数据库就是存储数据的仓库 本质上就是一套cs结构的TCP程序 客户端连接到服务器 向服务器发送指令 完成数据的操作
1.2 常见数据库
关系型数据库
就是将数据之间建立起关联关系. 数据之间可以通过自身找到对方
Mysql 免费开源 支持中大型企业
oracle 收费闭源 功能强大 分布式数据库
SQLServer 微软生态圈 仅支持 windows系统
DB2 IBM 开发的数据库软件 收费闭源 经常与IMB的机器绑定销售
非关系型数据库
通关key value存储数据各个数据之间没有关系 不是通用性数据库 有局限性,通常运行在将数据存储在内存中,以提高速度,所以非关系性数据库多用于缓存,与关系型数据库搭配使用。
Redis
Mongodb
Memcache
1.3 数据库与文件系统的对应关系
-
一个数据项 name=Jerry 本质就是文件中的某一行的一部分数据
-
一条记录 jerry , 18,man 本质是文件里的一行数据
-
一张表 本质是一个文件
-
数据库 文件夹
-
DBMS(DataBaseManagerSystem) 数据库管理系统 数据库的服务器端程序
-
数据库服务器 运行有DBMS的计算机
二 Mysql 数据库
2.1 安装mysq
-
下载解压包 解压到某个目录下
-
添加到环境变量 (将bin所在的完整路径copy到系统的path中)_
-
作为服务器 让其自启动mysql服务器
-
(mysqld --install 运行输入services(服务) 查看是是否成功)
-
删除服务 sc delete mysql 如果需要重装的话...
启动服务 net start mysql
停止服务 net stop mysql
注意 :后期打开cmd运行mysql就是客户端了 服务器后台在运行 一些指令可以在客户端输入 显示也在客户端显示
2.2 连接服务器
mysql -hip -P端口号 -u用户名 -p密码
实例:mysql -uroot -p (,密码没有设置)
mysql 5.6版本 默认是没有密码的
登录时不指定用户名和密码 默认是游客登录 是无法查询关键信息的 也不能进行操作
因为数据库本质是TCP程序 所以需要IP和端口 但是如果服务器是运行在本机上 那么可以省略IP 端口没有修改过 也是可以省略的
mysql -uroot -p密码
#修改密码
在知道原始密码的情况下可以使用mysqladmin
mysqladmin是一个用于管理数据库的程序,包括修改密码,数据备份等
修改密码:
mysqladmin -uroot -p旧密码 password 123
警告忽略即可
#破解密码:
#方式1:删除用于记录用户密码数据文件
没问题 简单粗暴 但是,这个文件里不只有你的账号信息 还有别人账号数据 还有授权相关的数据
所以你最好不要这么干!
那你在思考一下,服务器验证用户的本质是什么,是不是读取一个文件的数据来和你输入的数据进行对比,
那你可不可以这样子 我告诉我服务器说你不要去读那个授权文件,可以!
#方式2: 跳过授权表 进入系统修改授权表推荐
跳过这个操作是服务器相关的操作所以 咱的先关掉服务器重新开 在重新开的时候来告诉它
1.停止服务
2.启动服务器并添加参数
**mysqld --skip-grant-tables**
3.使用客户端登录服务器 执行修改命令 此时不需要输入密码
update mysql.user set password = password("123123") where user="root" and host="localhost"**
4.刷新权限
flush privileges
5.命令行中重启服务器验证新密码

补充
... unsigned表示为无符号 float(M,D) 浮点型 decimal(M,D) 定点型 比float更加的精准 M: 精度(总位数)D: 标度(小数位) ...

... NULL 不是假,也不是真,而是”空” NULL 的判断只能用is null,is not null NULL 影响查询速度,一般避免使值为NULL ...
