽"); atm.Attack(ref monsters[selectID]); for (int i = 0; i < monsters.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"{i}号小怪兽攻击了奥特曼"); monsters[i].Attack(ref atm); if (atm.isDeath) break; } Console.ReadKey(true); //foreach (var item in monsters) //{ // item.Attack(ref atm); //} } if (atm.isDeath) { Console.WriteLine("小怪兽赢了"); } else { Console.WriteLine("奥特曼赢了"); } atm.ShowInfo(); foreach (var item in monsters) { item.ShowInfo(); } } } }