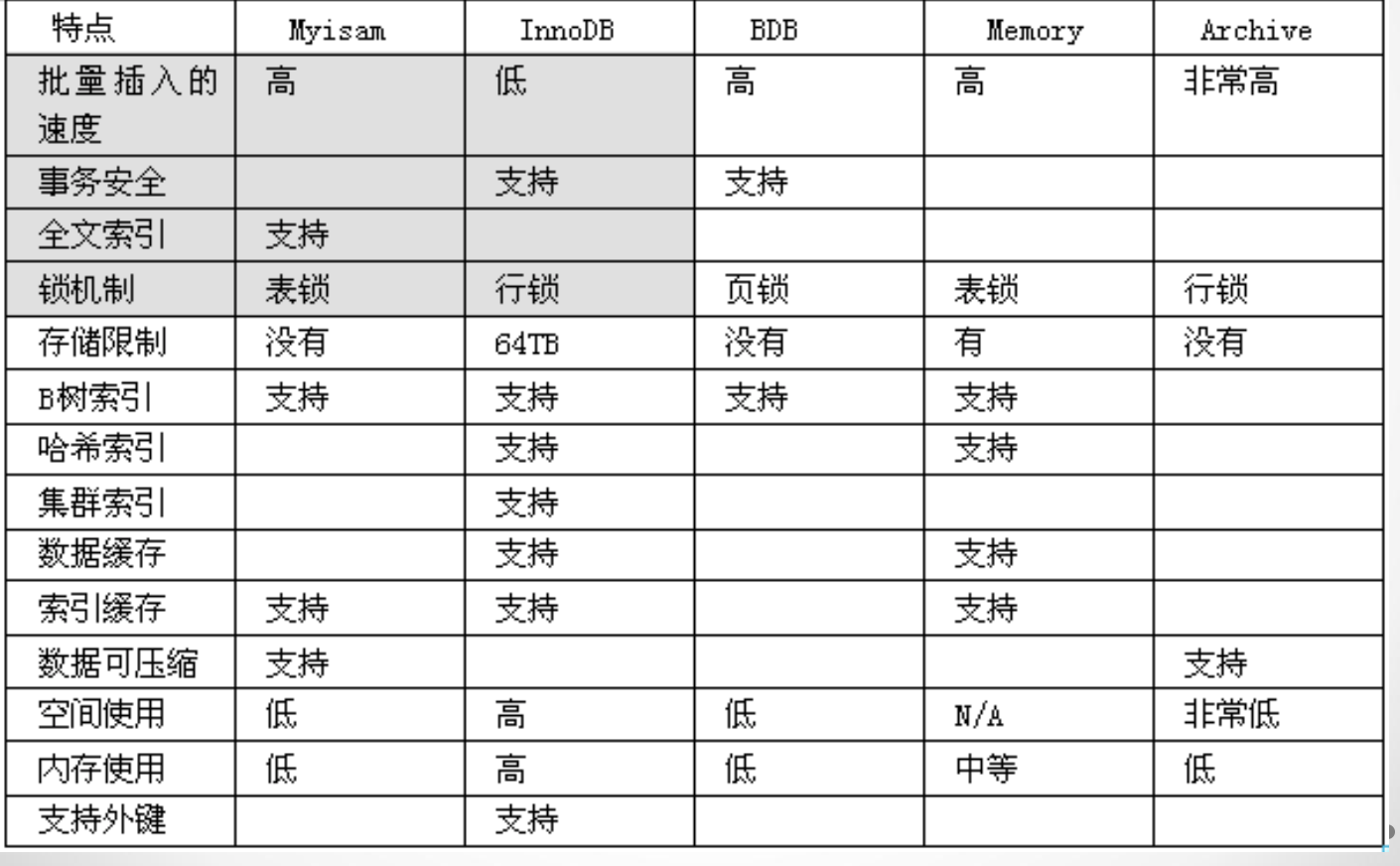
... 对不同的数据有不同的管理方式和存储方式,在mysql中称之为存储引擎 1). 文章,新闻等安全性要求不高的,选myisam 2). 订单,资金,账单,火车票等对安全性要求高的,选用innodb 3). 对于临时中转表,可以用memory型 ,速度最快 4). 中文全文索引:sphinx ...
# Innodb
1.(默认版本包含5.5)
2.支持事务
3.不支持全文索引
4.索引和数据都是在同一个文件中, .ibd
表的结构实在.frm文件中
# MyIsam
1.(默认版本5.5以下 5.3)
2.不支持事务
3.支持全文索引
4..frm: 表结构
.MYD: 表数据
.MYI: 表索引
# memory
所有的数据都保存在内存中
# 常用的全文索引: sphinx ES
数据库的基本操作
用
SQL语句: use 数据库名; 实例: use db1;
增
SQL语句: create database 数据库名 charset=utf8; 实例: create database db1; 创建了db1的库名 并指定格式为utf8
删
SQL语句: drop database 数据库名; 实例: drop database db1;
改 没有此操作 只能重写
查
show databases; 查询名下所有数据库名
数据表的基本操作
增
SQL语句: use 数据库名; 首先确定是在用哪个数据库 creata table 表名( 列名1 列类型 not null/null default 值1, 列名2 列类型 not null/null default 值2, 列名n 列类型 not null/null default 值n ) charset=utf8;
实例:
use db1; create table student( id int auto_increment primary key, # 这时设置主键的 primary key 主键 name char(32) not null default '', # 名字字符串类型 不为空,默认值为空字符串 age int not null default 0 # 设置年龄列为整形 不能为空 默认值为0 )charset=utf8; **注意最后一行是没有逗号的**
删
SQL语句 drop table 表名; 表中所有数据都会删除 实例 drop table student
改 分为改字段 新增字段
create table student( id int auto_increment primary key, # 这时设置主键的 name char(32) not null default '', # 名字字符串类型 不为空,默认值为空字符串 age int not null default 0 # 设置年龄列为整形 不能为空 默认值为0 )charset=utf8; # 这是原始数据
改字段
SQL语句 alter table 表名 change/modify 新列声明; alter table student change age stu_age int not null default 0 ; # 改单列 alter table student change age stu_age char(32), change name user char(32); # 改多列 需要用到多个change
新增字段
SQL语句: alter table 表名 add 新列声明; 实例: alter table student add gender char(32) not null default ''; # 增加单列 alter table student add gender char(32) not null default '',add class int not null default 0; # 增加多列
删除字段
SQL语句: alter table 表名 drop 列名; 实例 :alter table student drop gender; 删除单列 alter table student drop gender,drop class; 删除多列
查
SQL语句: show tables; 查看所有表 desc 表名; 查看表的结构 例如 desc student; show create table 表名; 查看表的创建过程
数据行的操作
增
insert into 表名 (列1,列2,'...列n) values (列1值,列2值,...列n值),(列1值,....列n值) ; # 一次性增加 实例:insert into student (id,name,age) values (9,'wsx',12); 增加单行 insert into 表名 (列名1, 列名2,) values(值1, 值2),(值1,值2),(值n,值n); # 增加多个值 insert into 表名 (列名1, 列名2,) select 列名1, 列名2 from 表名; # 从某个表名挑选出列名插入另一个表的列名
删
truncate 表名; # 也是删除表中所有数据 再次添加的时候, 重新开始 速快比delete快 delete from 表名 ; 删除表中所有数据 再次添加的时候, 继续会延续上一个 ID delete from 表名 where id=12; # 删除id=12 那行 delete from 表名 where 列名条件; # 选择性删除 delete from t1 where id>10; 等等 > < = != and or 等 delete from 表名 where id = 10 and name='xxx'; and : 并且 两个条件都必须要成立 delete from 表名 where id = 10 or name='xxx'; or : 或者 只要满足一个条件成立
改
update 表名 set username='zekai'; # 把表中username下所有名字改为zekei update t3 set username='tom' where id=3; # 改 id为3 的那列 update t3 set username='owen', pwd='123' where id=3; # 改id=3的多列
数据行基本查询
SQL语句; select * from 表名; 将表中所有列全部列出来 实例: select * from student; 将student的列全部列出 select 列名,列名 from表名; 将列名从表中展现出来 select distinct 字段名 FROM 表名; # 去重 实例 :select name,age from student; # 注意 尽量不要用 * 因为会降低查询速度
数据行高阶查询
1 where条件查询
a. where 条件查询: select * from 表名 where id=10; select * from 表名 where id >10 and id<15; select * from 表名 where id > 10; != : 不等与 >= <= b. between and: 闭区间 select * from t4 where id between 9 and 12; c. in: 在某一个集合中 select * from t4 where id in (9,10,11....); select * from t4 where id in (select id from t3 where id between 2 and 4) 是可以这样使用的, 但是不建议大家使用;
2 通配符: like %
select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' - ale开头的所有(多个字符串) select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' - ale开头的所有(一个字符)
3 limit 限制取
select * from 表名 limit 索引偏移量, 取出多少条数据;
select * from t3 limit 0, 10; 第一页 # 表示第一页显示10条内容
select * from t3 limit 10, 10; 第二页
page = input('page:')
page 索引偏移量 数据量(offset)
1 0 10
2 10 10
3 20 10
4 30 10
page (page-1)*offset offset
分页核心SQL:
select * from t3 limit (page-1)*offset, offset;
4 排序 order by
降序: select * from t4 order by 列名 desc; # descending 降序 升序: select * from t4 order by 列名 asc; # ascending 升序 多列: create table t7( id int auto_increment primary key, num int not null default 0, age int not null default 0 )charset=utf8; insert into t7 (num, age) values (2, 12),(3,13),(4, 12); select * from t7 order by num desc, age asc; 如果前一列的值相等的话, 会按照后一列的值进行进一步的排序.
5 分组 group by
分组是将相同的放在一起 只显示一列 select age, 聚合函数count(num)/sum(num)/max(num)/min(num)/avg(num) from 表名 group by 列名; select age, avg(num) from t7 group by age; select age, count(num) from t7 group by age; elect age, count(num) as cnt from t7 group by age; # 显示别名 as having的二次删选: select age, count(num) as cnt from t7 group by age having cnt>1; where 和 having的区别: 1). having与where类似,可筛选数据 2). where针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据 3). having针对查询结果中的列发挥作用,二次筛选数据, 和group by配合使用
6 去重 distinct
distinct 去重的意思 只能在查询的第一列使用 不能放在后面类使用 select distinct score.student_id,student.sname from score left join student on score.student_id=student.sid where score.course_id in(select score.course_id from score where score.student_id=1) and score.student_id!=1; # 这是对score表的student_id 这一列去重 不能放在后面进行去重
7 连表查询
select * from userinfo, department; (笛卡尔积) select * from userinfo, department where userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 左连接: select 所需查询 from 表名 left join 表名 on 左表.列名=右表.列名; select * from userinfo left join department on userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 左边的表全部显示, 右边没有用到不显示 右连接: select * from userinfo right join department on userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 右边的表全部显示, 左边没关联的用null表示 内连接: 左右两边的数据都会显示 ps: a.只需要记住左连接 left join b.可以连接多张表 通过某一个特定的条件
8 查询顺序
注意查询的顺序:where>group by > order by >顺序>限制
select name,sum(score) from 表 where id > 10 group by score having age> 12 order by age desc limit 2, 10
constraint 新建表的外键名 foreign key (新建表的列名) references 关联的表名(关联表的主键如id)
foreign key:外键的意思
references :引用的意思
primary key:主键
1 约束 2 节省空间
外键注意点
1. 不能将创建外键的语句单独拿出来 alter table userinfo add constraint fk_userinfo_depart foreign key (depart_id) references department(id); alter table userinfo drop foreign key 外键名称(fk_userinfo_depart ); 2. 外键关联的时候, 必须关联的是表的主键ID 3. 练习的时候, 将语句写在文本中, 然后考过去执行 4. 主键索引 : 加速查找 + 不能为空 + 不能重复
create table department (
id int auto_increment primary key,
depart_name varchar(32) not null default '',
num int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
create table userinfo (
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
depart_id int not null default 1,
# constraint 外键名(fk_userinfo_depart) foreign key (列名(depart_id)) references 表名(department)(关联的列名(id)),
# constraint fk_userinfo_depart foreign key (depart_id) references department(id)
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
外键分为 一对一 一对多 多对多
外键唯一索引 unique
表
外键的变种 一对多 一对一 多对多
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char not null default '',
phone int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user(id,name,phone) values (1,'root1',18),(2,'owen',18),(3,'Jerry' ,18);
create table host(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char not null default '',
age int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
create table host2name(
id int auto_increment primary key,
user_id int not null default 0,
host_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj1 foreign key (user_id) references user(id),
constraint wj2 foreign key (host_id) references user(id),
unique(user_id) # 设置唯一索引 值不能重复
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
3. 一对一:
用户表:
id name age
1 zekai 23
2 eagon 34
3 lxxx 45
4 owen 83
博客表:
id url user_id (外键 + 唯一约束)
1 /linhaifeng 2
2 /zekai 1
3 /lxxx 3
4 /lxxx 4
外键 一对一
外键唯一索引 unique
建user表
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char(32) not null default '',
age int not null default 0
)charset=utf8;
insert into user(name,age) values ('zekei',23),('egon',24),('lxxx',45),('owen',83);
建博客表
create table boke(
id int auto_increment primary key,
url varchar(32) not null default '',
user_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj1 foreign key (user_id) references user(id),
unique(user_id)
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
insert into boke (url,user_id) values ('/linhaifeng',2),('zekei',1),('lxxx',3),('lxxx',4);
对user_id设置了外键 另外对user_id设置了 唯一约束 表示这一行的数字不能重复 分别是2 1 3 4 假设是2234 就会报错
外键多对多 4. 多对多:
用户表:
id name phone
1 root1 1234
2 root2 1235
3 root3 1236
4 root4 1237
5 root5 1238
6 root6 1239
7 root7 1240
8 root8 1241
主机表:
id hostname
1 c1.com
2 c2.com
3 c3.com
4 c4.com
5 c5.com
为了方便查询, 用户下面有多少台主机以及某一个主机上有多少个用户, 我们需要新建第三张表:
user2host:
id userid hostid
1 1 1
2 1 2
3 1 3
4 2 4
5 2 5
6 3 2
7 3 4
创建的时候, userid 和 hostid 必须是外键, 然后联合唯一索引 unique(userid, hostid)
建zuser表
create table zuser(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char(32) not null default '',
phone int not null default 0
)charset=utf8;
建主机表
create table host(
id int auto_increment primary key,
hostname char(32) not null default ''
)charset=utf8;
建user2host表
create table user2host (
id int auto_increment primary key,
zuser_id int not null default 0,
host_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj2 foreign key (zuser_id) references zuser(id),
constraint wj3 foreign key (host_id) references host(id),
unique(zuser_id,host_id)
)charset=utf8;
注意:外键名称 不能重复 之前wj1已经用过 这里如果再是wj1就会报错
2.9 pymysql的使用
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123',database='db1',charset='utf8')
# 创建游标 和指定输出字典格式
cursor=conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 写出需要执行的SQL语句
sql = "insert into t3 (name,email) values(alix,122@163.com)" #在Pymysql中不需要;结束
# sql = "insert into t3 (name,email) values(%s,%s)"
# data=[('aaa','qqq'),('bbb','222'),('ccc','333')] 多条sql语句
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql) # 执行单条语句
# cursor.executemany(sql,data) # 执行多条语句
# 取出执行结果
res=cursor.fetchone() # 取第一行执行结果
res=cursor.fetchmany(10) # 取10执行结果
res=cursor.fetchall() # 取出所有结果
print(res)
# 在更新和删除时需要提交任务, 查询不需要这一步
conn.commit()
# 关闭资源
cursor.close() # 关闭游标
conn.close() # 关闭连接
SQL注入(SQLi)是一种注入攻击,,可以执行恶意SQL语句。它通过将任意SQL代码插入数据库查询,使攻击者能够完全控制Web应用程序后面的数据库服务器
-
案例
写sql语句的时候, %传值的时候, 需要加引号: sql = "select * from t4 where name = '%s' and pwd = '%s'" % (username, pwd) 上面的sql语句带来的风险是: 例一: username = zekai' # select * from t4 where name = 'zekai' #' and pwd = '' 例二: username = dbsahvbdsha' or 1=1 # select * from t4 where name = 'dbsahvbdsha' or 1=1 上面出现的问题,我们称之为 SQL注入 (**********************************) 出现问题的根源是: 因为太过于相信用户的输入, 导致我们在接受用户输入的参数的时候, 并没有对他进行转义
1. 自己手工对用户输入的值进行转义
2. 使用execute()自动进行过滤
sql = "select * from t4 where name = %s and pwd = %s"
cursor.execute(sql,(username, pwd))
#$## 插入一条
cursor.execute(sql, ('lxxx', '1234'))
### 插入多条
data = [
('aaaaa', 'aaa'),
('bbbb', 'bbb'),
('ffff', '666'),
('rrrr', '888'),
]
cursor.executemany(sql, data)
try:
cursor.execute(sql, ('lxxx', '1234'))
### 删除和更新的时候, 需要事物提交
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
cursor.lastrowid : 最后一行的行数
简记为ACID
-
原子性(Atomicity),原子意为最小的粒子,即不能再分的事务,要么全部执行,要么全部取消(就像上面的银行例子)
-
一致性(Consistency):指事务发生前和发生后,数据的总额依然匹配
-
隔离性(Isolation):简单点说,某个事务的操作对其他事务不可见的
-
持久性(Durability):当事务完成后,其影响应该保留下来,不能撤消,只能通过“补偿性事务”来抵消之前的错误
开启事务start transaction; 或者 begin; 执行sql操作(普通sql操作) 提交/回滚(commit/rollback)
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
money int not null default 1000
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user (name,money) values ('wangyong',1000),('liguo',1000);
# 正常操作
start transaction;
update user set money=1100 where name='wangyong';
updata user set money=900 where name='liguo';
# 出现异常 事务操作要么一起成功 要么一起失败
rollback;
# 最终结果, 数据未发生变化
mysql> select * from user;
+----+----------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+----------+-------+
| 1 | wangyong | 1000 |
| 2 | liguo | 1000 |
+----+----------+-------+
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
money int not null default 1000
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user (name,money) values ('wangyong',1000),('liguo',1000);
# 正常操作
start transaction;
update user set money=1100 where name='wangyong';
updata user set money=900 where name='liguo';
# 出现异常 事务操作要么一起成功 要么一起失败
rollback;
# 最终结果, 数据未发生变化
mysql> select * from user;
+----+----------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+----------+-------+
| 1 | wangyong | 1000 |
| 2 | liguo | 1000 |
+----+----------+-------+
优点: 1、所有的MySql列类型(字段类型)都可以被索引,也就是可以给任意字段设置索引 2、大大加快数据的查询速度 缺点:(耗费时间,空间.降低维护速度) 1、创建索引和维护索引要耗费时间,并且随着数据量的增加所耗费的时间也会增加 2、索引也需要占空间,我们知道数据表中的数据也会有最大上线设置的,如果我们有大量的索引,索引文件可能会比数据文件更快达到上线值 3、当对表中的数据进行增加、删除、修改时,索引也需要动态的维护,降低了数据的维护速度。
使用原则: 1、对经常更新的表就避免对其进行过多的索引,对经常用于查询的字段应该创建索引, 2、数据量小的表最好不要使用索引,因为由于数据较少,可能查询全部数据花费的时间比遍历索引的时间还要短,索引就可能不会产生优化效果。 3、在一同值少的列上(字段上)不要建立索引,比如在学生表的"性别"字段上只有男,女两个不同值。相反的,在一个字段上不同值较多可以建立索引
主键索引:加速查询 + 列值唯一 + 表中只有一个(不可以有null) 普通索引:仅加速查询 唯一索引:加速查询 + 列值唯一(唯一约束) (可以有null) 组合索引:多列值组成一个索引
# 第一种:
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种:
create table test(
id int not null default 0,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
alter table test change id id int auto_increment primary key
# 第一种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
index ix_name (name)
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create index ix_name on test (name);
2. 创建索引
create index index_name on table_name(column_name);
3. 删除索引
drop index_name on table_name;
4. 查看索引
show index from table_name;
1. 创建表 + 索引
# 第一种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
unique ix_name (name)
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种 create unique index 索引名称 on 表名(name);
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create unique index ix_name on test (name);
2. 创建索引
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(列名);
3. 删除索引
drop unique index 索引名 on 表名;
联合索引
组合索引是将n个列组合成一个索引
其应用场景为:频繁的同时使用n列来进行查询,如:where n1 = ‘alex’ and n2 = 666;
1. 创建表 + 索引
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
age int not null default 0,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create unique index ix_name_age on test (age, name);
create table in3(
nid int not null auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null,
email varchar(64) not null,
extra text
)
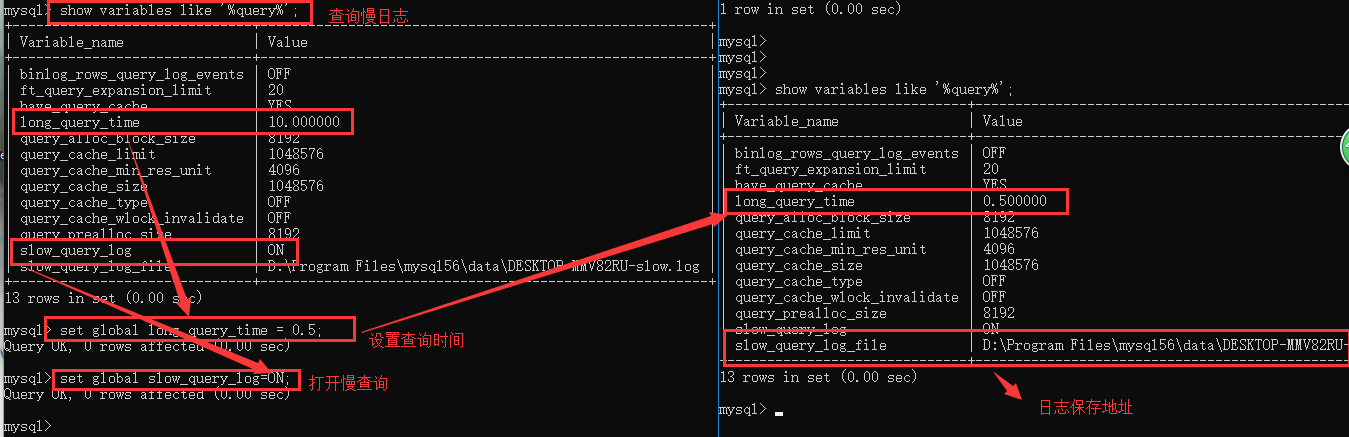
日志文件: 记录了执行速度特别慢的SQL语句
可以通过慢日志来检查查询的时间的等 然后呢针对性的做数据库优化
slow_query_log = OFF 是否开启慢日志记录 long_query_time = 2 时间限制,超过此时间,则记录 slow_query_log_file = /usr/slow.log 日志文件
1. show variables like '%query%'; 2. set global long_query_time = 1; 设置慢查询的时间 3. set global slow_query_log = ON 4. set global slow_query_log_file = E:programmysql-5.6.44-winx64dataoldboy-slow.log
SQL审计 (记录sql的操作语句) show variables like '%general%';

创建用户
create user '用户名'@'IP地址' identified by '密码';
creaee user 'zekai'@'192.168.1.123' identified by '123qwe';
creaee user 'zekai'@'192.168.1.%' identified by '123qwe';
create user 'zekai'@'%' identified by '123qwe';
#
删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'IP地址';
修改用户
rename user '用户名'@'IP地址' to '新用户名'@'IP地址';
修改密码
set password for '用户名'@'IP地址' = Password('新密码')
授权:
grant 权限 on 数据库.表 to '用户'@'IP地址' -- 授权
grant select on db1.* to 'zekai'@'%';
grant select on *.* to 'zekai'@'%';
grant select, insert, delete on db1.* to 'zekai'@'%';
记住:
flush privileges; # 刷新生效